The foundation and basement of the house are in contact with the ground, so in spring and autumn, when the water table rises, the basement is often damp or even flooded with water. This is dangerous: 80% of buildings are destroyed precisely because of the constant erosion of the foundation. The waterproofing of the cellar and the construction of the drainage system solve this problem.
- Why do you need internal waterproofing
- Functional features
- Waterproofing materials
- Penetrating insulation
- Cement-based waterproofing (cement mixtures)
- Liquid insulation (coating)
- Roll insulation
- Membrane waterproofing
- Injection protection against moisture (a kind of penetrating)
- Liquid glass
- Types of insulation according to the degree of exposure to moisture
- Stages of waterproofing
- Internal insulation errors
Why do you need internal waterproofing

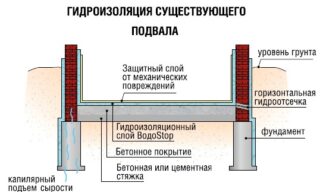
The surface layers of the soil contain water. Its amount increases sharply during rain, after snowmelt, due to an increase in the level of groundwater in spring. Diffusion of surface moisture and forcing water from the depths of the soil are the main reasons for the flooding of the basement and the dampness of the foundation.
Moisture is absorbed by the base material - brick, concrete, penetrates into the cellar and accumulates on the walls and floor. When the temperature drops, the water freezes, expands and destroys the material. Gradually, the foundation and walls of the basement floor become unusable.
Waterproofing the basement of a brick house from the inside solves the following tasks:
- prevents the destruction of the foundation and basement of the building, thereby avoiding damage to the entire house;
- prevents the formation of condensation on the inside of the walls and the accumulation of water inside the basement;
- prevents the appearance of mold, fungi and damage to products stored in the cellar;
- prevents corrosion and destruction of reinforcement.
A clean and dry basement creates an additional air insulation layer. In such a house it is warmer, it is easier and cheaper to heat it.
Functional features
According to their functional features, 3 types of insulation are divided.
- Vertical protection of walls - carried out if the water table is very high and water enters the basement through the walls, and not just through the floor. The walls must be waterproofed if a drainage system is not installed around the private house.
- Horizontal - often performed on clay soils, where water mainly comes from below. Often, horizontal insulation is combined with vertical insulation.
- Penetrating - we are talking about a material that creates a water-repellent effect. For example, if the concrete walls of the basement are impregnated with a hydrophobic impregnation, the basement material itself and the foundation will repel moisture and prevent it from penetrating inside.
Treatment with hydrophobic solutions must be repeated periodically.
Waterproofing materials

Basement waterproofing from the inside from groundwater is carried out with various materials. Some of them form a waterproof layer. Others impart water-repellent properties to the wall and floor material. Still others prevent the movement of moisture inside the building stone or concrete.
Penetrating insulation
The most reliable type of concrete processing. A waterproofing compound based on Portland cement, quartz sand and active components penetrates 30 cm into the material.Substances of the solution react with the constituents of concrete, forming dense hydrophobic structures, literally repelling water.
The waterproof layer obtained in this way creates resistance to the pressure of water, therefore, penetrating waterproofing is used in the construction of dams, tunnels, underground corridors.
Pros:
- absolute sealing;
- increase the overall strength of concrete by 20%;
- not afraid of temperature changes;
- does not interfere with air microcirculation;
- does not require a primer.
Minuses:
- not suitable for processing any aerated concrete - foam concrete, gas silicate bricks, as well as silicate bricks;
- the surface must be thoroughly cleaned before work.
The cost of penetrating waterproofing is quite high. But you can apply it with a regular brush.
Cement-based waterproofing (cement mixtures)

It is a conventional cement-based plaster. It is used with a low head of groundwater to protect walls, less often floors.
Advantages:
- strength - withstands pressure up to 7 atm;
- high adhesion;
- affordable cost;
- vapor permeability;
- the plaster dries and acquires waterproof properties in 24 hours.
Disadvantages:
- the surface must be very thoroughly cleaned before work;
- when the building shrinks, the plaster cracks.
- it takes some experience to properly plaster walls.
Liquid insulation (coating)

This category includes bituminous mastics and compositions based on polymer cement. Such materials are characterized by high elasticity and strength. Depending on the level of groundwater, the mastic is applied in a layer of 2 to 20 mm.
Pros:
- mastics are suitable for any surface: cement, brick, concrete, metal;
- waterproofing can be sprayed, which speeds up the work;
- bituminous mastics do not shrink;
- resistant to chemically aggressive substances.
Disadvantages:
- when waterproofing the foundation in this way, at least a blind area cannot be dispensed with;
- it is allowed to use the composition for hydraulic loading no more than 2 m or 5 m for bitumen-polymer mastics.
Liquid waterproofing can be applied both cold and hot.
Roll insulation

