Thermoplastic polymer is a transparent material that lets light into the room. The material protects well from the cold, therefore, translucent inserts are used in the construction of walls and roofs of greenhouses. Polycarbonate is available in various sizes, so a lightweight and flexible material can be selected for each type of structure and use. It is characterized by high properties of light transmission, heat resistance, shock resistance.
Characteristics of polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is resistant to any weather conditions. The low temperature at which the material becomes brittle is outside the operating temperature range. Compression resistance and hardness are comparable to those of aluminum.
Polycarbonate is:
- cellular (cellular);
- monolithic (solid);
- profiled.
Polycarbonate is the most durable of all types of transparent materials, so it is in demand. Manufacturers indicate a guaranteed service life of 10 - 12 years, but in fact the material does not deteriorate within 15 years.
Internal partitions of a honeycomb polymer panel are located at such an angle that they reduce the kinetic energy from an impact, for example, hail, by 1.5 times. With bends within reasonable limits, the material does not crack, which allows for arched and domed roof structures.
Polymer laminate withstands extreme temperature changes. It belongs to the group of environmentally friendly materials, does not react with chemical components of the atmosphere.
Benefits:
- The lightness of polycarbonate allows you to save on the elements of the supporting frame, their thickness is much less than when installing a glass covering.
- The density of the material is more than 2 times lower than that of window glass, and the thickness of, for example, a profiled polymer is 0.7 mm.
- To cut thin profiled sheets, they take scissors for iron, and cut the honeycomb with a circular, where a disc with fine teeth is inserted.
If polycarbonate is in an open fire, it does not burn, but melts without emitting harmful components into the atmosphere. This produces a cobweb-like mass that does not flow down. Without a source of fire, the material stops melting. If the surface cracks from a strong impact, the fragments do not fly away, but remain within the boundaries of the sheet.
The disadvantages include the need for careful handling of the plates. To move long panels, one worker is placed at 1.5 - 2.0 m along the entire length of the slab.
UV protection
Polycarbonate in its pure form does not show resistance to UV rays, therefore it is destroyed in the sun. During manufacture, a protective coating is applied to increase resistance.
There are two ways to apply:
- Co-extrusion method. Particles of a protective substance are implanted on the front surface. The layer prevents the sun's rays from reaching the plane of the sheet. The panels are installed with the treated side out.
- Spraying. The method is used by manufacturers of materials in the low-cost segment. The upper layer is gradually erased from the plane by dust particles, washed out by rain, blown away by the wind.
- The introduction of additives with stabilizers into the mass during production. The method leads to an increase in the cost of goods, therefore it is not often used, such polycarbonate is used at critical facilities.
Irradiation with ultraviolet light is harmful to plants, so the protective layer protects the surface of the material from deformation, as well as plantings in the greenhouse.
Effect of material thickness on its properties
Glass is considered to be the leader in light transmission, so the degree of its transparency is taken as 100%. The monolithic type of polycarbonate loses to glass only by 5%, and honeycomb - by 14 - 20%, depending on the thickness and color of the paint.
The dependence of light transmission on thickness:
- transparent honeycomb with a thickness of 4 and 6 mm - 86%, 8 and 10 mm - 85%, 16 mm - 76%.
- bronze color with a thickness of 4 mm - 50%, 6 and 8 mm - 44%, 10 mm - 42%, 16 mm - 29%.
Thermal transmission capacity of polycarbonate is lower than that of glass and plexiglass - monolithic conducts heat less by 17 - 20%. A honeycomb with a thickness of 4 mm is equated to glass, and a size of 6 - 8 mm is comparable to a glass unit. The effect is due to the air content in the cells. To maintain performance, insulate the open ends of the sheets during installation.
The thickness of the polycarbonate affects the sound absorption:
- monolithic 4mm - 25 dB, 6 mm - 27 dB, 8 mm - 29 dB, 10 mm - 31 dB, 16 mm - 36 dB;
- cellular 4 mm - 15 dB, 6 mm - 18 dB, 8 mm - 20 dB, 10 mm - 22 dB, 16 mm - 25 dB.
The strength of the sheets also depends on the thickness. The indicator ranges from 653 - 707 kg / m², and the tensile strength is 20400 - 23120 kg / m².
Standard sheet sizes
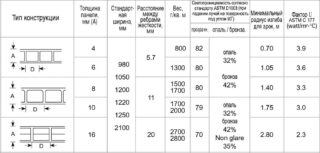
Each category of polycarbonate has its own dimensions, determined by the manufacturer of the material. Depending on the physical characteristics and dimensions, the method of transportation is chosen. Dimensions are also taken into account in the calculation when determining the wiring diagram and the layout of the panels in the structure.
Manufacturers sell the following sizes of polycarbonate plates:
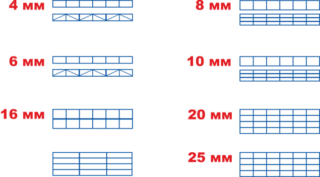
- Cellular panels are made hollow with different sheet thicknesses, their dimensions do not differ from those recommended by the standard and are 2.1 x 6.0 m and 2.1 x 12.0 m.The gap between the internal stiffening membranes in sheets with a thickness of 4, 6 mm is 5 , 7 mm, 8 - 10 mm - 11 mm, 16 mm - 20 mm.
- Monolithic panels are produced in the form of a solid material without voids inside. On sale there are sheets with dimensions of 2.05 x 1.25 m with a thickness of 1 mm. Plates 1.5 - 12 mm are produced with dimensions of 2.05 x 3.05 m.
- Profiled polycarbonate is stamped from monolithic sheets in the shape of a trapezoidal profile. The impact-resistant material has a thickness of 0.7 to 2.0 mm. Sheets are available in widths from 1.15 to 1.25 m, length is 2.0 - 3.0 meters. The calculation takes into account the height and wavelength to obtain a usable overlap area.
GOST R 56.712 - 2015 prescribes the standard width of polycarbonate 2.1 m, while the nominal length is 6 - 12 m. Material manufacturers can produce non-standard dimensions, make dimensions for a specific customer.
Bending radius
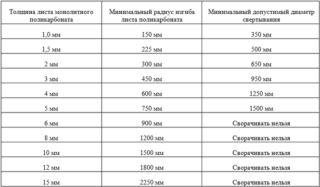
Polycarbonate is a versatile coating that can be bent without preheating or other preparation. The amount of permissible bending must be known in order to prevent destruction. A distinction is made between the permissible degree of bending during transportation and when installing the sheet in the mounting position.
In the first case, a radius is allowed depending on the thickness:
- panel 2.5 - 3.3 mm can be bent 250 - 280 mm;
- 3.5 - 3.8 mm - 300 - 310 mm;
- 4.0 mm - 375 - 400 mm;
- 6 mm - 500 - 600 mm;
- 8 mm - 700 - 800 mm;
- 10 mm - 900 - 1000 mm.
Sheets with a thickness of 12 - 20 mm are not allowed to be rolled up. This method is non-standard and is used by the buyer at his own discretion. The blame for the damage lies with the owner.

