During the operation of the building, precipitation and other weather phenomena affect the roof. If the height of the ridge of a gable roof is not chosen correctly, there is a danger of destruction of the structure even by a slight wind or hail. So that the structure does not have to be repaired or a new one built, it is important to be able to correctly calculate this parameter, as well as the value of the slope angle.
- Roof height-dependent characteristics
- The angle of inclination of the slopes
- Roof surface area
- Load-bearing capacity of the roof frame
- Nuances when calculating parameters
- Roof type
- Roof slope
- Roofing material
- Factors influencing design
- Wind strength and direction
- The nature of the use of the room
- Procedure and rules for calculating the height of the roof
Roof height-dependent characteristics
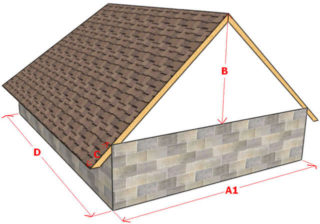
The height of a one-story house with a roof determines its appearance and is closely related to some of the characteristics of the roofing device. Calculating this parameter is also important to determine the consumption of resources for coverage.
The angle of inclination of the slopes
When calculating the height of the ridge of a gable roof, you should take into account: the greater its value, the steeper the slope of the roof will be. If the weather in the area is characterized by a large amount of precipitation or snowy winters, the angle should be sufficient so that moisture does not linger on the roof. Values in the range of 20-50 degrees are considered the norm.
Roof surface area
The height of the roof affects the area of the pitched surfaces. For the installation of a peaked structure, large volumes of roofing materials will be required. Thus, the cost of installation work in this case will increase.
Load-bearing capacity of the roof frame
The dimensions of the roof also affect the weight of the structure. At a high roof, it will be greater, as well as the load on the rafters created by the layers. Such heavy structures require a more powerful frame with more components.
Nuances when calculating parameters
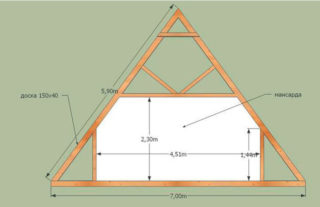
In order to correctly calculate the dimensions of the roof, it is important to understand its design features. The materials used, the architectural design and the slope affect the choice of height.
Roof type
If the structure involves a large number of layers, for example, reinforcing a waterproofing pad or arranging the lower roof, it is made flatter. The large number of slopes suggests sufficient height with a clearly visible tip.
Roof slope
A steep slope construction will have a high ridge. In terms of cost, it will significantly surpass a flat roof. This is due to the increased cost of coating materials. At an angle of 60 degrees, you will need 2 times more finance than for the implementation of a slightly sloping option (10 degrees or less).
Roofing material
If lightweight and easy to install roll materials are used, a high ridge is not necessary. Such coatings are well suited for flat and close to them roofs, but when laying, care must be taken to minimize joints and overlaps. The same rule applies to large sheet materials.
If you plan to lay out a covering of a large mass, the roof is made with a steep slope and higher. This is necessary to evenly distribute the weight over the area and to minimize the deflection of the rafter beams. The tallest and steepest structures are made for roofs, made of heavy material, including many single components, for example, ceramic tiles.This is due to the large number of joints in such configurations. Moisture penetrates into the gaps between the elements, which contributes to a deterioration in the performance of the roof. It is advisable to ensure the maximum possible outflow of water from the surface, and the design with a pronounced slope contributes to this.
Slate roofs should have a higher ridge than metal shingles. This is due to the fact that the first material has a limited length (usually 1.75 meters). Metal coatings can completely cover the slope vertically.
Factors influencing design

The dimensions and proportions of the roof are influenced by weather factors. The structure must be stable when exposed to strong winds and precipitation. In addition, it is necessary to prevent leaks and deterioration of the material caused by moisture.
Precipitation
The north of Europe is characterized by steep peaked roofs, which is associated with high air humidity and significant average annual rainfall. This helps rain and snow slide off the surface faster, without adding additional stress to the foundation and reducing damage to the pavement. In regions with a similar climate, the slope of the slope should be at least 45 degrees. This also applies to areas where the air is usually not humid, but there is a lot of snow in winter.
Wind strength and direction

If gusty winds often blow in the region, the structure is made flat. It is dangerous to make a steep roof with an angle of more than 20 degrees in such places - it can deform. In areas with a quieter movement of air masses, buildings with a flat and high roof can be erected.
The nature of the use of the room
Buildings without an attic are usually lightweight, not intended for permanent residence and serve as outbuildings. In such a room there should be a through passage 160 cm high and 120 cm long. In general, the structure should not be too cramped, and its dimensions should not impede maintenance. Compliance with fire safety measures is also important. If a residential building is being built, an attic space should be provided according to the rules. To use it or not, the owners themselves decide. The attic affects the height of the roof according to whether there is a need to move around it and in what role it is used - as a storage room or living room.
If the building is lightweight and erected on a suitable foundation, a high roof will put additional stress on the foundation, especially if it is made of heavy material. In this case, the height is calculated so that the structure is light enough. If the foundation and the total weight of the house allow, you can also mount a high roof. At the same time, you need to imagine how much its appearance will fit in with the architectural design of the building itself.
Procedure and rules for calculating the height of the roof
The calculation procedure in this case will look like this:
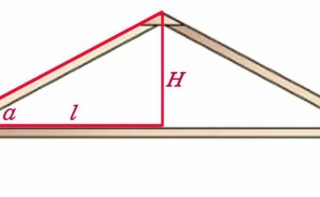
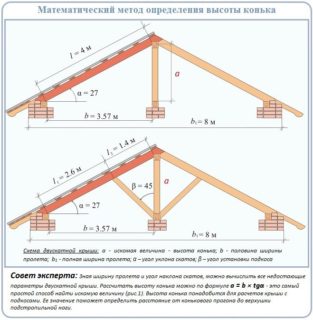
- Measure the side of the building adjacent to the desired roof slope angle. Divide it by 2. The result is the value of one of the legs of the figure.
- Find the tangent of the selected slope angle.
- The number obtained in the previous paragraph is multiplied by the length of the leg. As a result, you get the desired ridge height.
These calculations also illustrate the relationship between roof dimensions and slope angle. The more pointed the structure, the higher it will be. You can carry out calculations according to the same principle and according to the drawing, indicating the required parameters on it.









The author is carrying some kind of abstruse rubbish (tangents-cotangents ...) There are basic norms for TV construction, say, in a residential building a staircase is 15 cm high and 30 cm high. tread and, in place, as it turns out! Also, an individually dwelling house has a ridge height standard and equals - the length of the rafters - 3/5 of the width +50 cm! A house, say 10 m wide, divide by 5 and multiply by 3, it turns out -6m + 50 cm and this will be the base height of the ridge (the point where the rafters are connected! And the house will look normally - not pressed down and not with a raised roof! you need to look at the material of the roof, the purpose of the attic, etc.! WHAT EASIER-3/5 WIDTH + 50 CM !!
everything is just 2/3 of the length of the rafter tree or .2/3 of the width of the house + 50 cm
Make the height of the rafters 35-40 g relative to the horizon and the roof will look harmonious .. That's all.