In addition to brick, there are many other building materials. Cellular concretes have gained particular popularity: large blocks of regular shape with high porosity. Several types of such material are produced, of which the most famous are the foam block and the gas block.
Production technology and chemical composition

Aerated concrete got its name from its porosity. The material weighs much less than traditional concrete, has higher heat and sound insulation qualities, is easy to process and significantly speeds up construction.
This feature is due to the production technology. General manufacturing scheme:
- A starting mass is prepared from Portland cement, sand, and fiberglass or other fillers.
- A foaming agent is introduced into the solution. This substance reacts with cement and releases hydrogen. Gas cannot escape from a viscous heavy mass and forms many small round pores inside the material.
- The foamed mass is mixed to distribute the bubbles evenly and poured into molds.
- The workpieces are left to dry naturally.
To obtain higher quality material, autoclaves are used. They maintain a high temperature and pressure, at which additional chemical reactions occur inside the initial mass. Autoclave foam blocks are much stronger with the same thermal conductivity.
Autoclave concrete is a monolith. It is cut into blocks using special devices. This is how autoclaved foam concrete and aerated concrete are obtained. The latter cannot be made in any other way.
The fundamental difference between foam and gas blocks lies in the nature of the pores. In foam blocks, they are closed and the outer surface of the stone is smooth. In gas blocks, the pores are open and the porous structure of the material is visible. This provides an unpleasant property of gas blocks - hygroscopicity.
Comparison of the characteristics of the foam block and aerated block
Different production patterns and slightly different components provide differences.
The blocks obtained by the autoclave method should be compared. In fact, the consumer often chooses between non-autoclave foam concrete and aerated concrete, which introduces confusion.
Product geometry
Ordinary foam concrete is obtained by pouring the foam mass into a mold. With this manufacturing method, errors are possible: uneven filling, mold displacement, insufficient volume, etc. Therefore, both autoclave and non-autoclave foam blocks are somewhat heterogeneous. The dimensional accuracy is less here.
Aerated concrete is cut into blocks after complete drying. This allows you to get exactly the same blocks with the most accurate dimensions. However, it is precisely this method - cutting the monolith, which opens the pores.
The standard block sizes are close: the height of the gas block is always 200, the foam block is from 200 to 400, the length is 500, 600 mm. The width of the foam concrete bricks is 100–300 mm, and the aerated concrete blocks are from 75 to 500 mm.
Sound and heat insulation properties

These properties determine the degree of porosity and the size of the air bubbles. With autoclave production, the pores are the same and are more evenly distributed over the mass of concrete, therefore, these characteristics are better for the gas block.
Bearing capacity and thermal insulation properties are opposite to each other. Materials with different densities will have different characteristics. This must be taken into account when choosing. Thermal insulation - with the maximum number of pores - foam concrete has a thermal conductivity equal to 0.08 W / M * k, and aerated concrete - 0.1. The indicators of structural concrete of both types are much lower - 0.36 and 0.14 W / M * k, respectively.
Weight
The specific gravity of the block also determines the density. Heat-insulating concrete is lighter, structurally heavier. The weight of a stone with the same dimensions ranges from 300 to 1200 g.
Characteristics

