In ordinary rooms, the air circulates through the window valves and vents. There are no windows in the basement. For ventilation of the cellar, it is necessary to install separate air ducts for incoming and outgoing air flows.
- How to properly ventilate the cellar
- How the system works
- Basement air exchange and microclimate
- Basement ventilation types
- Natural ventilation
- Forced ventilation
- Materials and tools for installing ventilation in the cellar
- How to calculate the diameters of the ducts
- Basement ventilation pipes
- Checking the ventilation
How to properly ventilate the cellar

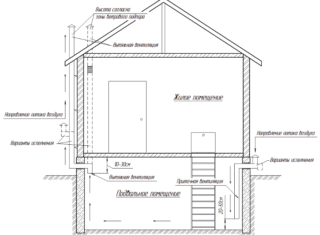
There is almost always a basement in a cottage or in a multi-storey building. It differs from the residential area in the following features:
- there are no windows;
- there are no special heating circuits, although there may be indirect ones;
- low wall temperature, which often leads to moisture deposition;
- low air temperature compared to living rooms.
The microclimate of the basement affects the temperature and humidity of the next floor. Therefore, the arrangement of at least the simplest ventilation - air in the foundation - is a mandatory element of construction.
Features of the hood, power, method of ensuring air exchange directly depends on the method of operating the basement.
- If the basement floor is used as a pantry - for storing vegetables and preservation, tools - air exchange is calculated based on the optimal temperature and humidity conditions.
- If a technical area is equipped in the basement - a boiler room, a boiler room, a gym, a workshop - ventilation is calculated according to SNiP standards for rooms where a short-term stay of people is expected.
There are no universal rules for calculating air exchange. Calculations are performed taking into account the equipment used and the purpose of the basement. The more powerful the boiler room, the more powerful the hood will have to be installed.
For special projects, for example, a wine cellar, a special ventilation system is developed that provides fine control of temperature and humidity.
How the system works
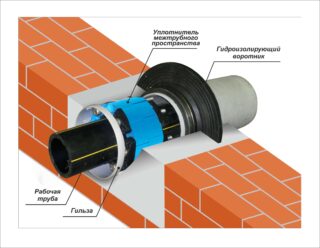
Correct ventilation in the cellar of a private house is based on the difference in density between cold and warm air. Cold outside air sinks to the lower part of the room, and when it warms up, it rises to the ceiling. Therefore, the supply pipe is installed closer to the floor, and the hood - as close to the ceiling as possible.
Since we are talking about an underground room, the supply and exhaust air in the cellar looks a little different. Both pipes are installed vertically. The end of the supply air is located at a distance of 50 cm from the floor. The air comes in here from the street and goes down. The inlet of the hood is located under the ceiling, and the pipe itself is led out to the roof.
For the ventilation mechanism to work, it is necessary that the inlet and outlet of the supply air are lower than the hoods. The outlet of the chimney must be located at least 1 m higher than the inlet of the supply air. To ensure normal traction, it is better to increase this difference. It is easier and more profitable to bring the hood to the roof than through the wall.
Basement air exchange and microclimate

