Aerated concrete is a popular material for the construction of a private house. However, the stone is hygroscopic and needs protection. Most often, plaster is used for this. For aerated concrete, the plaster mixture must be selected with certain properties.
Features of aerated concrete

Aerated concrete is a type of aerated concrete. The entire mass of the material is filled with small uniform round cavities - pores. This feature is the result of manufacturing technology.
Aluminum powder is added to the primary mixture of cement, sand, lime and water while mixing. As a result of a violent chemical reaction, hydrogen is released. Gas cannot escape from a viscous heavy material and forms a lot of air bubbles in its mass.
Aerated concrete is obtained by the autoclave method. The initial mixture is loaded into an apparatus, where it is treated with steam at a temperature of 200 C. The completely solidified material is cut into blocks.
The materials and technology used provide aerated concrete with a number of undoubted advantages:
- The porosity results in higher thermal insulation properties compared to conventional concrete. In the southern regions, a house made of aerated concrete does not need insulation.
- The material is much lighter than concrete, which reduces the construction time.
- The blocks are large, this also makes the work easier.
- Since aerated concrete is cut into bricks ready-made, the size and shape of the blocks are very accurate. This allows the blocks to be laid not on mortar, but on glue. The resulting seams are thin and the risk of cold bridges is minimal.
- The stone is easy to cut and saw, drill holes.
- The material does not burn, does not support combustion, is not prone to mold.
- Building a house from aerated concrete will cost 1.5 times less than from a conventional one.
There are also disadvantages:
- The pores of the blocks are open, because they are obtained sharp, so aerated concrete is hygroscopic and capable of absorbing up to 25% of water. The material must be plastered both inside the house and outside.
- Due to open pores, the frost resistance of the material is also low - no more than 25 cycles. So gas blocks cannot be used in the northern regions.
- Concrete does not hold fasteners well: heavy furniture and equipment cannot be fastened without walls.
The material is used only in low-rise construction. Aerated concrete cannot withstand high loads.
Basic requirements for plaster

Plaster mixes are distinguished by composition and purpose. They should be chosen very carefully.
The wall consists not only of a row of bricks or gas blocks. This design includes finishing inside the house, insulation, waterproofing that protects the insulation, finishing outside the building. All this multi-layer structure obeys a single rule: each next layer in the direction from the inside to the outside must have a higher vapor permeability than the previous one, so that moist air from the room can be discharged outside. If, for example, plaster outside the house has less vapor permeability than the wall material, moisture will be trapped inside the wall and will accumulate until it is destroyed.
The gas block is a material with high vapor permeability. Exterior plaster should be superior in this parameter. The material for indoor use can have both low and medium vapor permeability.
There are other requirements as well:
- Plastering a house made of aerated concrete is difficult due to the porosity and hygroscopicity of the material. It is necessary to choose a mixture with high adhesion.
- Due to these same qualities, the layer of plaster or paint on the surface of the gas blocks dries very quickly, which often leads to cracking or shedding. Therefore, deep penetration compounds are needed for finishing.
- The material absorbs moisture. The denser the consistency of the plaster, the less water will be inside the wall.
- To "close" the pores, thereby reducing water absorption, it is better to use special compounds that form a dense film not only on the surface, but also in the upper layer of the material. Such mixtures are taken for finishing wet rooms.
- Interior decoration should be not only practical, but also beautiful.
The less vapor-permeable plaster was used for interior decoration, the more the house needs additional ventilation.
Varieties of plaster

How to plaster a wall of gas blocks inside the house depends on the device of the wall cake. Insulation is located inside or outside, walls are finished or a ventilated facade is equipped - all this affects the choice of plaster for interior decoration.
It is best to use special mixtures developed for finishing gas silicates. If this is not possible, use other mixtures.
Lime-cement
A common mixture of this kind is the cheapest type of plaster. It has good vapor permeability, is quite durable, but it is afraid of water. Due to the large proportion of lime, such plaster has some antiseptic properties and prevents the appearance of mold and mildew.
For finishing aerated concrete, specially formulations with additives are taken. They are specially designed for aerated concrete. This plaster can be applied directly to the stone without prior priming.
Lime-cement plaster has high adhesive properties. If it is applied in a thin layer, no reinforcing mesh is required.
Acrylic