Before building a house from foam blocks or aerated concrete, you need to familiarize yourself with other characteristics of the material:
- Strength with equal porosity is higher for aerated blocks. But if the foam concrete is autoclaved, on this basis it is not inferior to aerated concrete.
- Uniform distribution and uniformity of pores relieves a gas block house from shrinkage - the indicator does not exceed 0.5 mm per running meter. Foam concrete shrinks by 2-3 mm.
- The high geometric accuracy of gas blocks allows you to achieve the most tight fit. Cold bridges are excluded. However, this can only be done using a special glue: it is applied in a very thin layer. This increases the cost of construction. Foam concrete can also be placed on ordinary mortar and even on cement.
- The main disadvantage of aerated concrete is hygroscopicity, moisture easily penetrates into open pores. The volume of absorbed moisture is relatively small, moisture accumulates in the upper layer. With poor ventilation, the house becomes damp on the inside faster than outside. The pores of the foam block are closed; it absorbs moisture no more than a silicate brick. The same property provides a higher frost resistance of foam concrete: F30 versus F25 with the same porosity. Therefore, foam blocks are preferable for middle latitudes.
- Because of the open pores, the walls of gas blocks need to be protected: plaster, treat with impregnations, paint. But due to its structure, it is much easier to plaster such a wall than a surface made of foam blocks.
- The ease of processing of both materials is the same: the stone is easy to cut, saw, drill. Both concretes hold the fasteners perfectly.
- The weight of the materials is the same, the requirements for the foundation of houses made of foam and gas blocks are the same. The lightest base is chosen, which reduces the cost of the project.
You need to choose materials not according to their absolute indicators, but taking into account the weather conditions of your region.
The price of a material depends on its density, purpose and manufacturing method. Foam concrete obtained by pouring into molds is the cheapest option. The gas block is more expensive due to the manufacturing method. On average, the cost of a cubic meter of aerated concrete ranges from 3200 to 3800 rubles. The price of foam concrete varies from 1400 to 2500 rubles.
Laying and debugging of foam concrete and aerated concrete

The algorithm for laying the wall is the same. The usual scheme is used: brickwork with an offset. Blocks are laid in 1, 1.5, 2 rows, depending on the required wall thickness. However, there are also differences.
- Building a house from foam blocks begins with preparation. Their dimensions are not entirely accurate, although the surface is smooth, but often with burrs, irregularities, chips. They should be removed using a float or drywall planer. Gas blocks do not need processing.
- Foundation waterproofing is a prerequisite. Otherwise, porous concrete will draw moisture from the base.
- Blocks are laid on the lighthouses. The first layer is placed only on a cement-sand mortar. Thus, it neutralizes differences in height.
- The following rows can be laid on either glue or mortar. The composition is applied on a horizontal surface - up to 10-15 mm thick, and on the side part - 8-10 mm. In this way, voids are avoided. The styling is as dense as possible. Excess mortar is immediately removed with a trowel.
- The first row of gas blocks is also placed on a cement-sand mortar. The rest of the rows are for glue only. The special composition allows you to achieve the tightest joining of blocks: the thickness of the horizontal seam reaches only 5 mm.
- It is recommended to reinforce walls made of aerated concrete. Reinforce the bottom row, window and doorways. For reinforcement in the blocks, grooves are pre-drilled and the rods are laid there during the installation of the row.
The foundation must not be made of aerated concrete. It's too hygroscopic.
What is better for building a house
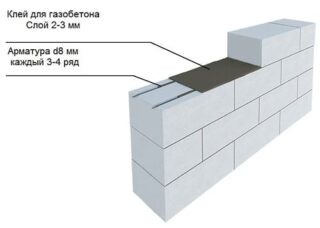
In terms of strength and accuracy of geometric dimensions, the gas block surpasses the foam block. However, its hygroscopicity poses a number of additional tasks for the builder.
The following considerations are relevant:
- Foundation - light and simple is required. It does not affect the choice.
- Strength of the walls - the gas block is stronger in itself, due to the tighter joint it forms a more reliable surface. However, the strength of aerated concrete is not too great. A house made of gas and foam concrete must be reinforced.
- Material consumption - due to the irregularities of the foam blocks, they are laid on the mortar. The seams are thick, so a lot of material is needed. Special glue for gas blocks is much more expensive. However, less is required. The difference in costs appears only with a large wall area.
- Installation on glue requires high qualifications. If you do not follow the technology, its advantage - the absence of cold bridges - will disappear
- The aerated concrete house needs finishing, as the material is hygroscopic. Plaster, primer should prevent moisture from entering the pores. This reduces vapor permeability. On the other hand, foam blocks look unsightly; the building of them also needs to be finished.
- The materials withstand the bearing load approximately the same, so the structure of the roof does not matter.
The quality of concrete depends to a large extent on the conscientiousness of the manufacturer. Violation of the temperature regime in the autoclave deprives the material of all its advantages.










I made a house in the country from foam blocks. Now the problem is how to hang wall cabinets