Recommended bending radii for installation on arched and domed roofs:
- sheet 2.5 - 3.3 mm can be bent with a radius of 450 - 530 mm;
- 3.5 - 3.8 - 550 - 580 mm;
- 4 mm - 600 - 700 mm;
- 6 mm - 900 - 1050 mm;
- 8 mm - 1250 - 1400 mm;
- 10 mm - 1600 - 1750 mm;
- 12 mm - 2000 - 2100 mm;
- 14 mm - 2350 - 2450 mm;
- 16 mm - 2600 - 2800 mm;
- 18 mm - 3000 - 3150 mm;
- 20 mm - 3300 mm.
If the sheets were bent during transportation, after unloading, they are laid in a horizontal position for storage.
Polycarbonate weight
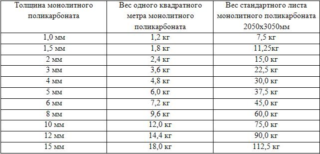
The mass of each species is determined by the weight of a square meter.The indicator depends on the thickness, cross-section of the material, while the overall size of the polycarbonate sheet for greenhouses does not matter.
Weight is also regulated by GOST standards:
- a square of a honeycomb sheet of 4 mm weighs 0.8 kg;
- 6 mm - 1.3 kg;
- 8 mm - 1.5 kg;
- 10 mm - 1.7 kg;
- 16 mm - 2.7 kg.
Monolithic panels have a weight:
- a square of a sheet with a thickness of 4 mm weighs 408 kg;
- 6 mm - 7.2 kg;
- 8 mm - 9.5 kg;
- 10 mm - 12 kg;
- 16 mm - 19.1 kg.
The weight of monolithic panels is 2 times less than the weight of glass, almost the same as that of plexiglass. The square of the honeycomb variety has a mass 10 times less than a glass sheet and 5 times less than plexiglass.
Material production

The production of polycarbonate sheets is technically a complex process. Quality products are obtained in compliance with the technology in combination with an established control system at all stages of production. The method of molding and processing of thermoplastic polymers is used. Products are made by high pressure casting, sheets for construction are produced by extrusion, molding of products from melt.
Production of cellular, profile and monolithic polycarbonate can be divided into 3 stages:
- preparation of the raw material;
- extrusion;
- cutting products to size.
The first procedure includes cleaning from dust and impurities of polycarbonate granules, for this, the cyclone method is used. The raw material is placed in a melting vessel at a high temperature. During the process, various plasticizers and additives to improve the quality are introduced into the mass. Heat-protective, water-repellent, dirt-repellent additives are used.
In the second period of production, the heated mass in a viscous state is fed to a special extruder machine for pressing. After passing through the conveyor, a tape of the required profile and section is obtained. Next, a press operates to give smoothness and the desired size in thickness.
The cooled tape is cut into products of a standard size, maintaining the standard length and width of a polycarbonate sheet. The panels are packed in foil, sent to the sale or to a warehouse.
Application of polycarbonate

Monolithic (cast) material is used as glazing for walls and roofs of greenhouses in summer versions. Transparent plates transmit infrared rays, but block ultraviolet light, which kills plants in large quantities.
Profiled polycarbonate is used to cover canopies, awnings, awnings. The material is characterized by increased strength, therefore it is placed on roofs with a slight slope, where there is a possibility of snow accumulation.
The honeycomb look of polycarbonate works great in heated greenhouses as windows and roof sections. It conducts heat and cold poorly, so its use saves heating resources.