Polyacrylate finish. The composition is not afraid of water, prevents the appearance of mold. Low vapor permeability. However, it is quite suitable for finishing inside the house with insulation outside.
Acrylic plaster is recommended for use in the kitchen, in the bathroom, in the bathroom - in rooms with high humidity.
Silicate
Such a composition is produced on the basis of "liquid glass" - potassium silicates. The mixture is not afraid of water, resistant to abrasion and dirt. Water vapor permeability is quite high. Covers up to 25 years.
Silicate plasters have 2 significant disadvantages. The main one is poor compatibility with many other finishing materials based on acrylic, latex, silicone. To paint the plaster, you need to choose a silicate paint. The second problem is the small color gamut.
Silicone
Such mixtures are made on the basis of organosilicon compounds. The composition is not afraid of water, steam, sun. Its peculiarity is high elasticity; cracks do not appear on the coating even after tens of years. The vapor permeability of silicone plaster is lower, but for interior decoration this is not so important.
The disadvantage of plaster is the high price.
Required tools and materials
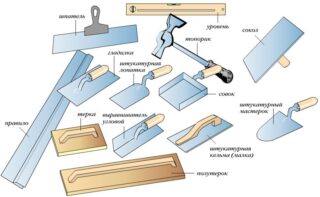
To plaster aerated concrete blocks inside the house, you will need:
- plaster composition;
- reinforcing mesh made of fiberglass or plastic, 100-120 cm wide;
- tile adhesive;
- notched trowel for applying the composition - the recommended distance between the teeth is 5-6 mm;
- deep penetration primer;
- roller or brush for priming.
Additional equipment is needed: a bucket, brushes and rags for cleaning, trestles or a ladder.
Preparatory work
To reduce material consumption, the wall must be prepared before plastering.
- Found cracks, cracks and chips are covered and leveled. Better to use aerated concrete glue.
- After drying, the wall of the room is treated with a stiff brush to remove dust, dirt and oil stains.
- Apply 1 layer of primer with a roller or brush. Sprayers can be used.
- After the primer has dried, dilute the glue according to the instructions and cut the plaster mesh to size.
- From below, glue is applied to the wall, moving up. The layer thickness is 5 mm, the width slightly exceeds the width of the mesh fragment.
- Apply the mesh to the wall, dipping it into a layer of glue. Smooth the adhesive with a notched trowel so that the grooves are horizontal: this increases the adhesion.
After the reinforcing layer has completely dried, plastering is started.
Aerated concrete plastering technology inside the house

The main plaster layer is quite thick. Even an experienced builder cannot apply it exactly "by eye". Plastering the wall is carried out along the lighthouses.
- Prepare a plaster composition. Make sure that there is a minimum of water in the mixture according to the instructions. The aerated concrete will absorb excess moisture and begin to dampen.
- Profiles - beacons, installed vertically, fixed with plaster mortar.
- It is recommended to mount perforated corners on the corners of the walls.
- With a spatula, sprinkle the solution over the entire fragment of the wall to the ceiling.
- The rule is to align the resulting layer with the beacons. Make sure that no gaps are formed between the rule and the wall when moving. If they are, you need to add plaster and re-level the surface.
- After drying, the wall is sprayed with a spray bottle and leveled again. Lighthouses are removed, the recesses are covered with plaster.
- Rub the layer until completely smooth.
After that, you can apply decorative plaster, putty to the surface, paint the wall, paste over with wallpaper.
Plastering an aerated concrete wall from the inside is a practical and reliable way of finishing. But it is important to choose a mixture that is suitable in composition and properties. Aerated concrete does not tolerate "excess" moisture in the plaster solution and is very picky about the adhesion of the material.








