Finishing of buildings is given special attention. It must be functional and reliable. The ventilated façade subsystem is the basis for the currently popular insulation and design technology. Manufacturers offer various types of components, you need to understand them in order to choose the right option, affordable in price and quality.
The concept of a ventilated facade
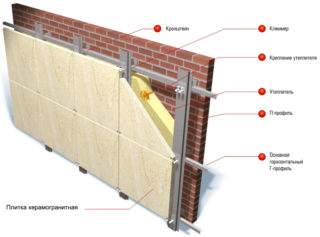
The structure includes several elements:
- The load-bearing base is the main wall of the building, which needs finishing and protection. All components are attached to the base.
- A vapor barrier layer to prevent condensation from entering the insulation.
- Facade subsystem for reliable, correct fastening and ventilation gaps.
- Sound and heat insulator.
- Wind and moisture protection from the side of the facade.
- Decorative finishing.
The assembled structure provides all the tasks assigned to it.
The type of facade subsystem and materials for its manufacture are selected depending on the characteristics of the finishing cladding. It is important to take into account the mass of structural elements and standard fastening methods, the availability of factory hardware on sale.
The façade finishing subsystem must be corrosion resistant and easy to install.
After all layers have been installed, there should be a ventilation gap between the outer cladding and the waterproofing. To do this, provide for a sufficient thickness of the strips or the possibility of their installation on brackets.
Materials for making

Depending on the operating conditions, the characteristics of the insulation and the cladding, the optimal material for the manufacture of the supporting structure is selected. Popular solutions are wood, aluminum, galvanized, stainless steel.
Wood
A façade subsystem made of wood is rarely used for the following reasons:
- fragility compared to metal options;
- susceptibility to decay and destruction by pests (woodworms, rodents);
- fire hazard;
- deformation after getting wet and dry.
The only correct way to mount the beams is to fasten them close to the bearing wall - in this case, bending can be avoided. For fastening, nails, screws or anchors are used.
The thickness is chosen taking into account the size of the insulation.
Most often, a wooden subsystem for a ventilation facade is used in combination with extrusive polystyrene foam, which is produced with a thickness of 20 mm or more.
Before installing, the bars must be treated with compounds from decay and fire. In addition to impregnations, durability is ensured by the installation of waterproofing.
Aluminum

The share of aluminum systems on the market is about 40%. Aluminum subsystem for ventilation facades is used for fixing composite and porcelain stoneware cladding plates.
The factory execution of the profile and components ensures the manufacturability of the assembly. All parts are made exactly to size and only needs to be adjusted to the length of the guides. Geometrical dimensions are standardized for installation of cladding by most manufacturers.
Depending on the type of panels, fastening takes place using mounting hooks (clamps), a slide with a pin, horizontal brackets or visible rivets.
It is advisable to purchase elements of the subsystem and cladding from one seller. In this case, the correct fastening will be selected, suitable specifically for the facade tiles.
Do not use aluminum in aggressive environments. For such places, the metal is protected by anodizing at the factory.
Benefits include lightweight construction and the ability to withstand any type of finish. Service life up to 50 years.
The main disadvantage is the high price.
Cink Steel

Galvanized profiles are an affordable material. Such systems are distinguished by their strength, durability, and ease of installation.
Galvanized products are used for the installation of ventilated facade subsystems with finishing of any weight. The profile and accessories are fireproof.
Among the disadvantages, a shorter service life is noted compared to aluminum or stainless types of products.
Increase the time of use by painting or protecting with polymer coatings.
Galvanized profiles for the installation of siding or profiled sheet are popular.
Stainless steel
Stainless steel products are absolutely unaffected by climatic factors.
Such subsystems are used in high-rise construction, since they are able to withstand any cladding, and in terms of durability they are comparable to the service life of a house.
The cost of the finished structure is high, so the market share of stainless subsystems is approaching 20%.
Comparison of options
When choosing the type of subsystem, many factors are taken into account:
- price per square meter;
- thermal expansion;
- corrosion resistance;
- mass.
A rough estimate of the options for subsystems for facades.
| Material | Thermal expansion | Corrosion resistant | Weight | The cost | Amount |
| Aluminum | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 7 |
| Galvanized | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 6 |
| Painted galvanized | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| Rustproof outer layer | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| Completely stainless steel | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 6 |
Points are awarded according to the principle: the better the indicator, the higher the score.
The sum of the points obtained shows that the difference between the subsystems is small, and the choice must be made taking into account the operating conditions. For example, stainless steel is more expensive than all types, but the service life will allow not to carry out repairs for the entire service life. On the contrary, galvanizing will last the least, but a complete replacement will not cost a lot of money.
The choice of insulation

The most common insulation materials are expanded polystyrene, extrusive polystyrene (penoplex), stone (mineral) wool.
Glass wool is not suitable for ventilated facades, as it quickly cakes under the influence of air humidity, and when it gets wet, it loses its heat-insulating properties.
Foamed polystyrene (foam) has a low coefficient of thermal conductivity, low weight, protects the house from the wind. It does not require the installation of a vapor barrier, which reduces labor costs and the total cost of finishing.
Polyfoam does not absorb moisture, self-extinguishing occurs 3-4 seconds after the cessation of exposure to open fire. Foamed polystyrene is the most budgetary option among all the others - a material such as PSB-15 is suitable for insulation.
Penoplex is a redundant solution for ventilated facades. It is twice as expensive as polystyrene, having the same characteristics. The only advantage is the presence of grooves in the ends of the plates, which excludes the use of wind protection and foaming of the joints.
In terms of thermal conductivity, stone wool roughly corresponds to polystyrene, but has a high specific gravity. To preserve the properties, you will need to install vapor and waterproofing membranes.
The ventilated façade subsystem is an important element. The service life and the appearance of the building depend on the right choice. Thanks to the design, the installation can be carried out independently in a short time. Universal options for fastening the cladding allow you to choose the coating you like, and over time, replace it with a new one without dismantling the guides.