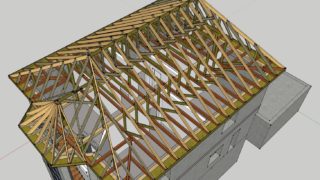
The rafter system is a supporting frame of a sloping roof, which forms its configuration and includes inclined beams, sheer racks, struts, rafter girders. A strapping Mauerlat is installed along the perimeter of the walls for support. The step of the rafters is the distance through which the oblique elements are installed, with the help of a correctly selected gap, the load is equally transmitted to the loaded walls.
- Factors that determine the distance between rafters
- Roof shape
- Roof angle
- Rafter parameters
- The structure of the rafter system
- The totality of all loads
- Lathing material and its parameters
- The minimum permissible cross-section of rafter legs
- Calculation of the amount of material
- Preparatory work
- DIY installation features
Factors that determine the distance between rafters

According to the norms, the gap does not exceed 1 m, and the minimum value is 0.6 m.For an insulated roof, the indicator is chosen so that the distance is equal to the width of the insulating material, otherwise there will be a lot of scraps, seams that need to be further processed. The step is determined depending on the quality of the wood and its bearing capacity.
The pitch of the oblique supports depends on the conditions:
- roof configuration;
- inclination of the rays;
- rafter sections;
- system type;
- the magnitude of the total loads;
- lathing material and its dimensional parameters.
The distance between the rafters of a gable roof or any other shape is influenced by the type of material. Profiled sheet, slate, soft flooring resist forces in different ways and differ in different weights. Natural tile has a considerable mass, therefore, a reinforced system of supporting structures is installed for its laying.
The metal tile weighs a little, but differs in rigidity, holds snow well, therefore, for it, the interval of rafters is increased from 0.6 to 0.95 m with a cross-section of an inclined run of 50 x 150 mm.
Roof shape
In pitched roofs, the slope is usually limited, so the rafters are subject to great efforts. The distance between the oblique stops is chosen 0.6–0.7 m. Light materials are used to cover the structures and a continuous crate is made of boards or chipboard panels.
A gable roof is often arranged, since the structure has high technical characteristics. In this case, the slope plays a role, on which the length of the oblique supports depends. The pitch of the rafters of the gable roof is set taking into account the flooring material, the type of lathing, the length of the span.
A mansard roof often consists of two parts with a different slope, usually the steepness of the lower section is greater to increase the roof space. Two rafter systems are being developed, in which they take different installation intervals. For the lower part, 0.9 m is taken, and in the upper slope, the rafters are placed at a distance of 0.65-0.75 m.
The hip roof is distinguished by a complex system with slopes at the ends and sides, which have a heterogeneous length and steepness. The roof frame requires a complex calculation, since the rafters do not rest on the ridge beam, but on the bowstring, which tightens the truss at an angle.
Roof angle

Angles from 20 to 50 ° are considered standard slopes, slopes of a lower value contribute to the accumulation of snow masses and an increase in the load on the structural roof system. Increasing the steepness also increases the force of the wind, which is especially important for multi-storey buildings.
There are standard indicators for the smallest slope of roofs from different materials:
- tile, slate - 22 °;
- soft tile, profiled sheet - 12 °;
- metal tile - 14 °;
- ondulin - 6 °.
The slate weighs a lot, at the recommended slope, sloped elements are placed under it with an interval of 0.8 m. The gap between the inclined beams under the corrugated board depends on the height of the corrugation on the sheets and corresponds to a value of 0.6–0.9 m. A large wave height increases the rigidity of the coating and resistance to the weight of the snow, so the distance is increased if the recommended roof slope is observed.
Rafters are mounted under the ondulin with a similar pitch, if the slope is small. The solid base is made of chipboard, sheets of waterproof plywood, so the step of the rafter legs is taken equal to half the width of the panel. Rafters for polycarbonate are made straight or semicircular at different slopes. Usually, due to the lightness of transparent sheets, the pitch is taken in the range of 1.5–2.0 m.
Rafter parameters

