During the construction of greenhouses, greenhouses, polycarbonate is used as translucent inserts on the surface of vertical and horizontal fences. The material transmits rays, but retains heat and cold, so its use is most relevant. Polycarbonate for greenhouses is produced in various types, sizes, so it is easy to make a choice for different conditions of installation and operation.
- Pros and cons of polycarbonate for greenhouses
- Characteristics of polycarbonate
- Polycarbonate 4 mm
- Material 6 mm
- Sheets 8 mm
- Panels with the abbreviation "Light"
- Criteria for choosing a material for a greenhouse
- Density
- Thickness
- Honeycomb geometry and polycarbonate strength
- With or without UV protection
- By color
- Famous manufacturers
Pros and cons of polycarbonate for greenhouses

Thermoplastic polymer has high heat resistance, impact resistance, light transmission, its characteristics are not affected by the weather. Greenhouses are not operated at temperatures that cause the material to become brittle. In terms of compressive strength and hardness, it is equated to aluminum.
Benefits of using:
- lightness allows you to reduce the massiveness of the foundation and supporting elements;
- the density of the material is lower than that of glass, but the thickness can be only 0.7 mm;
- sheets are simply cut, processed.
In a fire, the sheets do not burn, but melt, while the mass does not flow down onto other structures and people. Upon impact, the slab becomes covered with cracks, but individual fragments do not fly apart.
The disadvantages include the need for careful handling so as not to scratch the surface, which will lead to a decrease in the light transmitting effect.
Characteristics of polycarbonate
Types of polycarbonate are produced:
- cellular with internal partitions;
- cast (solid or monolithic);
- profiled in the form of slate.
The walls of the internal partitions are at an angle to the enclosing layers, due to which they resist the blows of hail and small stones. In this case, the kinetic energy is reduced by 1.5 times compared to flat coatings. Polycarbonate is a versatile material that can be bent within specified limits without heating or other preparation.
The layered thermopolymer does not react to sudden changes in temperature in winter and summer. The material changes its linear dimensions when heated, which must be taken into account when designing and installing. Included in the category of environmentally friendly products, it is not destroyed by the action of atmospheric chemistry.
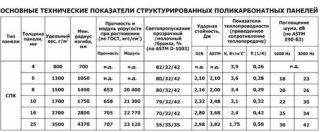
Polycarbonate 4 mm
The material is more often used to cover the arches of greenhouses, but it can be attributed to the budget option. It is advisable to install on spring-autumn structures that are not used in winter.
Features of 4mm thick honeycomb material:
- the cross-section of the cells is 4 x 5.7 mm;
- transparent transmits 86% of the rays, and colored, for example, bronze, only 50%;
- in terms of heat transfer capacity, it works like glass;
- delays up to 15 dB of sound;
- during transportation, it can be bent to a radius of up to 375 - 400 mm, during installation, the boundary bend is 600 - 700 mm;
- a square of a honeycomb sheet weighs 0.8 kg;
- thermal conductivity is 3.6 W / m2 ° C.
The panels are not strong enough to withstand the mass of adhered snow, even if you take a frequent step of the sheathing. Frequent slats will reduce the flow of light into the greenhouse.Polycarbonate sheets for greenhouses 4 mm thick do not save too much heat due to the insufficient distance between the top and bottom layers.
Material 6 mm
The thickness of 6 mm can be considered as a kind of double-glazed unit, so it can be installed in greenhouses used in late autumn. But for a frosty winter with snow drifts, it is better to choose a thicker material.
Characteristics of 6 mm polycarbonate:
- the cross-section of the cells is 6 x 6.7 mm;
- transparent transmits light in the amount of 86%, color - only 42 - 52%;
- Delays up to 18 dB of noise;
- during transportation, it can be bent up to a radius of 500 - 600 mm, and during installation in a structure, a radius of 900 - 1050 mm is allowed;
- weighs a square sheet according to the standard of 1.3 kg;
- thermal conductivity is 3.4 W / m2 ° C.
Light transmission is measured using the example of glass, the ability of which to conduct rays is taken as 100%. The air gap between the layers is 6 mm, but this volume is not enough to withstand subzero temperatures. In the room from spring to autumn, the temperature balance is maintained, heat is accumulated and correctly consumed.
Sheets 8 mm

The variant allows use in year-round greenhouses, in comparison with polycarbonate for a greenhouse of 4 or 6 mm, if room heating is provided. An eight retains heat in the autumn-winter period, but not as effectively as a ten. A metal or wooden frame is suitable for installation.
Features of 8mm polycarbonate:
- the cross-section of the cells is 8 x 10.6 mm
- transparent transmits light in the amount of 85%, color - only 40 - 50%;
- delays up to 20 dB of noise;
- during transportation, it can be bent with a radius of 700 - 800 mm, and during installation in a structure, a radius of 1250 - 1400 mm is allowed;
- the weight of a square of a sheet according to the standard is 1.5 kg;
- thermal conductivity is 3.0 W / m2 ° C.
When installing, the open transverse ends are closed with a special tape or a rigid pad to preserve the insulating properties.
Beam conduction efficiency will not be affected as long as no dust or dirt enters the honeycomb. If this happens, compressed air is blown through the channels using a compressor.
Panels with the abbreviation "Light"

