The pitched roof system is the most popular among private developers. The sloped surface ensures efficient drainage of water and snow, so that dirt and debris do not stay on it. At the same time, this design has a rather complicated structure. The main condition for its stability, strength and durability is the correct calculation of the rafter system. This is a procedure for which you need to have a lot of different data regarding the properties of the material of manufacture, the shape of the roof and climatic conditions. You can calculate the rafters yourself. To do this, there is no need to contact a design firm, but you will have to spend a lot of time. Mistakes in one direction or another are fraught with disastrous consequences for the building and risk to the health of its residents.
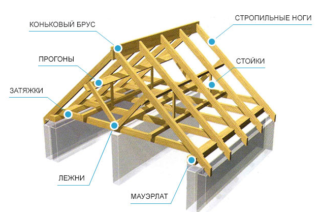
Classification of loads on the rafter system
- rafter - is the main element on which insulation, waterproofing and lathing are installed;
- Mauerlat - a powerful bar laid on external walls as a stop for rafters;
- lathing - slats on which the roofing is laid;
- run - a bar that ensures the longitudinal stability of the bearing fragments;
- bed - takes part of the load from the racks to the Mauerlat;
- rack - vertical supports redistributing pressure from the rafters between the bed and the Mauerlat;
- strut - designed to support the rafter leg and prevent it from sagging under vertical pressure.
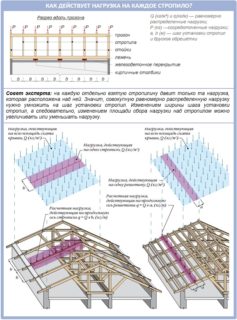
To correctly calculate the rafters, you need to familiarize yourself with the components of the load that affects any roof.
Classification of external factors affecting rafter structures:
- Basic. They are subdivided into permanent and long-term. Constants include the weight of the frame itself, insulation, waterproofing, membrane film and fasteners. Long-lasting - The weight of snow that lays on surfaces for more than one hour. Also, the slopes are under stress from the water flowing down it during an intense rainstorm.
- Additional. This implies the influence on the structure of a significant volume of ice, strong gusts of wind and the weight of the craftsmen in the process of installation and repair work.
- Force majeure. Extreme factors lasting for a short period of time are taken into account. These include explosion, hurricane, earthquake or landslide, fire.
To calculate the rafter system of a gable roof, values are taken that are as close as possible to the limit. Based on the comparison of the data obtained, the cross-section of the rafters is calculated, the calculation of the step of the rafters, the height and slope of the roof are set.
Roof loads and formulas for their calculation
The following types of loads are taken as a basis:
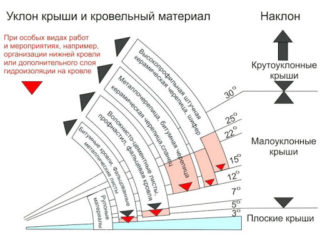
- Snowy. Obtained from card attachments. Information in the tables is entered according to the averaged results of long-term observations. For roofs with a slope of up to 25º, the load is within 80-560 kg / m² for snow regions of I-VIII categories with a step of 80. With a slope steepness of 30-55º, a reduction factor of 0.5-0.7 is introduced.
- Wind. These data are also obtained from reference tables filled in with statistical information.The calculation is carried out in kgf / m² for climatic zones and types of terrain. The load is 17-85 kgf / m² for terrain types I-VIII. Influences the result and the height of the building. The more it rises above the ground, the greater the coefficient, which is 0.75-1.25 for houses 5-15 m.
- The weight of the roof is one of the determining factors and is determined in the weight of one square meter of the covering, taking into account the technological overlays and seams. The specific gravity, as well as the pressure of the material, is in kg / m²: soft tiles - 12, corrugated board - 5, ceramic tiles - 50, slate - 13, bitumen - 6, slate - 45, rebate - 6. The total weight is determined by multiplying the specific weight per total area.
- Weight of subfloor and battens. The base for the roof does not particularly affect the strength of the frame and is made as light as possible in order to reduce material costs and the weight of the frame. The average weight of the lathing is 15-25 kg / m². This indicator is determined by the angle of the roof and the type of structure. In the case of a lattice scheme, it is minimum, and with a solid base, it is maximum.
- Insulation weight. The most common polystyrene and polyurethane foam today are so light that they are taken into account when designing complex structures for operation in difficult conditions, where literally every kilogram matters. Insulation weighs on average 10-20 kg / m². The heaviest, but also effective, is basalt wool.
- The weight of the rafter system. There is no alternative to wood, so light and durable pine and spruce timber is used to assemble the frame. The use of valuable wood species is justified only in a humid climate, especially in the coastal regions of the country. Depending on the selected material, the weight of the rafter system is calculated according to the standard 10-20 kg / m².
- The weight of the workers doing the repairs. Taking into account the specifics of the installation or repair of the roofing, no more than four people from each slope can be on the roof at the same time. In this case, pressure is exerted not only on the entire surface, but also pointwise - separately on each supporting part. Therefore, the load from the builders is considered to be the maximum and is calculated in the range of 80-120 kg / m², depending on the build of the repairer.
