Heating underfloor heating - a system of main or additional heating of the room. Heating elements are placed in the floor - in a concrete screed or a layer of glue. First of all, the floor and furniture are heated. This option creates a feeling of comfort and is more economical.
The main types and choice of underfloor heating

There are 2 main types of underfloor heating: water and electric. The first is a modification of a conventional water heater, where thin tubes are used instead of radiators. It requires no more gas or electricity to operate than heating with conventional batteries.
In the electric version, the heating elements are mains powered. Its cost is much higher, since electricity is an expensive source of energy. But electric underfloor heating is extremely safe and efficient. It can be mounted not only in residential and utility rooms, but also on a balcony, loggia or even on a porch.
Aquatic
The principle of operation is similar to that of a conventional autonomous system. From the boiler, the heated liquid enters the collector, where it is distributed along the circuits. Underfloor heating in each room - a separate circuit. It is not recommended to combine the entire system into one circuit, since then, in the event of a breakdown, the whole house remains without heating.
The basis of the heater is thin polypropylene tubes. From the collector, the heated liquid enters the tubes, heat is transferred to the floor surface. The distance between the pipes can be varied: if there are high ceilings in a two-story house, the step between the elements is made minimal in order to warm up a large room. If the ceilings are low with the same area of the room, the step between the tubes is increased.

The heating temperature is regulated by the collector. Until the set point is reached, the pump operates and the thermostatic valves are open, through which hot water enters the pipes. When the temperature is at the specified temperature, the pump is turned off and the valves are closed.
Underfloor heating by the type of water is allowed to be installed only in private houses. Even if the apartment has an autonomous boiler and the installation of the system will not affect the heating in another apartment, this is prohibited. Although pipes are laid in a concrete screed, there is a risk of leakage and damage. In case of leaks, flooding of the apartment from below is guaranteed. Considering that repairing a warm floor takes a long time, the costs will be very significant.
Do not connect water heating to central heating. This is strictly prohibited and punishable by a fine.
Water floors are distinguished by the material of the pipes:
- Copper piping does not corrode. Extremely durable - works up to 50 years without repair, withstands high temperatures and water shocks. Even when the coolant freezes, copper pipes do not crack. The disadvantage is the high price and complicated installation. When installing, you cannot connect steel and copper pipes, so you will have to buy bronze adapters.
- Reinforced plastic is no less durable and resistant to corrosion. Chemically and biologically completely inert. The pipeline weighs little, it is much easier to install than copper. Disadvantage: Risk of loosening of fittings during heavy use. This makes installation difficult, since it is necessary that only areas without joints are under the concrete screed.
- Polypropylene is rarely used due to its high rigidity, and pipes need to be bent during laying.It is used in extreme cases.
- XLPE piping is not subject to any kind of corrosion. Withstands operating temperatures up to +95 C, is not afraid of water hammer. The main advantage is high flexibility and absence of creases. The minus is flammable, which does not really matter for floor mounting.
Water underfloor heating is placed only in a concrete screed. The construction of such a floor requires a lot of labor and time - it takes only 28 days for the concrete to harden. The height of the room is reduced by at least 15–20 cm.
Electrical
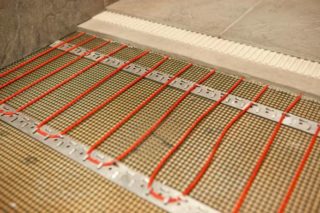
The source of heat is a material that heats up with the passage of current. The heating element is in the form of wires, rods, plates, films. Floor heating is possible both in apartments and in private houses. The heating temperature is regulated very precisely, the room becomes warm in a few minutes after switching on. A definite plus: the ability to install in the smallest areas and with the most complex area configuration.
The disadvantage common to all electrical appliances is electricity consumption. Because of this, this option rarely acts as the main heating. In living rooms, underfloor heating is combined with radiators, in the bathroom, in the bathroom, in the loggia it is used independently. But here the area is small, so the consumption is low.

