The roof lathing is designed to evenly distribute the weight of the roofing "pie" over the entire roof truss system. In addition, the roofing itself is attached to it.
Classification of battens

There are several types of lathing (frame), each of which is mounted depending on the type, weight and rigidity of the roofing used:
- The sparse one is suitable for installing large-sized roofing materials (slate, corrugated board, etc.).
- Standard (compacted) is used when installing piece roofing materials with standard dimensions, for example, metal tiles. This type of lathing is also used when laying thin corrugated board or elastic euro-slate.
- Solid (cladding) is intended for small piece roofs and various types of soft roofs.
- Double is used when erecting a roof of complex shape and arranging slopes that are exposed to increased stress.
Any type of lathing device is characterized by a number of design features:
- sparse are installed in increments of at least 60 cm;
- standard ones are attached to the rafter system with a gap of 25-50 cm, which gives the structure additional strength;
- solid ones are installed almost close to each other;
- double ones are formed from two layers: the lower layer looks like a sparse one, and the upper one - a standard or solid sheathing.
Elements of wooden elements of the crate and rafters must be treated with fire-fighting and antiseptic solutions without fail.
Materials for the lathing and requirements for them

In suburban construction, when installing the frame for the finishing roofing, boards, beams, slats, shield sheets made from different types of raw materials and even a metal profile are used.
Wooden lathing
The wooden frame for fastening the roofing is most often collected from well-dried sawn timber. Edged or grooved are used:
- bars with a cross section of 50x50 cm;
- slats 2-3 cm thick, their width should be no more than 7 cm;
- boards, the width of which, with a thickness of 2.5-5.0 cm, should be from 10 to 15 cm.
The optimal size of the boards for the roof lathing is 150x40 mm.
Sheet crate

For cladding, moisture-resistant sheet materials are used. Their use guarantees a perfectly flat surface, on which there will be no irregularities inevitable when laying boards.
The following are used as sheet material for arranging the cladding:
- wood-fiber boards Fibreboard, which includes wood-fiber raw materials with the addition of a small amount of resin;
- chipboard chipboard, consisting of a mixture of shavings and resin, joined together by hot pressing;
- multilayer oriented strand board OSB, in each layer of which the chips are oriented differently and fixed with resin;
- moisture-resistant plywood FSF, obtained by gluing thin sheets of wood.
Metal crate

Arrangement of a frame made of a hollow metal profile is carried out with a slope length of more than 6 m.It is often used if the building belongs to the category of buildings with increased fire hazard.
Only rarefied-type frames are constructed of metal. For this they use galvanized or stainless steel profiles of a suitable section (channel, I-beam, etc.).
The fastening of the elements of the metal frame is carried out with self-tapping screws. When the rafter system is assembled from metal, the lathing elements are allowed to be welded.
Advantages and disadvantages of lathing materials
Each of the materials used for the lathing has advantages and disadvantages. For example, cladding is the best option for fixing roll or soft roofs. The sheets lifted onto the rafter system are very simple and easy to assemble.
The disadvantages of sheet materials include:
- Installation must be carried out in dry weather. If they become saturated with moisture, they will most likely be deformed.
- Difficulties associated with lifting the dimensional sheets to the roof are possible.
- Increased costs for the purchase of building materials.
The cladding makes it difficult for air to circulate under the roof, which leads to moisture retention and the formation of condensation in the roofing "pie". To avoid this phenomenon, it is recommended to equip a two-layer crate.

The advantages of using sawn timber are considered to be light weight, low cost and environmental friendliness. Among the shortcomings, the deformation of the elements of the crate is most often noted when they are laid in damp weather. One of the most important disadvantages is the high labor intensity of the work and the need for professional skills in laying the sheathing and finishing roofing material.
Frames assembled from metal elements have the most advantages:
- high strength and resistance to snow and wind loads;
- no deformation when weather conditions change;
- corrosion resistance;
- the ability to carry out work in any weather, etc.
Of the shortcomings, the most significant are the high cost and the need to attract workers with experience in welding and installation work at height.
Criterias of choice
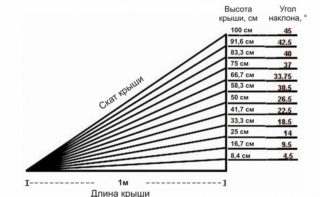
The choice of the type of lathing and the materials required for its arrangement is carried out on the basis of a comprehensive analysis that takes into account all the design features of the rafter system and the roofing "pie". Pay special attention to the following criteria:
- type of roofing material;
- the angle of inclination of the roof slopes;
- weather.
A thorough analysis of the main criteria will help you choose the right material for the lathing and the necessary distances between its elements.
The type of the proposed roofing material allows you to choose the type of lathing. If the developer has chosen a rigid covering that does not deform during operation, choose a crate that provides minimal roof support - standard or sparse. With a soft finish, equip the cladding.
The angle of inclination of the roof slopes allows you to determine the snow load on the roof. With a steep slope, the mass of accumulated snow and the load on the rafter system are reduced. In this case, you can increase the distance between the elements of the frame.
If the construction of a building is carried out in a region characterized by snowy winters, the frame is supplemented with elements that can withstand an additional load.
How to make a crate with your own hands
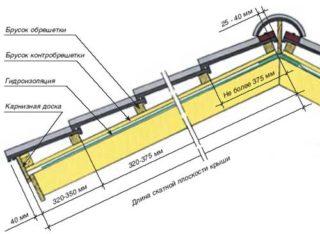
The process of laying the lathing with your own hands begins after the construction of the rafter system, laying and fixing the vapor barrier, insulation and waterproofing.
The roof lathing is mounted in the following sequence:
- If necessary, counter-lattice slats are nailed along the rafters. If there is no insulation in the roofing "pie", the presence of a counter-lattice is not necessary.
- The first sheathing board is nailed horizontally to the lower edge of the eaves board flush with the overhangs. In this case, it is imperative to verify its position in relation to the horizon.
- The lower edge of the waterproofing is released from the top of the lower sheathing board.
- The horizontal elements of the lathing are attached to the rafters at the same distance from each other. To facilitate this operation, it is recommended to make a simple template from the pieces of the board.
- The installation of the battens is considered complete after the last board is nailed in the upper part of the rafter system.
If the lathing is mounted end-to-end, for example, for further laying of a soft roof, a possible deformation of the boards is envisaged and small (1-2 mm) gaps are left between them.








