Before you start insulating walls in your apartment or house, you need to familiarize yourself with many of the questions accompanying this event. Among them, the choice of material for thermal insulation of premises, as well as the use of known methods of protection. You will need to master the existing methods of warming the walls of the house from the outside and from the inside.
Thermal insulation materials

The following materials are traditionally used to insulate walls from the inside of a dwelling:
- mineral wool;
- extruded polystyrene foam;
- Styrofoam;
- polyurethane foam or cellulose.
Each of the proposed materials has its own pros and cons, so the final choice is up to the user.
Particular attention is paid to the efficiency of the heat insulator, its cost and ease of installation. The most preferred in this sense are lightweight artificial insulation made on the basis of polymeric materials: foam and polyurethane foam. However, very often mineral wool is used for this, which has proven itself in a variety of operating conditions of protected objects.
Pros of insulation
Wall insulation in the rooms of residential buildings is usually organized in two ways: by thermal insulation of the inner surfaces or the outer side of the building. Each of these approaches has its own pros and cons, which will need to be considered separately.
External finishing with a protective layer

The outdoor method may seem quite complicated and costly. However, it has the following indisputable advantages:
- additional strengthening of the facade of the house, which is under the constant influence of bad weather;
- extension of the overall service life of the building;
- the ability to decorate the facade in the style that the owner likes;
- preservation of the volume of the usable area, which is reduced by the internal insulation of the dwelling.
The disadvantages of the outdoor method are the need to work in not very comfortable conditions, as well as additional material costs for the arrangement of forests.
Insulation from the inside

Arrangement of thermal insulation from the inside is most common among amateurs, since it seems quite easy and effective. However, in reality, the only plus of this approach is the ability to carry out the work yourself, without leaving your home. The disadvantages of this method include the following points:
- When protecting the load-bearing walls of a building, condensation may accumulate on their inner surface under the insulation.
- Wet surfaces lose their thermal insulation properties, as a result of which mold and mildew appear on them.
- The walls in the apartment will begin to retain heat worse.
- Due to the thickness of the insulation, square meters of living space that are important for many users are lost.
The unpleasant side of the option of arranging thermal insulation for the walls from the inside is the remaining "cold bridges" that require additional protection measures.
Warming methods
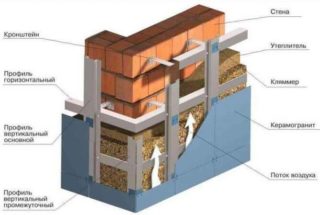
There are three ways to insulate walls from the outside:
- arrangement of a "wet" facade, mounted directly on the plaster;
- insulation of structures consisting of 3 non-ventilated parts;
- thermal insulation with arrangement of a ventilated facade.
In the first case, the protective material is simply glued on the outside, and then, for reliability, it is additionally fastened with dowels. Other types of coatings may be applied on top, including intermediate, reinforcing and decorative finishes. This method requires experience in carrying out such work or the help of specialists. A novice user is unlikely to be able to insulate the facade on his own using this technique.
When using the second method, the heat insulator is placed in an internal niche formed by two walls - it turns out to be locked between the fences. This method is quite effective, but it is only suitable for an already rebuilt residential building.
The ventilated facade is similar in its structure to "well" masonry, in which the facing material acts as the outer layer: siding, drywall, tiles, etc. We will have to take additional measures, consisting in the preparation of the frame, on which the heat-insulating blanks of the selected type are attached. This method should be attributed to the most effective approaches, which many manage to implement with their own hands. It will cost much less when compared with the "wet" version.
Preparing walls for insulation

Preparation of internal and external surfaces for insulation pursues the following goals:
- get absolutely dry surfaces suitable for subsequent finishing;
- provide the necessary level of insulation from vapors generated inside the room;
- create conditions for laying or subsequent gluing of insulation blanks on the prepared surface.
To solve these problems, you first need to clean the walls from the remnants of the old finish and foreign contamination, then in any convenient way to increase the temperature in the rooms. After the walls are well dry, you can do insulation.
It is recommended to prepare a plastic wrap in the right amount, used as the simplest means of isolation from vapor fumes.
The ideal preparation option is the construction of an additional wall of foam blocks, which allows you to create a protective air gap (thermal cushion). However, in most modern dwellings with limited space, this option is unacceptable.
Do-it-yourself warming process

Step-by-step instructions for arranging high-quality thermal protection in the house:
- At the stage of preparation, the surface must be treated with preparations that prevent the spread of fungi.
- After the walls have dried, they proceed to the construction of a frame base, on which the sheets of the heat insulator are subsequently mounted. For its manufacture, metal profiles of the required length are most often used, fixed on the wall with self-tapping screws or dowels with a step equal to the width of the sheets. It is allowed to use a wooden crate, equipped in exactly the same way. If you intend to lay a soft heat insulator, the distance between the posts should be reduced by 1.5-2.0 centimeters.
- Sheets of the appropriate size are placed between the previously fixed frame elements.
- The resulting cracks are carefully filled with polyurethane foam.
- After drying, the rest of the aggregate is cut off with a sharp cutter so that the cut is flush with the plane of the base.
- A layer of waterproofing is laid on top of the insulation and all this is covered with sheets of drywall.
Next, you can proceed with the final decoration of the walls using a decorative coating chosen at the discretion of the user.
Finishing

The effectiveness of insulation procedures to a certain extent also depends on how well the final finishing is organized. This point must be taken into account throughout all measures for arranging thermal insulation, starting with the stage of surface preparation.
It is important to consider the following:
- To close the resulting "rough" coating, it is allowed to use any finishing materials that can be easily mounted on top of insulation blanks. Both gypsum plasterboards and modern finishing panels can be used.
- When using decorative plaster, it is important to follow the basic rules for forming a protective layer and apply it only with a special tool (grater). In this case, it is imperative to use a preliminary and finishing putty, which is equipped directly over the plaster layer.
At the final stage, the walls are primed, which will allow them to be subsequently processed with any decorative and protective dyes.
Professional advice and existing alternatives

To obtain the best result, experts advise taking into account the following points:
- Regardless of what type of insulation is chosen for work, before starting work, you should thoroughly clean the walls from mold and other layers. It is strictly forbidden to mount insulation on untreated surfaces.
- To ensure that the plaster applied over it adheres more firmly to the insulation and does not crack over time, a polymer reinforcing mesh is gently pressed into its first layer.
- It is possible to exclude the appearance of condensation inside the coating if during installation a small gap is left between the heat-insulating plates and the wall.
- On the contrary, no gaps are left in the areas where the finishing material adjoins the frame grille. Otherwise, moisture can get inside the insulating "cake", significantly increasing the likelihood of mold formation.
Immediately before starting work, it is recommended to calculate the required thickness of the insulation, which is done taking into account the basic laws of heat engineering. Too thin a layer of a heat insulator such as penofol will lead to a low efficiency of insulation procedures, and its excessive thickness will somewhat reduce the useful area.
Alternative options

The considered methods of wall insulation from the outside and from the inside are not the only options for keeping warm in an apartment or in a private house. In practice, other techniques are often used:
- The use of "warm plaster", which is a special mixture, which, when insulated, is simply applied to the surface.
- Application of foamed polyurethane foam, prepared in liquid form.
The first method is optimal for thick brick or aerated concrete walls of capital buildings. In this case, there is no need for the construction of a frame base and preliminary preparation of surfaces. A similar picture is observed when using foamed polyurethane foam, applied like polyurethane foam.
Before insulating the walls of the house from the outside and from the inside, it is important to familiarize yourself with all materials suitable for this event.








