The lathing is installed over the rafters in the form of a continuous covering or a lattice system, the structure is designed to fix the roofing flooring. The slats increase the strength of the supporting roof frame and can be arranged in one or two layers. A wooden or steel crate is placed under the corrugated board, the pitch of the lumber is determined by the weight of the material, snow, wind, depends on the steepness of the slopes, the thickness of the corrugated sheet and the height of the corrugation.
Features and application of corrugated board

The lightweight and durable cover is made from steel strips. Rigidity is provided by a wavy shape. Corrugation can be of different configurations and sizes in height and width. GOST documents regulate the wave height of not less than 3.5 cm. The larger the size, the higher the load that the profiled sheet can withstand without losing the declared qualities. Profiled sheeting is used for industrial and residential buildings, hangars and trading floors are covered with it.
On the construction market, there are varieties of corrugated board:
- corrugated strips of simple iron without surface coating and galvanized;
- flat sheets without stamping elements;
- embossed products with a galvanized layer without polymer coating;
- molded galvanized sheets with a double-sided protective layer of polymers;
- corrugated plates made of aluminum, nickel, iron-chromium alloy;
- corrugated plates for specific applications, for example, curved, with a special embossing option.
The material of the first type does not sufficiently resist corrosion, therefore it is used for outbuildings and temporary structures. It is welded to a metal crate, since there is no protective layer that would collapse from the action of high temperature. Flat options are used for roofing housing, but perforated varieties are more often used, taking into account the pitch of the roof sheathing under the corrugated board.
Profile sheet properties

The film protects the sheets from destruction under the negative influence of the atmosphere, the material does not fade from the sun. Protection can be acrylic, polyester, polyurethane, contains plastic and polyvinyl fluoride elements.
The quality of the material depends on the characteristics:
- base and galvanized layer thickness;
- the type of polymer used;
- the thickness of the polyurethane film;
- steps between corrugation protrusions.
It is convenient to install the profiled sheet on the roof, while it hides small irregularities due to the volumetric shape. Strips are produced up to 12 m long, therefore, most often the slope is covered with a full sheet without joining along the length. The material is produced in a wide range of colors. Due to the low weight, you can save money by reducing the cross-section of the bearing rafters and the distance between the slats of the roof sheathing under the corrugated board.
Negative properties are manifested in the fact that the material sounds when raindrops fall or birds move along the roof, so you need to put an additional layer of sound protection. When cutting the strip to size, the protective polymer layer is destroyed at the point of contact with the tool.
Marking of corrugated board in accordance with GOST 24045-1994:
- H - reinforced steel strips with increased load-bearing capacity;
- C - standard type of material for roofs and wall coverings;
- NS - a universal version with many options for the height of the corrugation;
- PC - profiled roofing decking;
- PG - bent version for semicircular hangars, sheds, arches.
Reinforced sheets provide stiffening ribs and grooves for draining water. The PK brand is used for small roofs and canopies as an economical option.
The step of the rail for corrugated board and the requirements for the parameters
The distance between the slats is determined by the thickness of the material, the magnitude of the load and the steepness of the roof. If you take the wrong step of the sheathing for the profiled sheet, the coating will bend in winter with a snow drift. Installing too many bars will waste material and money. Experts recommend making a project and ordering the correct calculation.
Profiled strips are fixed to the battens, like other types of flooring. The step of the lathing is prescribed in building codes (SNiP 2.26 - 1976), taking into account the slope of the roof.
Stingray parameters:
- small - slope less than 25 °;
- medium - up to 40 °;
- steep - over 40 °.
The roof of a low slope is installed on a continuous flooring, or the pitch of the lathing under the profiled sheet is within 400 mm (depending on the thickness of the iron and the type of profiled sheet). Single-pitched and gable roofs of medium slope are covered with corrugated board with a lathing step of 300 - 650 mm, and in steep between the bars, a distance of up to 1000 mm is left.
Step size depending on the brand of profiled sheet to calculate the spacing between the slats:
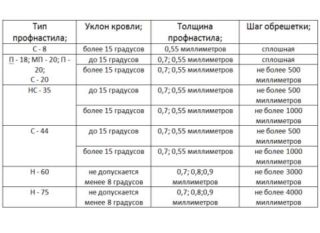
- С8, sheet 0.5 mm thick, roof slope greater than 15 ° - solid base;
- С10, thickness 0.5 mm, tilt up to 15 ° and more than 15 ° - solid lattice or 300 mm pitch, respectively;
- C20, thickness 0.5 or 0.7 mm, tilt up to 15 ° and more than 15 ° - solid lattice or distance up to 500 mm, respectively;
- С21, thickness 0.5 - 0.7 m, slope up to 15 ° and over 15 ° - step 300 and 650 mm;
- НС35, thickness 0.5 - 0.7 mm, tilt up to 15 ° and higher - step 500 and 1000 mm;
- Н60, thickness 0.7 - 0.9, inclination not less than 8 ° - step 3000 mm;
- Н75, thickness 0.7 - 0.9 mm, slope above 8 ° - step up to 4000 mm.
Manufacturers recommend placing the material on roofs with an inclination of at least 12 °, the maximum slope can exceed 60 °, but according to SNiP standards, an inclination of 20 - 35 ° is recommended.
Methods for fixing the grating under the corrugated board
The rafter system is an engineering structure, where every little thing matters, especially the technology for assembling the sheathing for the corrugated board. The scheme involves the use of individual bars, boards or sheets of moisture-resistant plywood, chipboard, OSB. When choosing a different type of wood, the crate is solid or sparse.
The solid flooring also has gaps of 1 cm, such a base is suitable for weakened grades of profiled sheet. Continuous flooring is placed in the area of crossing the slopes, for attaching the ridge, on valleys, ribs, gutters. Sometimes the continuous base in these places is changed with additional slats. Strengthen with bars the areas of chimneys, expansion joints, fire hatches,
Rail mounting features:
- the bars are fixed so that they stand perpendicular to the plane of the rafter with their lateral surface;
- for fastening, metal brackets, bolts with nuts, nails are used;
- a board is placed along the eaves, which is wider than the rest of the elements;
- the standard thickness of the support elements is 50 mm;
- before installing the sheathing, a wind protection is placed so that it protrudes above the wave of corrugated board.
Dowels with self-tapping screws are used to fix the battens in a concrete base or cement screed. If the lathing consists of a metal corner, dowels are used for fixing, and the steel profile is connected to each other with self-tapping screws for metal.
Parts of the lathing for the metal profile are joined along the length if necessary, but the junction is placed on the rafter leg, and not by weight. The slats are installed at the building level, so that later the roof looks visually without protrusions and depressions on the surface. To do this, pull the marking cord to the desired height.
Material preparation