Wood is a common material; such rafters are installed in residential buildings and outbuildings. Metal elements, reinforced concrete girders, trusses are mounted during the construction of industrial facilities with large spans.
The parameters of the rafters depend on many conditions, for example, the coating material:
- Decking. Take bars with a cross section of 50 x 75 mm, 75 x 100 mm, or put boards 25-50 mm thick, up to 150 mm wide.
- Profiled sandwich panels for the roof. Such a flooring requires a minimum cross-section of the timber, since the products are very rigid. A bar of 50 x 50 mm is used.
- Polycarbonate. They put a metal square profile (under the arches) with a section of 45 x 45 mm or wooden slats for a pitched rectangular roof with a section of 50 x 50 mm
- Ceramic tiles. The transverse dimensions of the bars are 50 x 150 mm, with a heavy load they take 60 x 200 mm.
The rafters are made of dry wood, the percentage of moisture should not exceed 15%. Roof beams are laid with horizontal beams with a section of 100 x 150 mm. Fillets (rafter legs) are taken with a cross-section in which the dimensional dimensions are half the size of the rafters.
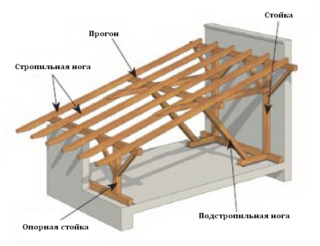
The structure of the rafter system
To find the distance through which the rafters are placed, take into account the structure of the supporting roof scheme.
The design includes elements:
- inclined rafters;
- sheer racks;
- braces, puffs, filly.
In wooden or frame structures, inclined rafters are supported on the upper crown or frame strapping. Along the perimeter of the stone walls, a support-strapping bar with a section of 150 x 100 mm is installed. Sometimes the Mauerlat is placed only under the rafters. The braces and racks are made from boards measuring 25 x 150 mm.
The rafter legs are fastened together at the bottom with puffs, which are connected by the cutting method. The filly lengthens the bottom of the rafter to create an overhang and is a piece of plank. Narozhnik is a shortened inclined beam to support the ramp between the cornice and the girder.
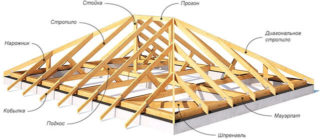
The totality of all loads
The project is developed taking into account the type of roof, the steepness of the slopes and the type of flooring. To determine what distance should be between the rafters, the values of all the forces acting on the system are found and added.
The list of standard and non-constant loads includes:
- the mass of materials of the supporting system and lathing;
- weight of flooring, insulation layers;
- weight of decorative and structural parts of the attic;
- wind action;
- a lot of snow;
- weight of maintenance workers on the roof.
For the calculation, they take the length of the slopes and multiply by the length of the overhang, so the square of the roof is obtained. Estimated wind and snow loads are taken according to information tables in SNiP 2.01 - 1985 "Loads and Impacts".
The end result gives an approximate idea of the minimum allowable interval, since the size of the insulation and the features of the lathing are taken into account.Take into account the construction of skylights and the passage of the chimney, so as not to reconstruct the rafters later.
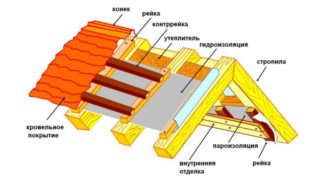
Lathing material and its parameters