There are 4 main types of electric underfloor heating:
- Cable - the basis is single, double-core and self-regulating cables. The wires are laid in a concrete screed according to one of the schemes. Depending on the pitch between the hinges, the floor heats up more or less.
- Thermomats - the same cable, but fixed on a grid with a step of 9 cm. Such a device facilitates installation, but at the same time limits the area: the mats cannot be shortened.
- Film IR heaters - carbon strips act as a heating element. When current is passed, they emit infrared radiation. It heats not air, but surfaces, objects and people, and only then the air. This makes the temperature feel warmer, reducing heating intensity and saving energy. The IR-film is laid both in the screed and in the glue layer.
- Rod - a type of infrared heater, where carbon rods are used instead of strips. By design, they are closer to thermomats: the rods are fixed on a plastic mesh. Its price is noticeably higher than film, but it is much more durable - up to 50 years.
It is possible to reduce electricity consumption even in a two-story building by installing an electronic programmable thermostat. At night and when there are no people in the house, it reduces power to a minimum.
Advantages and disadvantages of underfloor heating as the main heating

The main advantage is comfort. A warm floor under your feet creates a feeling of warmth and comfort much faster than the hot air of a room. There are other benefits too:
- Uniform heating of the room. Heat comes from the entire floor area, while the radiators partially heat the walls and distribute heat only in a certain area.
- The system works completely silently.
- Since the heating elements are enclosed in the screed, heating has less influence on the humidity level.
- You can choose an option with different thermal inertia. The water floor heats up slowly and cools down for almost a day. IR film instantly heats the floor surface and cools down just as quickly.
- Heating with underfloor heating is cheaper than radiators. The cost of electric heating is not so attractive.
- The systems are installed on the smallest areas, even on stair steps.
- Batteries do not decorate the room and do not fit into the interior. Underfloor heating elements are hidden from view.
Disadvantages:
- Arrangement of underfloor heating is a laborious and lengthy process. Hydro and thermal insulation is laid on the base base.Then reinforcement mesh or laying mats are placed. Place the pipes, make the connection, pour the concrete screed, lay the substrate and lay the finishing floor. This takes time and money.
- Water underfloor heating takes at least 10 cm in height, and electric - from 3 to 5 cm.
- The repair is very difficult: in case of damage, it is necessary to remove the cover, break the screed, eliminate the defects and re-lay the floor.
You can install an electric underfloor heating not only on the floor, but also on the walls.
Recommended power
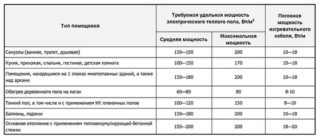
A warm electric floor as the main heating does its job if it has the appropriate power. The calculation depends on the type of heating element:
- Heating cable parameter - linear power. On average, it is 18 W / m. Knowing the value, it is easy to calculate how much cable is needed for heating 1 sq. m.
- The indicator for the cable mat is the specific power. They produce products with a power of 150 W per 1 sq. m. Modifications with a power of 200 watts are less common.
- Infrared films are more powerful - from 130 to 230 W / sq. m. They are more often used as the main heater.
- Rod mats are produced with a capacity of 130 to 160 W per 1 sq. m.
The indicator is selected based on the purpose. In living rooms, the main heating requires floors with a capacity of 120 to 180 W / sq. m, for a bathroom - 120-150 W / sq. m, for a loggia - up to 230 W / sq. m.
Calculation and selection of equipment

Heating a house with underfloor heating requires an accurate calculation:
- The useful area of the room is calculated - the warm floor is not placed under furniture or stationary equipment. In this case, the heated area should be 50, or better 70% of the total.
- Calculate the power of heat loss in the room. It depends on the overall insulation, the number of windows and doors. Calculate the value with a margin of 30%.
- If the system is installed in a thermal storage screed, the correction factor is increased to 1.4.
- Heating power under a wooden or tiled floor must be less than the heat loss power multiplied by a factor. If the heat loss in the kitchen, for example, is 1000 W, the power of the floor heater must be at least 1000 * 1.3 = 1300 W.
- The power density is calculated by dividing the required area by the useful area. If in the kitchen it is 7 sq. m, to heat it, you need a warm floor with a capacity of 1300/7 = 186 W / sq. m.
- They select a system. If a heating cable is laid, a wire is selected from the entire list, whose power coincides with the calculated one. Purchase a cable of the same length as indicated in the table.
- The laying step is calculated: the useful area is multiplied by 100 and divided by the cable length. During installation, this distance is carefully observed.
According to a similar scheme, the powers of other options are calculated: a heating mat, an infrared film, a core floor.








