The veranda is a multifunctional structure. The room is being built simultaneously with the construction of the house or added later. There are many options for construction, a variety of materials are chosen for the construction. A small veranda is easy to build on your own.
Features of the veranda

Codes of rules for the design and construction of multi- and single-family houses to the concept of a veranda include a closed unheated room, attached, built-in or built-on on the ceiling of the first floor. The same premises, but open, the documents are called terraces.
Verandas equipped with plumbing and sewerage are referred to as auxiliary rooms. The regulation includes heated verandas in living quarters.
The division by type is important for the owner, as it can lead to an increase in the amount of annual property taxes.
Household use of the veranda
In the warm season, a glazed veranda attached to the house performs any functions inherent in a full-fledged living space:
- is a recreation room or bedroom;
- serves as a kitchen;
- becomes a living room;
- protects from precipitation and insects;
- things and tools are kept on the veranda.
Having installed an electric heater, the extension is used in the autumn and spring.
Construction Materials
Suitable for construction are any building materials that can withstand high humidity and are strong enough to take the load from the roof.
If the veranda is being built at the same time as the house, the foundation, walls and roof are made as a whole. For the walls, choose the same material as for the entire structure. The roof is also made in the same style.
Verandas that are added later may differ in building materials from the house.
Brick and expanded clay concrete blocks

The glazed terrace to the brick house is close in characteristics to the capital structure. Building advantages:
- resistance to external loads and the ability to withstand the weight of the roof with snow;
- durability;
- environmental friendliness;
- frost resistance;
- Fire safety;
- good soundproofing qualities;
- manufacturability and availability of construction on their own.
For the construction of the walls of the veranda, the masonry is made in one brick (25 cm) or in half a block (20 cm), this is enough for the stability of the structure. They choose brick of the M-100 brand - it is cheaper than standard products, but the strength is sufficient to withstand the load of one floor and the roof.
The disadvantage of brick buildings is increased requirements for the arrangement of the foundation, which must be strong and resistant to heaving under the influence of moisture and frost.
Beams

Verandas made of timber or rounded logs are suitable in design for houses made of the same material.
Solid wood products are strong, durable, environmentally friendly. The material retains heat well in winter and cool in summer. For the construction of walls, you need a lightweight foundation on piles or pillars.
Disadvantages of a wooden veranda attached to the house:
- glazing is carried out only after complete shrinkage of the building, which takes up to 6 months;
- fire hazard and susceptibility to decay;
- the need for careful sealing of joints;
- fragility of the lower rims.
Before construction, the timber is treated with antiseptic compounds and fire-prevention agents. The procedure must be repeated after a maximum of a year.
Metal

When arranging a veranda, metal products can be used to strap a screw foundation and erect a frame.
The frame struts can withstand a large mass. The roof in such a structure can be made almost horizontal, which saves building materials. The spaces between the frame channels are filled with any resistant and durable material - brick, polycarbonate. Filling made of OSB boards of wood or plywood is subject to a protective finish to prevent the impact of climatic factors.
Steel frames are not subject to shrinkage, therefore, glazing is carried out without temporary pauses.
Another option for using metal in the construction of a veranda is the use of sandwich panels, the outer side of which is made of metal.
The frame is mounted from channels, into the space between which panels cut to size are inserted. Before construction, the dimensions of the products are specified in the trade organization so that less waste is obtained. For example, if the plant supplies panels with a length of 6 m, the veranda is made 3x3 or 4x2 m in size.
Frame cladding materials
Frame verandas are sheathed:
- wooden clapboard;
- plastic or metal siding;
- imitation of a bar;
- OSB panels or plywood;
- boards.
To give the building an attractive appearance and protect it from climatic conditions, finishing is carried out.
Heaters

For maximum use of the veranda in the autumn and spring, the walls are insulated. Installation is carried out using wet or ventilated facade technologies.
Suitable as insulation:
- expanded polystyrene, which is often called polystyrene foam;
- extruded polystyrene (penoplex, technoplex, etc.);
- stone mineral wool;
- roll insulation based on foamed polymers.
Sawdust is popular among the materials at hand, but in terms of quality and durability, they are inferior to products of the chemical industry. The same materials are used in frame construction technology. Insulation is placed between the outer skin and the inner lining.
Roofing materials
The outer part of the roof is made of the following materials:
- slate - asbestos-cement and cellulose-bitumen;
- profiled sheet or metal tiles;
- ceramic or soft tiles.
If necessary, the roof is insulated.
Construction stages
To attach a veranda with plastic windows to the house, you must perform a number of sequential operations:
- decide on the place and main purpose of the extension;
- choose a project and prepare materials;
- equip the foundation;
- build walls and a roof;
- glaze the building;
- finish the interior and exterior.
Each stage is related to the previous one, as different building solutions may be required.
Features of the layout