- The bearing capacity of the material depends on such factors as the type and grade of wood, its section (height and width of the timber), the degree of drying and processing with special fluids.
To calculate the need for the material and draw up a competent drawing of the rafter system, you need to find reliable data, summarize them, and then reduce them into a single formula. At the same time, every nuance matters in the project - the angle of the roof, the installation frequency, the length and thickness of the rafters.
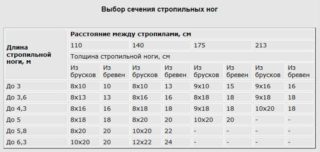
Calculation of the cross-section of the rafter leg and tightening
The tables available in SNIP should be used to calculate the following parameters of the pitched system:
- Slight slope angle (sloping roof). When it is less than 25º, the gravity of the panels, insulation and the frame itself acts more on the rafters. In this case, the wind load tends to raise the roof and tear it away from the Mauerlat. With a flat structure, sagging of no more than 0.05% is allowed, and the length of the rafters should be minimal. The required stability is achieved by reducing the size of the overhang and additional fixation to the walls of the house.
- A steep roof with a complex shape. Here, the bending pressure of the rafters is minimal, since they are located at an angle to horizontal structures. But the structure is experiencing much greater pressure from the air masses, which tend to overturn it. The so-called sail is the main enemy of steep roofs.
- Snow cover thickness. Taking into account climate changes, one should focus on the maximum historical indicators. You can get the information you need from your local hydrometeorological office or government agency.
- Average annual temperature. You need to pay more attention to the winter period. The possibility of heavy rainfall followed by a cooling cannot be ruled out. Such phenomena lead to the formation of ice and the accumulation of a large amount of snow on the roof. This is what most often causes the destruction of the rafters.
- Rose of Wind. Air currents have a strong peel or vertical effect on the coating. The wind direction should also be taken into account in order to give the roof the most aerodynamically optimal configuration and location relative to the cardinal points.
- Strength (degree of bending) of wood. In most cases, spruce and pine are used. Larch and cedar are more durable, but much heavier and more expensive, therefore they are practically not used. 1st grade of spruce and pine withstands a load of 140 kg / cm2, 2nd grade - 130 kg / cm2, and 3rd grade - 85 kg / cm2. From this it can be understood that it is not worth saving on materials.
- Weight of construction materials. We are talking about crate, insulation, waterproofing and membrane. If an attic is being made, the weight of the interior decoration of the ceiling and walls, which are fixed to the rafter system, is taken into account.
Based on the comparison of the data, calculations of the need for materials are made and an estimate is made for the arrangement of the roof.

This document consists of the following points:
- mauerlat;
- roof trusses;
- lathing;
- counter lattice;
- lie down;
- racks;
- supports;
- screeds;
- runs;
- struts;
- eaves nodes of the roof overhang, pediment outlets;
- interface with pipes, chimneys and ventilation ducts;
- structures for roof or ventilation windows;
- fasteners.
The estimate must be calculated with a reserve of 10-15% for errors, trimming, losses during transportation, storage, carrying out lifting work.
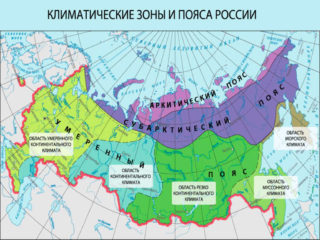
Accounting for the climatic map of the region
On the other hand, the effect of temperature on all roof elements cannot be underestimated. Both strong cooling and heating lead to their deformation. This becomes the reason for the deviations of the supporting structures from the technological axes, which significantly weakens their bearing capacity. The way to solve the problem is to increase the thickness of the rafters in accordance with the temperature section of the technological chart.
It should be remembered that the main danger for large roofs is wind. Information on the direction and speed of movement of air masses can be found in each atlas, where detailed climate information is available for each region.
Building codes
In accordance with the provisions of SNIP II-26-76, the pitch and section of the rafters are determined by calculation, depending on the existing loads. The step size and shape of the rafters are determined according to the tables set out in the document.
It consists of the following sections:
- General Provisions.
- Norms and rules of construction (duties of officials involved in the development and implementation of the project).
- GOSTs for construction - rules for carrying out design work, construction features for each region.
- Rules for the execution, delivery and acceptance of works. All items required for implementation.
Following the requirements specified in the normative act, you can draw up a project that will not be much inferior to a document from professionals.
Examples of calculation of inclined systems
You can calculate the parameters of the rafter system using the formula with pre-collected data:
- Snow load: S calc = 199 kg / m² × 1.4 = 278.6 kg / m².
- Wind load: Wcalc = 28.02 kg / m² × 1.4 = 39.23 kg / m².
- Permanent load: Gcalc = 53.11 kg / m² × 1.1 = 58.42 kg / m².
It remains to introduce the strength coefficients of the roof at an angle of 35 degrees with a rafter pitch of 900 mm from grade I pine, up to a ridge of 7 m with corrugated board as a roofing material. The result will be as follows: rafters with a section of 125x200 mm.