This category includes roofing material, membrane films, polymer-based materials. The material is produced in the form of rolls, which fits the mounting on a vertical and horizontal surface.
Benefits:
- low cost;
- versatility in application;
- high isolation speed - the work is very simple.
Minuses:
- short service life - up to 5 years;
- it is necessary to additionally waterproof the seams when laying;
- low maintainability;
- it is possible to protect the structure only from the side of the use of insulation.
It is more reasonable to use roll materials for external waterproofing.
Membrane waterproofing
This is a type of roll waterproofing with improved properties. In fact, the membrane is a one- or two-sided film that allows steam to pass to one side and does not allow moisture to pass through. Membranes are much more elastic and more durable, therefore their thickness is much smaller than that of roofing material. Usually the film is reinforced with a reinforcing mesh.
The advantages of roll material are added high elasticity, increased tensile strength - by 20%, and the ability to work in the cold. Short service life disappears from the disadvantages: membranes "work" up to 50 years.
Injection protection against moisture (a kind of penetrating)

It is usually used for waterproofing junctions, inaccessible places, seams. The technology is unusual. A 50 cm depression is drilled in the concrete, a nozzle is installed there, and an injection solution is injected under a pressure of up to 240 atm. The composition penetrates 50 cm deep into the material, swells and fills voids, completely blocks the penetration of moisture even through the capillaries.
Benefits:
- the injection is able to stop the leakage of even the dam;
- used for waterproofing concrete, brick, stone;
- the service life is not less than that of a reinforced concrete structure;
- provides complete water resistance.
Disadvantages:
- an accurate calculation of the dose and place of water is required;
- such processing requires high qualifications and special equipment;
- high price.
In domestic conditions, the injection method of waterproofing is rarely used.
Liquid glass
A type of coating waterproofing. In this case, soda glass is used for surface treatment. Apply it to a layer of clay and tar. Use a brush or spray.
Additional benefits: very high water resistance and ease of handling. Minus: strong and unpleasant odor. Work must be done in a respirator and the basement must be ventilated for a long time.
Types of insulation according to the degree of exposure to moisture
- Anti-pressure - performed if the groundwater pressure exceeds 10 m. Its essence is to place the waterproofing material so that the water pressure presses it to the surface, thereby protecting it. This is usually done outside. From the inside, only solutions of very deep penetration work this way.
- Free-flow - used at low pressure as an option for protection against intermittent flooding. Use mastics, roll materials, coating waterproofing.
- Anti-capillary waterproofing - prevents moisture from entering the foundation and walls of the basement through the capillaries that are in any stone. This is difficult to do. This effect is usually provided by injection waterproofing.
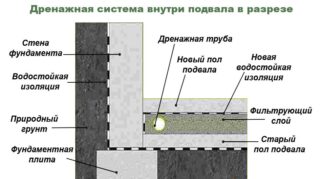
In a residential building, moisture seepage into walls and damping is cheaper to prevent by carefully waterproofing the foundation during construction and equipping a drainage system.
Stages of waterproofing

The general scheme of work is almost the same for all materials.
- Surfaces are prepared: cleaned, sometimes leveled. You need to remove not only dirt and dust, but also greasy stains, traces of leaks, traces of mold removal, and more. If, after removing stains and damaged material, deep recesses remain, they are sealed with cement plaster.
- The surface is treated with a primer. Such formulations improve adhesion. Some materials can be laid without priming: roofing material, for example, bituminous mastic.
- Dry the surface.
- Waterproofing is carried out in the chosen way: roofing material is laid, it is glued with a hot method, the composition is sprayed onto the walls.
After waterproofing in the garage or in the basement, it is recommended to perform the most primitive finishing work.
First of all, they waterproof:
- damaged areas - cracks, breaks that appear after shrinkage, deepening and spalling of concrete;
- areas near utilities;
- joints between the ceiling and walls, corners, working seams.
Partial waterproofing does not solve the problem. However, you need to pay close attention to these places.
Internal insulation errors

The result of work is easy to nullify if you make too many mistakes.
- Wrong choice of material - if you plaster the walls of the garage or basement with a high pressure of groundwater, this will not work. Penetrating waterproofing, for all its effectiveness, is useless if the walls of the basement are lined with silicate bricks.
- Incomplete waterproofing - seams and joints are often very difficult to process. Inadvertent insulation in such places will result in leakage.
- Lack of preparation - it is impossible to carry out waterproofing work in a wet or damp room. Before the procedure, the basement must be dried, the surfaces cleaned, and the accumulated water removed.
- Performing work in unsuitable conditions - most materials are allowed to be used at temperatures above +5, or even +10 C. Neglecting the recommendations in the instructions leads to a violation of waterproofing.
There is only one way to prevent the basement from cooling and damage to the foundation - to waterproof the base and the basement. With a low head of groundwater, an excellent result is provided by the internal waterproofing of the cellar.