Frame construction in the private sector is at the peak of its popularity. According to statistics, buildings of this type make up more than half of all ongoing projects, significantly ahead of their counterparts made of brick, timber and foam concrete. This trend is explained by the numerous advantages inherent in the technology used.
Description of the frame-panel house

Frame buildings are made in several stages. Omitting the moments of arranging the foundation and floors, one should dwell on the main characteristic of the project - the walls. They are collected in a specific sequence. The initial stage is the installation of vertical racks, then the upper strapping and crossbars are made. As a result, lattice frames are obtained from boards, beams or steel profiles. The structures are sheathed on the outside with slabs, then the cells are filled with insulation, waterproofing and interior decoration is performed.
Panel-type buildings differ somewhat in the assembly principle. A frame is also made, but with larger openings. Its filling is carried out not sequentially with different materials, but with ready-made blocks. The master needs to insert, align, secure and seal the remaining gaps. Shields can be made independently in size or purchased ready-made in the retail network.
Another option is the use of panels, which, in addition to insulation, perform the function of external decoration (facade panels). They are attached over the frame, after filling with insulation, it is sheathed only from the inside.
Both approaches have their own characteristics, pros and cons. The first solution is optimal for zones with warm and temperate climates. The second is for the northern regions, since double thermal insulation is provided without losing the internal volume of the premises.
Design features

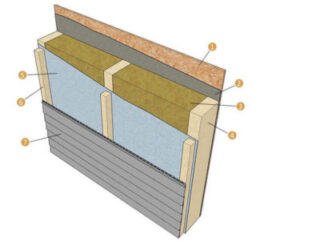
Frame-panel buildings have such a device:
- Foundation. Since the structures are lightweight, light columnar, pile, strip bases are usually made for them, or a slab with a thickness of 100-150 mm is poured.
- Overlapping. A bar of 200x50 mm or 150x50 mm is used. Insulation is laid inside. From below, the logs are hemmed with galvanized iron, and from above they are covered with OSB, chipboard or a massive board.
- Frame. It is made of coniferous timber 50 mm thick and 100-150 mm wide. The wood is impregnated with an antiseptic, fire retardant and hydrophobic agent. Mounting is carried out with corners made of stainless steel or aluminum.
- Filler. Basalt wool is considered the best option. Its performance characteristics are much higher than that of polystyrene, fiberglass and slag counterparts. The insulation is closed on both sides with a steam membrane and a windproof film.
- Roof. Consists of rafters, battens, counter battens, insulation, film and roofing.
External and internal finishes are selected based on the priorities of the owners and the climatic conditions of the area. As a rule, indoors they are sheathed with imitation timber or drywall, outside - with siding or tiles.
Pros and cons of a panel house
Considering the pros and cons of a frame house for year-round living, you need to take into account all the nuances that can affect the quality of your stay in the room.
The advantages of such buildings:
- Ease of construction. She does not need a powerful expensive base.
- Lack of wet work. The possibility of construction at any time of the year.
- High level of thermal insulation. There is no need to warm up the building in the spring and cool down in the summer.
- The speed of construction. With a few helpers, a home can be set up in just a couple of months.
- Small budget. The materials are inexpensive, and there is no need to use heavy equipment.
- Low heating costs, as the walls do not absorb heat, perfectly isolating the premises from the external environment.

It should be noted also the disadvantages:
- Complete tightness of the premises. Effective forced ventilation is needed.
- Risk of infection by insects and rodents. The problem is relevant, but can be eliminated with the help of careful sealing of cracks and regular treatment with antiseptics.
- Relatively limited strength to wind loads. This drawback can be eliminated, but requires the use of a reinforced frame and fasteners.
Disadvantages are inherent in any project. Provided that quality raw materials are used, the building can last up to 100 years.
Preparatory design
Frame construction rules are regulated by modern SP 352.1325800.2017 and old, more detailed SP 31-105-2002. The documents set out the provisions regarding the choice of material, its fastening, insulation and cladding. There are also recommended calculations of maximum permissible loads and design principles. For those who decide to build a house on their own, this is a great help.
Design is a responsible event where you need to take into account all the nuances. Initially, you should choose a suitable place, orient the building to the cardinal points, take a soil analysis, then draw up detailed drawings of each functional structure.
Choosing the right material is essential. This primarily concerns wood. It must be dry, pre-dried. Better to take glued laminated timber, impervious to moisture changes. An equally important planning step is the organization of ventilation. No matter how high-quality the materials are, they will not last long in conditions of high humidity.
The use of frame technology in construction

Frame construction is not limited to the private sector. It is widely used in the construction of multi-storey buildings for a wide variety of purposes. The essence of the method is that first a skeleton is made of reinforced concrete racks and floors. Then the openings are laid with lightweight shields, including those with window openings. Internal partitions are installed in the same way.
In order to avoid drafts, inserts are installed, and in cold areas - facade thermal panels. Houses are being built quickly, inexpensively, and are distinguished by an acceptable level of comfort.
DIY construction of a frame-panel house
Construction can be carried out at any time of the year, but it is better to start it in the spring, after thawing and shrinkage of the soil.

Sequence of work:
- Installation of the foundation. You can work on pile, columnar and bored foundations right away, the cast structures must stand up to 28 days.
- Floor arrangement. First, the logs are laid and the bottom hem is made. Then thermal insulation is carried out and the subfloor is laid.
- Installation of the lower strapping. Usually, a 200x200 mm timber from cedar or larch is used for this.
- Securing vertical supports. The step is taken within the range of 60-80 cm for the width of the insulation, the height is 250-280 cm. Temporary supports are placed.
- Installation of the upper harness, rigidly fixing the rack.
- Installation of crossbars.The distance between them is determined up to 100 cm, with the exception of places for openings for windows and doors.
- Arrangement of the roof, where thermal insulation and ventilation are included.
- Fastening a windproof film from the outside and vapor-permeable from the inside of the frame.
- Installation of OSB boards from the facade, drywall or plywood sheets from the inside.
If ready-made panels are used, they are fixed in the openings, after which the cracks are blown out with foam.
In conclusion, the surfaces are finished with materials selected by the owners.