The letters are found in the marking of polycarbonate, mean a material with lightweight characteristics. The cost of panels remains at the level of standard sheets with similar indicators of width, length and thickness, but the dimensions themselves can be reduced.
For example, with a declared thickness of 4 mm, it may in fact be only 3.5 or 3.3 mm. Material with a specified thickness of 6 mm has an actual size of 5.5 mm.
A decrease in indicators affects strength, thermal conductivity, and other qualities. The durability of such material is lower. In the "Light" category, inexpensive UV additives are used that do not last long.
Criteria for choosing a material for a greenhouse
In the greenhouse, you need to ensure the standard humidity and temperature in order to grow crops effectively. Structures are characterized by a large square area and significant spans, therefore, polycarbonate with a low weight and the required strength indicators is selected.
Polycarbonate boards are chosen according to their properties:
- density;
- panel thickness;
- the strength and location of the inner honeycomb;
- degree of protection against ultraviolet rays;
- the colors of the sheets.
Monolithic panels show good light transmission, but cool quickly. Such building material has significant weight, therefore, requires a reinforced frame, which leads to unnecessary costs. For greenhouse structures, cellular polycarbonate is chosen, which best meets the proper selection criteria.
The cost of sheets of cellular polycarbonate matters, which depends on the quality of raw materials and the structure of the material. Inexpensive categories are produced in violation of technology, do not comply with dimensional parameters, therefore, quality characteristics suffer.
Density
All types of polycarbonate have different density values, so they are used for different purposes. In the technical documentation from the manufacturer, all parameters are indicated, most often the data is given in the quality certificate.
Average density values:
- monolithic slabs - 1.18 - 1.2 g / m³;
- honeycomb panels - 0.52 - 0.82 g / m³.
Indicators affect the weight of the sheet, but the thickness in millimeters will remain the same. Materials with a high density are more expensive, so you need to determine the purpose of the acquisition and installation. If the greenhouse is temporary, there is no need to overspend.
For greenhouses, sheets with an average density are selected as standard. This option has the necessary properties and does not require extra costs. High density is used for glazing houses, offices, shopping pavilions.
Thickness
The indicator is referred to as the determining factors in the calculation. Thin polycarbonate does not gain the required strength, and massive polycarbonate transmits less light.
The choice is influenced by factors:
- local climate;
- prevailing wind strength;
- strip pitch for fastening the material;
- time of use (seasonal greenhouse or year-round);
- type of structure (pitched roof or arched).
A calculation that takes into account all conditions is complex, only professionals can do it. You can independently choose a coating, taking into account the practice of using polycarbonate on similar structures or from neighbors.
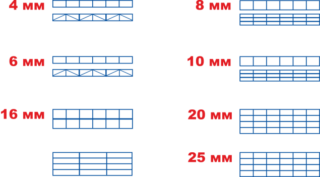
Cellular polycarbonate is produced in dimensions 2.1 x 12.0 m or 2.1 x 6.0 m. Between the stiffening walls inside the profile, a distance is made for a thickness of 4 or 5 mm - 5.7 mm, in a size of 8 or 10 mm in thickness they provide the interval is 11 mm, for a thickness of 16 mm, the cyclicality of the membranes every 20 mm is characteristic.
Honeycomb geometry and polycarbonate strength
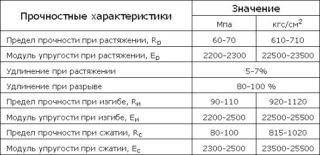
The membranes inside the product form cells, the shape of which affects the strength and reliability of the building material, determines the bearing characteristics.
Honeycombs are performed in the sheets:
- The rectangular shape is most often done. Durability is average, but it transmits light more than all other types. Used in greenhouses without electricity.
- Square cells also differ in similar strength indicators, withstand average loads from snow and wind.
- Hexagonal. They give the material increased strength due to the walls, which are located at an angle. Indicators of transmission of rays are reduced, therefore, they are rarely used for greenhouses or artificial lamps are provided.
In terms of light-scattering indicators, they produce a standard (90% translucency), a special material with a lower non-fogging layer, light-scattering panels with the introduction of resins and an improved structure.
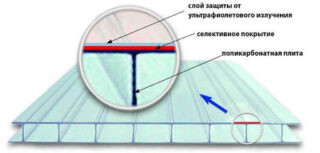
With or without UV protection
Standard untreated polycarbonate is not resistant to sunlight and therefore degrades.
UV protection is used, which is applied by one of the methods:
- Co-extrusion method. The molecules of the protective substance are implanted on the plane of the sheet. The layer does not transmit harmful radiation to the surface, protects against deformation.
- Spraying method. Used by manufacturers of low-cost segments. The layer on the surface becomes thinner, erased by dust, washed off by rain drops, blown out by wind currents.
Use the addition of stabilizers to the total mass during manufacture. The method leads to an increase in cost, therefore, such sheets are used in critical buildings.
By color

The color of polycarbonate for the greenhouse can be chosen from a wide variety of shades. The addition of pigment to the mass reduces the transmission of light rays. Transparent views in the southern regions allow you not to spend additional money on the installation of artificial lighting.
Colored varieties are not suitable for greenhouses. Opal, bronze, green, blue and yellow panels transmit 35 to 60% of the light. Sometimes owners choose reddish hues because these colors are considered beneficial to crops. But along with this, fewer useful rays pass, and the plants suffer.
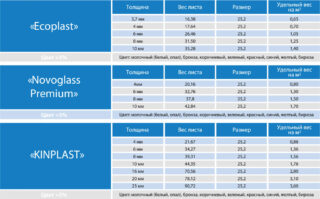
Famous manufacturers
There are various brands on the market that differ in quality and technical characteristics.
Famous foreign brands are represented by brands:
- MARLON - BRETT MARTIN - super strong, transparent lightweight with good quality;
- SUNTUF - PALRAM - with extended temperature range of application;
- LEXSAN - SABIK - dense material with high strength;
- ONDEX - panels with a high modulus of elasticity;
- SALUX is a line of transparent and colored varieties.
In Russia, polycarbonate is produced by the PLASTILUX-GROUP plant. The association manufactures brands: ROYALPLAST, POLYNEX, SUNNEX, GREENUSE-nano, ULTRAMARIN.