The battens support the deck and provide additional rigidity to the supporting structure. The cross-section of the rails and the spacing between them depend on the material and the steepness of the slopes.
Decking requires a decrease in the pitch of the sheathing with an increase in the steepness of the slopes. If the rafters are at a distance of 0.8-0.9 m, and the roof has a slope of less than 15 °, then the frequency of nailing of battens 100 mm wide after 50 mm is recommended.
Types of lathing:
- solid - the gap is not more than 10 mm;
- normal - interval 20 - 40 mm;
- sparse - an interval of 50 - 75 mm.
A solid base of veneered material is often placed under a soft roof so that the coating does not bend and withstand the forces from snow and wind. For wavy bituminous ondulin, an ordinary plank crate is placed. Smooth asbestos-cement slate is attached to a continuous crate, and for corrugated one they provide a sparse one.
The minimum permissible cross-section of rafter legs
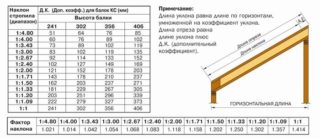
For the manufacture of rafters, a board is more suitable, since it can withstand heavy loads and is an inexpensive option for the material.
The cross-section is determined based on the distance between the rafters and their length (roof height):
- step 2.0 m, leg length 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, m - section, respectively: 100 x 150, 100 x 200, 100 x 250 mm;
- step 1.75 m, leg length 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, m - section: 75 x 150, 75 x 200, 100 x 200 mm;
- step 1.1 m, the size of the rafters in length 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, m - section: 75 x 150, 75 x 175, 75 x 200 mm;
- step 0.9 m, leg length 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, m - section: 50 x 150, 50 x 200, 75 x 250 mm;
- step 0.6 m, rafter size 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, m - section: 40 x 150, 50 x 150, 50 x 200 mm.
The material of the flooring is taken into account, for example, for slate or natural tiles, the section size is increased compared to light corrugated board or ondulin.
Calculation of the amount of material
The length of the roof overhang is divided by the approximate pitch of the rafters. The result obtained is rounded up and one is added. This is how the number of rafters is obtained. To find out the exact distance between the elements, divide the length of the eaves by the number of rafters.
Calculation example:
- overhang length 27 m, approximate spacing 0.8 m;
- calculation of the number of rafters: 27 / 0.8, get 33.75 (34) pieces, add 1, get the number of 35 pieces;
- the exact size of the interval: 27/35 = 0.77 m.
The number of battens is determined by dividing the length of the ramp by the step distance. The total length of the boards or slats is calculated by multiplying their number by the size of the overhang along the length. It is taken into account that in difficult junction points, the ridge area, a double crate is placed on the cornice.
Preparatory work
The walls and floors of the building are being prepared, although the differences may not be visible visually. The difference in height becomes apparent when the support bar is laid successively. They try to align the corners of the house. The masonry is equalized with a solution, performing a screed in the right places, and the wooden frame is brought to readiness with the help of linings, the bulges are constrained.
To correct the log house, a lace is used, it is attached to the two extreme beams at the desired height. The slabs are squeezed so that horizontal areas are obtained at the edge of the beams. The control template is applied to three beams at the same time and the level of the horizon is checked. If the rail with the device is small in length, tie a long bar. The sampling sites are marked for the rafter teeth, pieces of control rails are placed, which indicate the central axis.
DIY installation features
The slots for supporting the rafters must always have horizontal platforms and vertical walls. Violation of the rule leads to loss of stability and displacement of load-bearing elements.
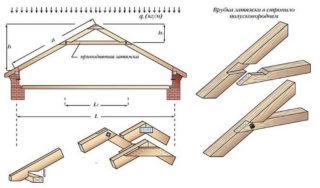
Making a template for a truss structure:
- Two boards 25 mm thick, 10 cm longer than the rafters, are bolted at the top so that there is a possibility of turning.
- The calculated height of the system is measured on the rail in the center of the spike.
- The bonded boards are placed on the end crossings so that their edges rest against the tooth selection.
- Combine the attachment point and the marks on the rail to determine the length of the rafters.
- At the bottom edge, the size of the tooth is laid, the template is lowered to the ground and the thorn is cut out.
- Try on the workpiece on the spot, driving the spikes into the designated cuttings.
If, after installation, the vertex does not coincide with the mark on the rail, it is corrected by releasing the bolt, and the new position is marked on the rail. Measure the dimensions of crossbars, racks, fillies, puffs and other elements of the truss truss. After the required products have been manufactured, they are placed in the mounting position.









Yes, I read it and was surprised! He has worked for more than 30 years in the mine, how much lumber and money fly into someone's pocket, although there are people who do not count money!