The pitched roof is an integral part of the building that protects it from precipitation and is an element that largely determines the style and architectural appearance. Roofing systems are divided into simple and complex, residential and utility, steep and flat. The classification includes many forms of roofs used in private construction. Each of them has its own characteristics, pros and cons, construction technology.
The structure and main elements of the pitched roof

The most common option in private construction is a multi-pitched roof. It is a structure in which there are two or more inclined surfaces on which the covering material is fixed.
A standard pitched roof has the following structure:
- Rafter system. Depending on the chosen shape and size, layered and suspended structures are used. The former are used to equip small buildings without internal load-bearing walls. Hanging rafters are used when covering large buildings, when it is necessary to save as much usable space in the attic as possible.
- Insulation. Designed to create a thermal barrier between the street and rooms located under the floor slab. Most often, developers choose basalt wool, polystyrene and polyurethane foam.
- Waterproofing. Serves to remove moisture from the attic and prevent its penetration from the outside. The membrane sheet provides effective drainage of accumulated condensate, preventing water from entering the outside.
- Roofing material. Performs the functions of protecting internal fragments from precipitation, as well as shaping the appearance of the building. In construction, roll, flexible, piece, sheet materials made of iron, copper, ceramics and fiberglass impregnated with an insulating composition are used.
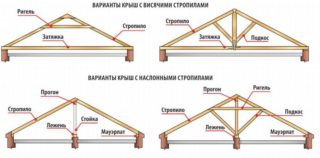
The roof frame can consist of the following parts:
- mauerlat;
- rafter;
- skate;
- crossbar;
- tightening;
- rack;
- run;
- sill;
- wind board;
- counter-lathing;
- lathing.
In order for the roof slopes to have high-quality ventilation, an airtight connection between themselves and the wall, additional elements are used. These include corners, abutments, valleys, gutters, ridges, adapters, and aerators.
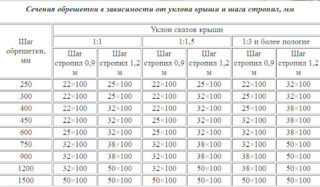
Sizing calculation
A roof slope is a surface that is affected by the following factors:
- Wind. The higher the vaults, the higher the pressure they experience. The force exerted by the currents of the atmosphere tends to overturn and lift the dome from the base.
- Snow load. Snow melting angle is individual for each type of material used in private construction. Also, coatings have different bearing capacities. With a large accumulation of snow, they can deform under its weight or the frame will not withstand.
- The mass of workers who will carry out repair or installation work. Added to this are tools, equipment, belay devices.
- Weight of roofing, insulation and waterproofing. If sheet metal exerts little pressure, then products made of clay, copper and asbestos cement create a rather serious load.
In accordance with building codes, regardless of the slope, the overhangs of the slopes should protrude beyond the outer walls at a distance of at least 40 cm.It is impractical to increase it more than 100 cm, as this leads to an increase in the lifting wind load on the overhangs and the entire structure as a whole. As for the distance between the rafter legs, for gentle slopes it is taken 60-80 cm, and for steep slopes it can increase up to 120 cm.
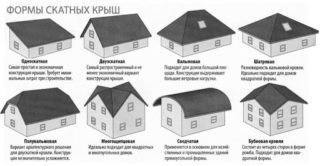
Basic forms and their distinctive features
In private construction, the following roof forms are used:
- Shed. The simplest design and implementation of the structure, consisting of one inclined arch. Mostly it is used for the arrangement of summer cottages and utility structures.
- Gable. It is the most popular construction in private construction. Consists of side arches and pediments at the ends.
- Hip. It is a modification of the four-slope structure, where there are trapezoidal vaults on the sides, and small triangular slopes (hips) on the sides of the building.
- Tent. Consists of the same or two pairs of triangular slopes, forming a kind of tent with a square or rectangular base. It is characterized by excellent tightness due to the absence of gables.
- Mansard room. This is a kind of gable and hip structure with broken side arches. This layout allows you to make the most of the usable space under the roof. Gables are used for the installation of windows and stairs with an entrance group.
- Multi-pliers. The most complex structure in planning and execution, consisting of many inclined rafters, ribs, valleys. It is used for the arrangement of buildings with a polygonal wall configuration.
- Vaulted. Consists of curvilinear slopes of concave or curved shape passing into each other or joining at an angle. During construction, arched rafters are used. The design is used for residential and recreational buildings.
- Diamonds. A beautiful structure with flooring of a diamond-shaped broken configuration. Convex and concave transitions between the slopes take place.
Modern technologies and materials allow you to independently assemble a roof of any complexity.
DIY construction features

When erecting a pitched roof with your own hands, you must take into account all the nuances at each stage of this process.
- Work with a quality and sharp tool. This is the only way to create clear shapes of parts and reliability of connecting nodes. The use of sharp saws will avoid cracks in the structural members.
- Cutting precision. If a mistake is made, then it is better to replace the defective element and make a new one than to risk the entire rafter system.
- Wood preparation for installation. From the blanks, you need to cut off the bark, remove the areas affected by fungus and insects. After that, the timber and boards should be treated with an antiseptic and fire retardant.
- Maintaining the alignment, vertical, horizontal and slope of each part. Violation of the geometry leads to a weakening of the frame and a violation of its stability.
- Insulation of metal parts used for fasteners. When the temperature drops, the hardware becomes covered with condensation, which is absorbed into the wood and causes it to rot.
- Compliance with the rules for laying roofing material. The formation of cracks, distortions, holes is not allowed. Seals, sealants and mastics should be used if necessary.
It is necessary to correctly approach the design of the overhangs. They need to be hemmed to provide a presentable look while maintaining free air circulation.
Selection of roofing

The following materials are provided at the disposal of a private developer:
- ondulin is a universal coating in the form of sheets with a wavy profile;
- clay tiles - a classic proven over the years, distinguished by their strength, presentability and rather high cost;
- slate - heavy asbestos-cement slabs with a wavy section, gradually coming out of use;
- corrugated board - a light and inexpensive coating, which is a profiled steel, powder-coated;
- flexible tiles and stripes - can be used on difficult curved surfaces with any slope.
The choice of roof covering directly affects the appearance and performance of the roof.