Cellar ventilation provides the following:
- sufficient air exchange;
- permissible temperature;
- acceptable humidity.
An accurate calculation is rarely required: if the basement area is large and is used in different ways, if a wine cellar is organized and in other special cases.For the rest, rough estimates are enough.
- If the basement floor is used as a technical room, the air exchange rate is from 0.2 - for a vegetable store, warehouse, up to 1.5 volumes per hour. If a powerful boiler room is installed in the basement - more than 10 kW, the multiplicity is increased to 3 volumes per hour.
- If the technical room assumes a short-term presence of people - a boiler room, a room with a washing machine and an ironing press, air exchange is increased to 5–7 volumes per hour.
- If a living room is arranged in the basement, the air exchange rate increases to 8. In the gym, especially for non-slip people, the air must be completely renewed at least 10 times per hour.
In the last two cases, forced ventilation is required.
Basement ventilation types
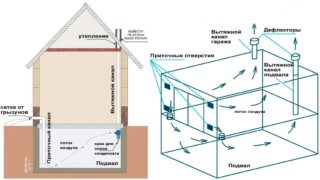
There are 2 types of hoods: natural ventilation in the basement and forced ventilation. The first is set up by default. If its power is not enough, the circuit is converted, including a fan or mechanical devices that improve traction.
Natural ventilation
It uses only the effect of creating traction when the temperature changes outside and in the cellar. The circulation is self-contained, no electrical or mechanical devices are required. The scheme includes:
- vents - make several vents in the cellar when laying the foundation;
- inflow - air supply pipe;
- exhaust duct - a pipe that removes heated air.
The advantages are obvious: it is independent of electricity, very easy to install with your own hands, much cheaper to maintain. However, the system cannot develop high power. In addition, the higher the temperature difference, the more efficient it is, so in summer, for example, the thrust in the system is much lower. This is not a problem for the pantry, but already in the workshop or boiler room the air becomes stale and damp.
In order for natural ventilation to provide good air exchange, the following are taken into account when arranging:
- ideally, the pipe should be strictly vertical, corners and bends reduce traction;
- the upper part of the hood is insulated to prevent the appearance of condensation and overturning of the draft;
- the chimney should rise 20-25 cm above the roof ridge;
- it is recommended to cover the outlet with a cap;
- the inflow is introduced through the foundation;
- the inlet of the pipes is covered with a metal mesh;
- the diameters of the supply and exhaust pipes are the same;
- traction is regulated by means of dampers.
In a small cellar, it is allowed to build one-pipe ventilation.
If the cellar area is less than 50 m², only natural ventilation is installed.
Forced ventilation

To ensure constant draft under all conditions, the system includes an exhaust fan for the cellar. Depending on where it is installed, there are 3 types of hoods:
- exhaust - the device is placed in the lower third of the channel;
- supply - the fan is mounted at the outlet of the lapping pipe;
- supply and exhaust - devices are mounted at the inlet of the hood and outlet of the supply.
Such a system is installed if the basement area is large or it is used in an unconventional way. The advantages are as follows:
- optimal traction regardless of weather conditions;
- the ability to accurately regulate air exchange depending on the frequency of use of the basement;
- independence of complexity - bends and turns of pipes are allowed;
- the possibility of additional equipment - ventilation can include air purifiers, heating blocks, automation for treatment, switching on the air exchange regulation.
The disadvantages are as follows:
- higher cost;
- the system depends on electricity and is more expensive to maintain.
Often forced and natural ventilation are combined. Establish a standard scheme for natural in accordance with all requirements, but fans are also mounted.In winter or in windy weather, when the natural draft is already strong, the fans are not turned on. In summer, the hood works in forced mode.
Materials and tools for installing ventilation in the cellar
- pipes - plastic or tin;
- a fan or other device such as a deflector;
- clamps for fastening;
- branch pipes for the output of pipes through the ceilings;
- welding machine for metal and soldering iron for plastic ducts.
If ventilation is installed after building a house, you will need to drill holes in the foundation and floors. This requires a special tool.
How to calculate the diameters of the ducts

The diameter of the pipes is calculated based on the area of the basement. According to the standards, 1 m² of the room must have at least 25 cm² of the duct cross-section. In fact, the cross section is increased by 10-15% of the calculated one. To regulate traction, dampers are installed.
However, there is a certain limitation. The diameter of the hood cannot be more than 25 cm. If more active air exchange is required, fans are installed. In this case, you need to calculate the power of the device.
Basement ventilation pipes
Plastic pipes are much lighter than iron pipes, do not corrode, do not need maintenance. Their installation is much easier. Even if pipes need to be welded, the simple science of soldering is much easier to master.
Galvanized sheet metal blowers are much more durable. Thanks to the zinc coating, they are also not afraid of moisture and do not rust. However, it is more difficult to mount them: the pipes are heavy, and the connection is only allowed welded.
Checking the ventilation

The ventilation system is considered complete if it passes the test.
- A strip of tissue paper is applied to the exhaust port. If it is attracted, then there is a craving.
- You can check the air circulation with a lighter. In the presence of thrust, the light deflects; in the absence, it burns evenly.
Proper basement ventilation is a system that maintains optimal temperature and humidity in the room. If the air exchange is sufficient, vegetables do not shrink or rot in the cellar, it is easy to breathe in the boiler room, and the air in the gym is cool and dry.