The common space inside the house is divided by walls and partitions. The latter are much lighter, rely on the floor, and not on the foundation, and are more varied in execution. No special permission is required for the erection and transfer of the partition.
Arrangement of partitions in a wooden house

Partitions in a wooden house perform the same functions as in a brick or frame house: they divide the floor into rooms and restrict access to them. They can also play the role of screens and delimit the room not completely, creating a different type of zone. This solution is typical for studio apartments.
The partition has a number of features:
- It is intended only for the formation of the interior and does not bear a structural load.
- It is not a support for the floor. Ignored during calculations.
- Like a regular wall, an interior barrier must provide good sound and heat insulation.
The bulkhead may not be included in the initial design, since it does not create a significant load on the foundation and does not affect the structural features of the room. They are usually easy to erect and dismantle when needed.
The difference between partitions and walls
Partitions in a brick or wooden house and walls differ in purpose and design:
- The main wall rests on the foundation and serves as a support for the ceiling slab. The bulkhead only divides the space.
- Both external and internal walls impart rigidity to the building. The wall is designed taking into account the loads on the foundation. The structure does not matter.
- The wall is made only of structural materials with a high load-bearing capacity. The bulkhead is made from the lightest.
The partition can have a purely decorative purpose or a special one - for example, soundproof.
Material for partitions in a wooden house

Internal partitions in a frame house are made of any relatively light material. Their crowds are usually small. Most often used:
- Wood - for a log house or a house from a bar, this solution is the simplest. The tree, with its low weight, holds the fasteners well and is strong enough so that shelves can be installed on the bulkhead, equipment can be fixed.
- Drywall - The barrier is a metal frame sheathed with drywall. This option is built in a matter of hours, weighs little, has good soundproofing properties. The material, however, is too light to attach furniture or appliances to the surface.
- Frame-panel board - includes a wooden frame and filler made of plywood, drywall, chipboard sheets.
- Glass is an expensive option. The basis is a metal frame, only shock-resistant or tempered glass is taken. Usually the design includes sliding doors.
- Designer - wood and plastic, metal and paper, plywood and fabric can be combined here. Forged bulkheads are very graceful.
Which partitions are better in a private multi-storey building depends on the bearing capacity of the floor slabs. The lighter the barrier, the better.
Requirements for structures
There are only 2 basic requirements for partitions in a house made of logs or timber:
- safety - the bulkhead is carefully secured to prevent falling or destruction;
- the possibility of dismantling - this will significantly facilitate the repair if the owner of the house wants to make redevelopment.
The design should be attractive and match the interior of the room.
Varieties of partitions in a wooden house

Interior partitions in a log or wooden house are made of lightweight materials that do not exert additional stress on the foundation.
Bulkheads on the frame
The frame structure is simple. It is constructed from wooden beams, boards or slats with a minimum cross-section.
- Mark the bulkhead on the floor, wall and ceiling. At the mark, the lower horizontal bar is fixed to the floor.
- The lower end of the vertical rack closest to the wall is supported and fixed with nails or self-tapping screws. The edge of the plumb line is determined by its height.
- According to the marking, the upper beam is fixed to the ceiling.
- Install vertical elements in increments of 55 cm.
The frame barrier is sheathed with gypsum board, chipboard, plywood.
Panel and joinery
The bulkhead can be solid. In a wooden cottage, it is often made from a bar of the same breed, but less thick than for load-bearing walls. Lay the material in the usual way.
Panel structures are installed in technical rooms. They are distinguished from the usual frame by their great simplicity. The components are shields: wooden frames sheathed with boards. They are fastened to each other on metal corners and fixed to the floor and ceiling.
Frameless
Quite a rare option in private construction. The base of the barrier is an aluminum or steel frame fixed to the floor, ceiling and walls. The filler is sheet material, if it is possible to fasten it to connectors or special fasteners. Most often it is glass and plastic - transparent or colored.
DIY installation
Installation of a wall made of gypsum plasterboard is no more difficult than a frame version.
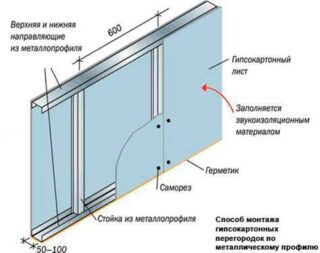
The basis for the plasterboard bulkhead is a metal profile. This is more convenient, since the profiles are configured accordingly, which makes installation easier.
- Aluminum slats are cut to length. The rack profile should be 1 cm less than the physical height of the room. Fasten the strips with self-tapping screws to each other and on dowels to the surface.
- First, a guide profile is installed - PN, on the walls, the floor and ceiling. It forms a supporting frame. If a door is provided in the bulkhead, a profile bend is made in the place of the opening.
- The rack profile is inserted into the frame in 60 cm increments. If the barrier is small, the distance is reduced to 40 cm. For the doorway, the racks are mounted separately and reinforced with a horizontal crossbar.
- If necessary, the partition can be insulated. To do this, foam sheets or thin mineral mats are placed between the posts and fixed with glue.
- Plasterboard sheets are screwed onto the rack profile with self-tapping screws, stepping back from the edge of the sheet by 8-10 mm. The fasteners are deepened into the sheet. A technical gap of 2-3 mm is made between the plates: this is how deformation is prevented, which is possible with temperature and humidity changes.
- If the sheathing is two-layer, the sheets are fastened apart, with an offset of at least 45 cm.
The plasterboard partition can be painted, pasted over with wallpaper, trimmed with clapboard, plastic panels and ceramic tiles.