In small private houses and apartments, heating independent of electricity is valued. For small towns and villages, a typical situation is when, for various reasons, a substation fails, wiring is damaged, and so on. The natural circulation heating system does not include any module that would be powered by the mains.
Features of the natural circulation heating system
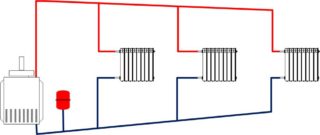
Any heating scheme includes several mandatory elements:
- The boiler that heats water - gas, wood, peat. A prerequisite is piezo ignition, otherwise it will be impossible to start the device without electricity.
- The supply line supplies heated water to the radiators. Pipes are placed with some slope - 0.5-1 cm per 1 m, so that the water can move by gravity. "Hot" water conduits are placed with a slope towards the radiators.
- Heating devices - batteries of any type. The main transfer of heat takes place through them.
- Return pipeline - through it the cooled coolant returns to the boiler. "Cold" pipes are installed with a slope of 0.5-1 cm per 1 m towards the boiler.
- Expansion tank - located at the highest point of the system. When water heats up, it expands. The tank compensates for this excess.
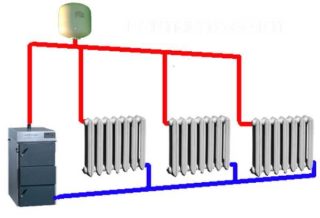
The system works like this: the water heats up in the boiler, expands, its density decreases, and the liquid rises along the central riser. The expansion tank is filled to equalize the pressure between cold and hot water. Then, from above, the water goes down through the supply pipeline to each battery, where it is cooled, giving off heat to the air and surfaces. The cooled liquid moves through return pipes to the boiler. Since the density of the cooled water is lower, returning to the boiler, it squeezes out the less dense heated liquid, forcing it to rise.
In addition to the pressure compensation function, the expansion tank also has another role. Air enters the pipes together with water. When it accumulates, an air lock occurs, which does not allow the coolant to move through the pipes. However, in convective systems, air bubbles rise into the expansion tank due to the sloping piping. Since this device is open and in contact with air, bubbles leave the system.
The design is simple, but requires very precise calculations. Water moving through the pipe creates friction, slows down and gives off heat faster. When changing direction - turns, branches, channels in batteries - friction increases. If you do not take into account the water resistance in the calculations, the system will not work.
Convective heating works well in small areas. Thus, you can burn a one- or two-story private house or apartment. This option is not suitable for a 9-storey building.
System advantages and disadvantages

Natural circulation provides the heating system with the following advantages:
- The main advantage is independence from electricity. Convective heating works in all conditions.
- With proper installation and maintenance, the gravity version functions for more than 30 years.
- Installation is very simple, preventive inspection and repair are also not difficult.
- High thermal inertia - a large volume of water circulates here. It cools down more slowly and gives off heat longer.
- Water convection heating is silent: there are no noise-generating electric pumps.
- The energy consumption is minimal. However, this is true if the pipes and the building are well insulated.
- The minimum cost of the system itself and installation.
It is not difficult to integrate a pump into the circulation circuit. This can be done during installation or later. When there is electricity, the heating works in forced circulation mode, and in its absence it automatically switches to the mode of natural water movement.

