In the general case, the combined roof is an original constructive solution, in which the roofing components additionally play the role of attic floors. This approach allows you to combine the under-roof and attic space, which in turn provides significant savings in material and financial costs, as well as simplifies and speeds up the processes of roofing and erection of buildings in general.
Combined roof structure

Combined roofs are a popular roofing option that is used in the construction of industrial and residential buildings and structures. The efficiency and speed of construction of this type of roof became the key to its widespread use in private construction.
The structurally aligned roof has a very different design:
- pitched (traditional);
- inversion;
- horizontal;
- two-layer.
The combined roof fully fulfills its functional tasks when the protection of its heat-insulating layer from getting wet and waterlogged is structurally provided.
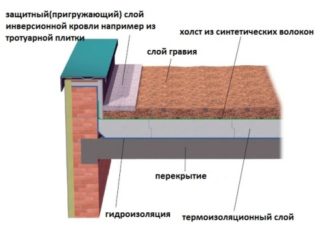
Horizontal roof combined
The roof is adjacent to the structural elements of the building. To smooth out the daily temperature difference, it is usually covered with gravel (fraction 16/32 mm), the thickness of which should be at least 5 cm. When arranging such a roof, special attention is paid to vapor barrier.
In practice, you can find several subspecies of the horizontal combined roof.
- In private houses - a combined flat roof, which is often used to equip a summer terrace. In addition, it can also have an attic space.
- In civil engineering, a two-layer combined roof is used - it is a flat, usually unexploited roof, with two layers of insulation. As the latter, mineral wool is most often used, the upper layer of which is thinner than the lower one. On top, the insulation is covered with a waterproofing film membrane, which reduces the number of "cold bridges" and increases resistance to heat transfer.
Inversion combined roof
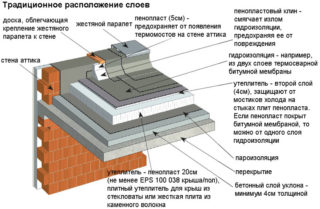
Traditional pitched roof
Arrangement of combined roofs in the traditional way (heat insulator at the bottom, waterproofing membrane outside) has become ubiquitous due to its simplicity and practicality. In this case, the plate heat insulator is an element of the rafter system.
Thermal insulation protection methods
A technically correctly designed and equipped combined roof retains heat, does not let moisture into the under-roof space and protects against noise during rain and other adverse weather conditions.Depending on the method of protecting the insulation from getting wet and waterlogged, the combined roofs are:
- unventilated;
- partially ventilated;
- ventilated.
Non-ventilated combined roof
In non-ventilated roofing systems, the thermal insulating layer is combined with the supporting structure and adheres tightly to it. In the general case, an unventilated combined roof is a "layer cake" consisting of a reinforced concrete base on which the following is placed in succession:
- vapor barrier material;
- insulation (loose or slab);
- cement or asphalt screed;
- waterproofing;
- roll roofing.
In some cases, unventilated combined roofs are supplemented with an attic space, which also serves as protection against moisture penetration into the insulation.
Ventilated
The ventilated combined roof differs from the non-ventilated one in that a ventilated layer is included in its "puff cake". The most common option includes roofing panels fitted with special channels or pores. An air gap is left next to the insulation, through which air circulates freely, while removing condensate. With this design, the combined roof has improved thermal insulation and virtually eliminates the swelling of the topcoat.
Partially ventilated
Partially ventilated roof roofing is an intermediate option between the two structures discussed above. It is based on a reinforced concrete slab with an additional layer of concrete, which has special channels with a diameter of 30 to 40 mm. The structure of such a roof contains a micro-perforated interlayer, which keeps the thermal insulation layer dry. The installation of the roofing carpet is completed by the installation of the roll covering.
Water outlets
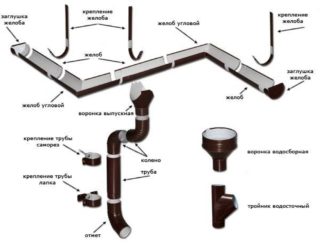
The durability of the roof and the building itself largely depends on the availability of a drainage system and its rational arrangement.
To remove excess water during atmospheric precipitation, plastic or metal pipes are used, installed at the corners of the building and connected with special gutters. Their absence leads to the fact that moisture, getting into the microcracks of the walls of the building, provokes the destruction of the latter. This is especially dangerous in the off-season, characterized by significant temperature changes, as a result of which the walls begin to crumble. This will be avoided by the correct installation of drainage pipes and funnels. In this case, the gutters are installed with a slope of no more than 2 °. Triangular slopes called envelopes are often attached to the funnels. All this will increase the area of the spillway to 800 m². for one funnel. In this case, the length of the drain should not exceed 25 m.
When equipping a combined roof in multi-storey residential buildings of urban development, builders often use ribbed slabs with a padded insulation. These slabs, made of cement fiberboard or technical wool, are interconnected with expanded clay-concrete ribs, arranged simultaneously with the slope of the upper panels. In this case, the internal drainage is made along the valley from the tray nodes. The roof connection to the internal drainage must be airtight and non-ventilated.
When arranging the drainage system, special attention is paid to the joints, which, during the operation of the building, experience high temperature loads.
Subtleties of design and installation features of the combined roof
- The thermal insulation layer must be at least 17-18 mm thick. The number of layers of densely packed insulating material is determined by the angle of inclination of the roof.In this case, voids and cracks should not be.
- It is imperative to arrange a slope, the value of which should be in the range from two to 7 ° (3 mm or more). Insulation or building mixture is used for this.
- The order of the materials of the "roofing pie" is determined by the type of roof - traditional or inverted.
- The presence of unused channels and openings for utilities is prohibited.
- It is recommended to organize drainage systems when erecting buildings in any climatic zone of the country. At the same time, the presence of an internal drainage system guarantees the roof an extended service life.
Repair, operation and maintenance of the combined roof greatly facilitates the presence of a specially equipped exit.
Roof exit
The exit to the roof with a combined roof in different houses is made out in different ways. For example, in private houses, it is most often presented in the form of a dormer window. The exception is houses where the combined roof is used as a recreation area. In this case, a convenient exit to the roof is provided with the help of a small architectural structure, which often serves as an additional decoration for the house.
On the roofs of large industrial buildings, there are engineering structures and communications that require regular maintenance. The exit looks like small buildings with windows and a locking door.