Membrane waterproofing film is one of the types of roll-type soft roofing, widely used in the arrangement of flat roofs of industrial and residential multi-storey buildings. In low-rise suburban construction, a roofing membrane is rarely used, since private houses are characterized by a sloping roof architecture, for which sheet material is more suitable for covering.
Membrane roofing application, advantages and disadvantages

As a rule, a membrane for a roof is used in the construction of buildings with a roof of complex geometry (up to a spherical one). This type of roof is used when arranging flat roofs, on which additional usable space is supposed to be created (summer dining rooms, recreation areas, etc.). Membrane-type roofing is laid on the roofs of industrial and residential buildings.
Compared to other roofing coatings (soft roofs, metal tiles, etc.), a waterproofing membrane roof has significant advantages:
- long service life (from 30 to 50 years) with the preservation of all functions;
- resistance to biological and chemical influences;
- the formation of a favorable microclimate in the interior of the building due to the fact that excess moisture comes out;
- the ability to form complex geometric shapes;
- high fire resistance.
The disadvantages of membrane roofing include low strength and high cost.
Device and main characteristics
Depending on what materials were laid in the basis of the membrane roof during its production, the consumer may encounter three types of products manufactured at different enterprises.
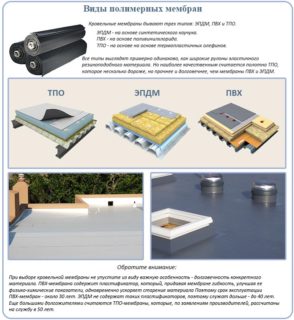
TPO membranes
Roll coating made using thermally plastic olefins is a new generation polymer material. During the production process, it can be reinforced with polyester or fiberglass and therefore is considered the most resistant to high temperatures.
TPO membranes are characterized by the properties of plastic and rubber, which gives them high tightness and strength. Performance characteristics allow the material to be used in the Far North and in regions with hot climates.
The disadvantages of TPO-roofs include insufficient elasticity and the need for regular maintenance. When installing the roof, it is necessary to use special welding equipment, which ensures the connection of the panels to each other using hot air.
The most famous manufacturers of this popular material: Genflex (USA), Trelleborg Building Systems (Sweden), Sarnafil International AG (Germany).
PVC roof membrane
Laying PVC roofing is not difficult, however, it requires strict adherence to the instructions.PVC membrane for roofing has been used in construction since the 50s of the last century, which was largely facilitated by a simple and affordable method of its installation.
PVC membranes are manufactured by such well-known concerns as Protan (Norway), Carlisle (USA), SIKA (Switzerland), etc. In recent years, the domestic companies Technonikol and Penoplex have also joined them.
The main disadvantage of PVC membranes is aging under the influence of sunlight. Traditional PVC roofing is protected from this with a special dressing, and TechnoNIKOL roofing membranes are manufactured using the unique TRI-P® technology, which extends the life of the material by changing the structure of its upper protective layer with a thickness of 200 microns.
EPDM roof covering
The joining of the canvases to each other is carried out using glue, which reduces the reliability of the roof during long-term operation.
One of the most famous manufacturers of EPDM membranes is the Turkish company Aktas, whose official distributor in Russia has recently become Technoprok.
There is a five layer composite type EPDM membrane. The top layer is based on synthetic rubber, and the bottom is a bitumen-based polymer material. Reinforcing mesh made of fiberglass is located between the layers. The membrane is used in the construction of complex roofs that are subject to increased mechanical stress. Such material is produced, for example, by the company Foenix (Germany).
Purpose of membranes
Depending on the layer in which the polymer membrane is used, its purpose is different.
- Breathable - made of synthetic fibers and protects the roof from precipitation. Capable of passing water vapor from inside the building.
- Anti-condensation - absorbs and removes condensate that forms inside the main roofing. Such properties are given to the membrane by a polypropylene base with a waterproof coating.
- Vapor barrier - made on the basis of polyethylene and protects the roofing "pie" from moisture in the air escaping from the interior of the building. Among the manufacturers of this type of membrane, the Danish company Rockwool is the most famous.
- Polymer - designed for roofs with a soft roof. The membrane is made of polyvinyl chloride, which gives it water resistance and durability.
- Super diffusion - protects internal structures from atmospheric influences and removes moisture that forms in the under-roof space outside. This type of membrane is characterized by high strength and flexibility.
The super-diffusion membrane Decker Proffessional, presented in the CIS markets by the European industrial association Eurovent, is especially popular with roofers.
Installation technology
- ballast;
- mechanical;
- glue;
The method of fastening is chosen based on the climatic conditions of the building and the geometry of its roof.
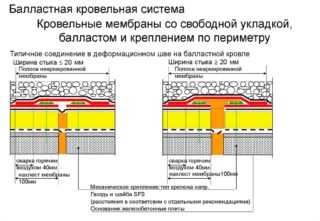
Ballast method
Fastening with ballast when laying a membrane covering is used when the roof slope is no more than 15 °. Installation technology is as follows:
- The membrane sheet is freely rolled over the surface of the roofing "pie", overlap the adjoining edges by about 100 mm, connected at the joints with self-adhesive tape and fixed to the protruding elements of the roof.
- The membrane attached to the roof is covered with ballast, which can be rounded gravel or crushed stone. River pebbles are also suitable.
One square meter of the surface of the canvas must account for at least 50 kg. ballast.If unrolled stones are to be used as ballast, the membrane must be protected from mechanical damage by laying a dense non-woven fabric over it.
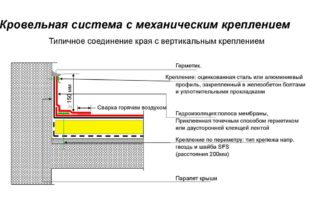
Mechanical method
- The roof surface is covered with non-woven geotextile material.
- Roll out the membrane sheet on the roof with an overlap of the adjacent edges by about 100 mm.
- The joints of the canvases are hermetically connected with self-adhesive tape.
- The entire surface of the canvas is pressed against the roof surface with overhead (mounting) rails, plastic umbrellas with a special hat or large disc holders.
The installation step of the fasteners depends on the weather conditions on the roof, and should not exceed 200 cm.
Glue method
Fastening the membrane with adhesive mixtures is used only in the most extreme cases - with complex roof geometries or in areas where the roof is exposed to strong gusts of wind.
The membrane is not glued over the entire surface of the roof, but only along the perimeter and where the canvases overlap. The membrane sheet is glued to all vertical and projecting parts of the roof. The adhesive is applied to the back of the membrane and to the surface of the roof that is free from dirt and dust.
When glue is applied to the entire roof surface, the reliability of the connection is significantly increased. However, this increases the complexity and cost of work.