The gravity version has significant drawbacks, which noticeably limits the application:
- The system serves only small one-story or two-story cottages.
- To reduce hydraulic resistance, pipes with the largest allowable diameter are used. This makes installation difficult, and the cost of water pipes with a large diameter is higher.
- It is recommended to use only steel pipes. It is allowed to use polypropylene. Other non-metallic models are prohibited.
- It is not possible to adjust the temperature in each room manually or automatically.
- Indirect heating boilers cannot be included in the scheme, which increases the cost of obtaining hot water.
- It is impossible to equip a warm floor.
The operation of convective heating is significantly affected by constrictions. You can not use metal-plastic pipes, since they are connected by fittings, the diameter of which is smaller.
Types of heating systems
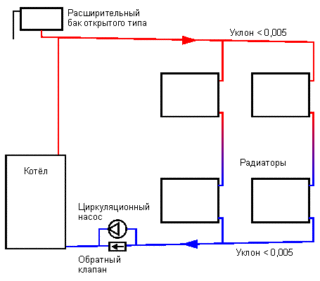
The heating circuit can include 1 or more circuits of different lengths, with different radiators. However, any option is a modification of only two models - one-pipe or two-pipe.
Single pipe
The device is as simple as possible. The same pipe, in turn, supplies the coolant to each radiator and returns to the boiler. The cheapest option and the most problem-free is heating only with pipes, without radiators. If batteries are included in the circuit, there should be a minimum of pipes and valves.
Water, consistently moving to the last radiator, cools more and more. This feature is taken into account when calculating the number of sections.
There are 2 schemes of one-pipe version:
- With the top connection - water enters the battery from above through the upper branch pipe, exits through the lower one. The efficiency of the system is maximum for hot water heating.
- With a bottom connection - the coolant enters the radiator from the bottom and also exits through the lower branch pipe. The path of passage of water increases, so the heat transfer of the system is noticeably lower. Radiators with a large number of sections must not be installed here. However, despite the lower efficiency, he prefers to install such a scheme in apartments, since it is more aesthetic.
The classic version can be upgraded by installing a bypass - branches with a three-way valve and branches with valves. With their help, you can regulate the water supply to a different radiator and turn it off if necessary.
Two-pipe systems
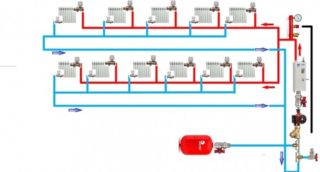
The version with a return pipe is called a two-pipe version. Hot water is supplied to the radiator under one pipe, and cooled water is discharged from each heating device through the return pipe. The system is much more efficient: each radiator receives almost the same amount of heat. The degree of heating can be adjusted on each battery, if necessary, exclude it from the heating circuit. A big plus is a simpler calculation of the parameters of the pipeline and batteries.
Both upper and lower connection are performed:
- In the first case, the pipes are located above the radiators.
- In the second, the supply pipe is placed below the battery. This option is more aesthetically pleasing, but the pressure drop is too low, so the scheme is used very rarely.
The calculations take into account the direction of water drainage. If it coincides with the direction of the hot liquid, a passing scheme, the length of the cycles is equal. In this case, the radiators heat up in the same way. If a dead end is used, cold and hot water move in different directions, those batteries that have a shorter cycle heat up faster.
How does the circulating head appear?
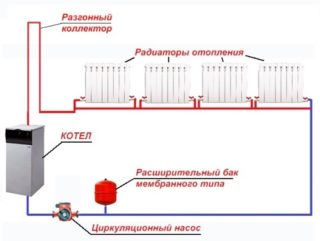
The movement of water in convection heating only provides a difference in the density of hot and cold water. When heated, the density of the coolant decreases and it rises; when cooled, it increases, and it displaces a warmer liquid. The greater the difference in the hydrostatic pressure of the cold and hot water column, the higher the circulating head, the better the heating works.
The main task in the organization of the system is to achieve the maximum pressure drop.
- An obligatory element of the circuit is the acceleration manifold or the main riser. It is a vertical pipe that rises from the heat exchanger to the top of the system. An expansion tank is mounted here - an open or closed diaphragm with an air valve for air removal.
- The main riser must have a maximum temperature, so the collector is insulated. Its height is no more than 10 m. Ideally, the riser does not come into contact with return pipes.
- To create a sufficient pressure drop, a large column of cold liquid must be created. This is achieved by installing the boiler at the lowest point of the system. In a private house, the device is placed in a basement, in an apartment - in a recess. The higher the level of the batteries is above the level of the boiler, the more pressure cold water forms and the more actively it displaces hot water.
To improve the circulating pressure, batteries with the largest possible working surface are selected. The better the coolant gives off heat and the colder the water enters the boiler, the better the heating works.
The principle of building a heating system with natural circulation
The main parameters of natural circulation heating are circulation head and hydrostatic resistance. The first indicator is calculated as follows:
P = h (p0-p1) = m (kg / m3-kg / m3) = kg / m2 = mm Hgwhere:
- P - pressure in the system;
- h - the difference in height between the center of the lowest battery and the center of the boiler;
- p0 - density of the heated liquid;
- p1Is the density of cold water.
The greater the difference in height, the higher the pressure drop. However, the indicator has a limitation - no more than 3 m.

It is almost impossible to calculate the value of the second factor - hydraulic resistance. The model that describes it is extremely complex and includes many variables. Here we are limited to approximate calculations.
To improve the efficiency of the system, the recommendations are followed:
- Pipes with the largest possible diameter are selected. In this case, the flow rate decreases slightly, but the resistance falls more strongly.
- Install as few valves as possible. Make sure that the circuit includes a minimum of turns and constrictions.
- At the bottom connection, the radiators must be supplied with Mayevsky taps in order to bleed off excess air.
- A metal pipe is used for the manifold, since it is important to achieve maximum heating to create a pressure drop. The pipes serving the batteries can be made of polypropylene.
Proper thermal insulation improves heating performance. Insulate the acceleration collector, supply and return pipes if they pass through unheated rooms.








