One of the stages in the construction of private and municipal buildings is insulation works. In most cases, mineral wool or penoplex is used for this, since against the background of analogues, these materials have the best performance. A comfortable atmosphere in the house and its service life depend on the choice of one of these heaters. In order not to be mistaken, the better to insulate the walls of the house from the outside, you should consider the features and characteristics of each product, taking into account all the accompanying factors.
Specifications

Mineral wool is woven fibers obtained by heat treatment of raw materials, passed through a pressurized chamber. Thermal insulation is made from volcanic rocks, steel slag and a mixture of broken glass with lime. The width of the mats and rolls varies between 60-80 cm, and the thickness is 10-40 cm.
Penoplex is manufactured under pressure by extrusion. The heated mixture is foamed and then pushed through the slots, where it solidifies and takes on a given shape. In volume, the material is a porous substance, 98% composed of air, which is the best insulator. The standard form of release is slabs with sides of 100 cm and 200 cm.The industry produces products with a thickness of 5 cm, 10 cm, 12 cm and 20 cm.For finishing window slopes, 2 cm thick PPP is produced.
To decide which is better, penoplex or mineral wool for wall insulation, you should start by comparing the technical characteristics of both materials.
The data are presented in the table:
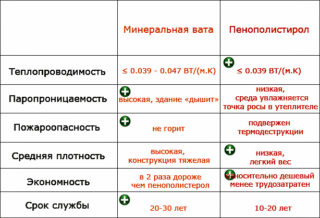
| Indicator | Mineral wool | Penoplex |
| Release form | slabs, rolls | slabs |
| Place of installation | inside Outside | inside Outside |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient W / mK | 0.037-0.041 | 0.031 |
| Compressive strength MPa | 0.01-0.02 | 0.05 |
| Density kg / m³ | 15-30 | 12-15 |
| Moisture absorption coefficient% | 4-10 | 1 |
| Vapor permeability coefficient mg / mhPa | 0.1-0.5 | 0.03 |
| Price per square meter rub | 130-140 | 140-150 |
| Noise isolation effect by 1 cm dB | 6-10 | 7-9 |
| Service life years | 30-50 | 30-50 |
Similar properties of foam and mineral wool

Making a decision when choosing between mineral wool or foam for insulation of an apartment is complicated by the fact that both materials have almost the same technical characteristics.
If the monetary factor in most cases is of decisive importance, here it can be ignored. The price of the slabs is almost the same, a slight difference is neutralized by the need to purchase additional finishes.
General properties of expanded polystyrene and mineral wool:
- Durability. Both heaters are designed for at least 30 years. The service life is not affected by external factors, because the materials are not susceptible to changes in temperature and humidity. They are avoided by insects, animals and pathogens.
- Excellent thermal insulation. This quality is the highest among the analogues on sale. Only polyurethane foam can be compared, but its price is much higher than that of plate heaters.
- Ease of use. Materials do not require special conditions for transportation and storage. They are lightweight, you do not need to make efforts for installation and involve assistants. Plates are easy to cut and saw with any tools at hand.
Comparison of similar indicators is only one side of assessing the characteristics of heaters.Differences should also be taken into account, since in each case the building has its own characteristics and is operated in certain environmental conditions.
Distinctive properties of materials
The following differences in material performance should be assessed:
- Moisture absorption. If the foam has practically zero, then the mineral wool can gain it up to 30% of its volume. This leads to a deterioration in the insulating qualities and increases the load on the supporting structures. Damage to internal and external finishing materials is not excluded.
- Flexibility. Expanded polystyrene is hard and practically does not bend. It is allowed to be laid on smooth surfaces without bulges and bends. For mineral wool, there are no such requirements for the base. Moreover, it can be mounted on uneven and even curved surfaces.
- Elasticity. At first glance, this quality may seem insignificant, but during the installation process it is noticeably manifested. Gaps between polymer boards are inevitable, it takes time, glue and foam to seal them. Slabs of cotton wool are inserted into the shape of the rasp, plugging all the irregularities with their edges.
- External finishing methods. Expanded polystyrene only needs protection from ultraviolet radiation and mechanical damage. For this, plaster, plastic or metal siding is used. With porous slabs, it is somewhat more difficult. They require a vapor barrier and a strong external fence.
- Installation method. The foam boards are fixed rigidly by screwing them through to the base. This takes time and effort to grout and drill. It is enough to simply insert the cotton blocks into the frame, slightly squeezing their edges.
- Environmental Safety. Even in a static state, this indicator varies significantly. If the foam is neutral, then the mineral wool releases a lot of volatile fibers into the air. When in contact with the skin and respiratory system, they cause severe irritation. The situation changes if the air temperature rises. Almost no changes occur with cotton wool. Expanded polystyrene melts, burns, emitting toxic substances harmful to human health.
- Work rules. When working with foam, it is enough to use gloves so as not to cut yourself with a knife. Installation of mineral wool involves a full range of protection - a sealed suit made of dense fabric, a mask and gloves. In addition, after the installation is completed, high-quality cleaning of the room is required.
The listed aspects will serve as another reason for reflection. Comparison of pros and cons, common and different characteristics will allow you to make the best decision.
Areas of use
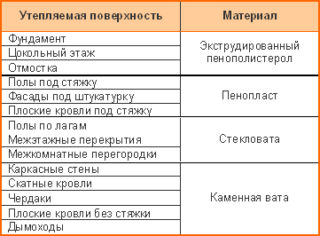
Both materials can be used for external and internal insulation of housing. It is quite clear that there are more such opportunities for a private house.
Mineral wool can be used for structures:
- Ventilated facade. The structure is a partition that is installed at a distance of 3-6 cm from the walls of the building. The material is closed on both sides with a membrane sheet, and on the outside - with a rigid tile-type finish.
- Frame insulation. It is more often installed from the outside, as it takes up to 20 cm of usable area. It is used for finishing walls, ceilings, roof ceilings and underground structures.
Due to its composition and physical characteristics, penoplex has a wider range of applications:
- Wet facade. This technology is a sequential process of gluing and screwing boards to the wall, reinforcing them with mesh, plastering and painting. It is used for finishing concrete walls, most often in apartments in multi-storey buildings.
- Thermal insulation of auxiliary structures. This applies to floors, sheds, garages, swimming pools, car washes. Plates perform well the function of insulation for blind areas, walkways, underground floors and cellars.When installed underground, penoplex does not need additional finishing, which reduces construction time and costs.
It is impossible to say unequivocally which material is better, since the choice is largely determined by the conditions of their operation.









And it turns out from the video that with "the same" heat source, Epps loses to Tepofol by half a degree due to the lack of foil, although Epps also has foil, and wins from cotton wool by a degree. The fact that Epps cools down faster only means that when heating a house with a stove (not a constant source of heat), it is better to use Tepofol or cotton wool, and with a constant source of heat, cotton wool loses more, plus it is afraid of moisture, which increases labor-monetary costs for steam hydropyrog. Here are my conclusions.