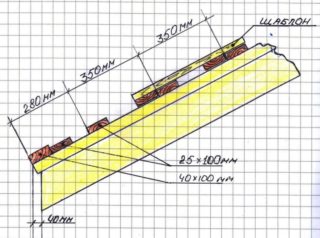
They take a rail with a cross section of 50 x 50 mm, sometimes a size of 25 x 50 is enough. Unedged or edged lumber with a thickness of 35 and 50 mm is used, the width is taken as 100 or 150 mm. When calculating the material, additional elements are taken into account for arranging the junction points.
Varieties of base for professional sheet:
- Solid. One-piece flooring is made in the case of a low sheet wave (up to 20 cm) and steel thickness up to 0.5 - 0.7 mm. Such a roof covering holds its shape without load, but small forces from the snow lead to deformation, so a solid base is needed. Particle sheets of various modifications are used.
- Lattice. The distance between the longitudinal elements is 200 - 450 mm. The board or bars are placed under the main types of corrugated board, which are used most often.
- Sparse. This type includes a base in which the rail is placed at a distance of 500 mm. Rare support parts are made of a metal corner 50 x 50 mm or a square profile with a side of at least 40 mm.
Choose a suitable wood species. Larch, spruce and pine are more commonly used. The material has sufficient strength and flexibility, it is distinguished by a small number of knots in the thickness of the wood. The slats should be even, without cracks, knots and rot. Humidity is up to 15 - 20%, a higher indicator threatens deformation over time. The material can be dried independently in the shade under a canopy, while the unfolded slats are evenly loaded.
Reiki, boards are treated with antiseptic preparations to increase resistance against moisture, microorganisms, bugs. Compositions are used to increase fire resistance.
Installation steps
They put a layer of waterproofing on the rafters or concrete base before installing the crate, use special membranes or plastic wrap. Protection from moisture is fixed with bars, the use of which gives a small gap for ventilation.
Sheathing installation method:
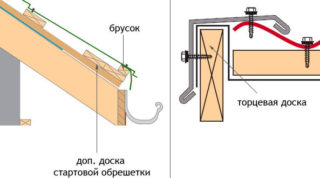
- an end element in the form of a board or additional bars is placed on the edge of the cornice;
- the installation of the lathing is done according to the established dimensions, check the evenness of the connected elements, horizontality;
- the bars are collected from the bottom up, the support is attached to each rafter leg intersecting with it by one nail;
- lumber is fixed on the rafters with two hardware of such a length that takes into account the thickness of the board for lathing the roof under the corrugated board;
- on one rafter the adjacent bars do not join, the joints alternate.
The double-layer lathing contains an additional counter-lattice. The lower layer is always made of laths, and the upper one is made of bars or slabs, in accordance with the calculation. Solid sheets are placed in the direction from the ridge to the cornice, diagonal layout of chipboard panels is allowed.
Moisture-resistant plywood is staggered on the rafters, while the adjacent sheets are fixed with self-tapping screws throughout the seam. The ridge rail is placed so that it does not reach the top of the rafter by 5 - 7 cm for an organized ventilation gap.
Fastening the corrugated board to the crate
The edge of the sheets on the pediment is mounted flush with the ends of the bars. An L-shaped steel bar is nailed over the windboard to the ends of the rivers for protection from snow and rain.
The vertical overlap depends on the slope of the roof:
- tilt 10 - 15 ° - sheets overlap each other for more than 200 mm;
- 15 - 30 ° - 150 - 200 mm overlap;
- more than 30 ° - 100 - 150 mm.
At an inclination of less than 12 °, the entry points are sealed with silicone compounds. Lateral overlaps are performed by the size of one wave. An overlap is made for two waves for a profiled sheet, the height of the corrugation of which is less than 10 mm.
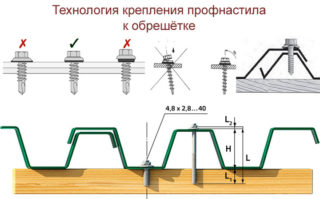
The corrugated board is fixed with special self-tapping screws for this coating. The fasteners are covered with an ethylene-propylene layer and have a springy pad. The ridge is mounted using long hardware, and the sheets are fastened with short ones, in the crest of the wave. The size of the self-tapping screws is chosen so that the end of the fastener goes into the rail by 30 - 35 mm.
The central strips are fixed at the rate of 5 - 7 hardware per square of the roof, and the side strips are fixed in each crate along the length of the sheet. Along the width, the screws are twisted on the pediments every 300 mm, the ridge - into each ledge of the wave, while the axis of the fastener runs perpendicular to the bar.