The most common option is to add a veranda to the side of the house where the front door is located. This allows you to move in any weather without going outside.
Depending on the purpose and the existing layout of the site, they choose the option of building a terrace near other walls.
It matters which side of the world most of the glazing faces:
- The south side is chosen in the northern regions to make the most of the light and warmth of the sun. For warm regions, such an arrangement is inconvenient - in the summer the building will be very hot, it will be uncomfortable to be in it.
- North facing windows are suitable for southern areas. The same option is chosen in the northern regions, thus insulating the northern walls of the main building.
- The eastern direction is suitable for hot regions, when the veranda is used mainly in the evening.
- The windows are positioned to the west to extend the evening relaxation in natural light.
When choosing a place, take into account the location on the site of outbuildings, trees, compost heaps, toilets, paved paths. Each of the factors can be important. For example, a toilet next to a veranda is a source of unpleasant odors, and moving outside paths in the rain is unpleasant and dangerous.
Foundation and foundation

The type of foundation depends on the chosen material for the walls. For a veranda made of bricks or blocks, a shallow foundation is poured or built from concrete blocks 40x40x20 cm.
Sequence of work:
- Dig a trench 60-70 deep and 30 cm wide.
- Coarse river sand or a mixture of sand and gravel is poured into the bottom. The height of the cushion is 10-15 cm. The base is spilled with water and compacted with rammers.
- On loose soils, formwork is installed from boards or other scrap materials.
- Reinforcement is installed - at least 2 strips from a rod with a diameter of 10 mm.
- The foundation is poured with concrete of the M-100 brand, which, as the formwork is filled, is rammed by vibration.
- Until completely dry, water the foundation 2-3 times a day, preventing cracking and premature setting of the cement.
Complete hardening of concrete occurs on the 28th day - if massive walls are to be erected, they must wait for this period.
For frame structures, columnar or screw versions of the foundation are prepared. In the first case, columns are built of bricks or blocks, going deep into the ground by 60–80 cm. A popular option is when the columns are made of monolithic concrete.
Due to the speed of construction and low price, screw foundations have become popular. Piles for them are sold in large chain stores of building materials and entrepreneurs engaged in the manufacture of metal products.
After curing with columns or screwing in all the piles, they are strapped with wooden beams or metal beams. Below the beams, a grillage is arranged to protect the underground part from the ingress of debris, snow, birds and animals.
Floors

The covering consists of a subfloor and a final floor.
There are different options:
- The space from the ground to the top of the foundation is covered with a mixture of sand and crushed stone, rammed. The subfloor is made in the form of a concrete screed.
- Wooden logs are laid on top of the subfloor, to which the final floor is attached from boards, plywood and similar materials. For the finishing layer, choose linoleum or painting. In winter, there is high humidity on the veranda, so it is impractical to lay laminate or carpet.
- On a columnar (pile foundation, the rough floor is often made of a floorboard. For this, logs are attached to the foundation strapping, to which the board is nailed).
- From the side of the ground, the subfloor must be protected with waterproofing, it will also prevent outside air from entering the house. The draft layer is covered with a vapor barrier and finishing is carried out.
The height of the floor is chosen above the ground level so that rain water does not get into the house.
Walls
Solid walls are built to a height of 50-80 cm, after which space is left for glazing.
For a bundle of bricks and blocks, a cement-sand mixture of a grade not lower than M-100 is used.
A bar or a rounded log is fastened with dowels.
Fastening of the cladding of frame structures is performed with hardware intended for these purposes.
For outdoor work, do not use "black" screws. Due to the difference in thermal expansion, such fasteners are destroyed in the cold.
Roof

Common roofing options for verandas:
- single-slope with a slope of 20 °;
- gable;
- hip;
- flat.
The lags are not attached to the wall of the main building, but the gap is sealed with foam and closed with a corner.
The outer edge of the lag is laid on a Mauerlat beam.
The roof option depends on the chosen design and the financial capabilities of the developer.
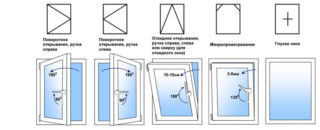
Glazing options
The type of plastic windows is chosen based on the cost, ease of use and the purpose of the veranda:
- Swing. The frame consists of 1, 2 or 3 parts. One or two sections open. Savings are achieved due to the fact that fixed sections are cheaper.
- Sliding ones are suitable for small verandas, as the frames move along runners relative to other sections. The frame does not open inward and does not fill the space.
- The swivel sections are attached to the axle, they can be moved along the runners. Suitable for "cold" glazing, as there are often gaps in the frames.
- Swivel and tilt open for ventilation, which is convenient in winter.
- Sliding multi-frame do not provide sufficient sealing, therefore they are installed only on verandas of summer cottages or balconies.
The installation of glazing ends with the embedding of the slopes inside and outside the building.
After glazing, the veranda is finished. Possible options: wallpaper, lining, plastering and painting.
If the veranda is not planned to be heated, MDF panels are not used - at high humidity, the products are destroyed.