When heated, the volume of liquid always increases. To compensate for these temperature fluctuations in the heating system, it is necessary to install expansion vessels. For every 10 degrees, the volume can grow up to 0.3%. The liquid is incompressible, so the excess has nowhere to go. It will enter the expansion tank until it cools completely. If excess water is removed, the remaining empty space will fill with air after the circuit has cooled down. This creates air pockets that can block all heating. An expansion tank will be able to eliminate this problem. In order for the heating to function correctly, you need to know how to calculate the expansion tank for heating.
- The choice of an expansion vessel for various types of heating systems
- Open
- Closed
- Requirements when choosing an expansion tank
- Tank size calculation methods
- General selection method
- Calculation by formulas
- Calculation of the volume of the coolant
- Geometric
- When filling the system
- Generalized method
- Consequences of incorrect calculations
The choice of an expansion vessel for various types of heating systems

When installing heating equipment, open and closed expansion tanks can be used.
Open
Open-type devices are intended for use in a natural circulation heating system. The tank is an open container with a connection at the bottom. The container itself is located at the highest point. Because of this, inconvenience in use arises. The tank must be installed in the attic, roof of the house, in order to control the liquid level, you need to constantly go up to the attic.
Open expansion tanks must be covered with thermal insulation. It is made from sheet steel. An inspection hatch should be provided on top of the device. The maximum liquid level limit will be controlled by an overflow tube that goes outside.
Open-type expansion tanks perform several functions:
- maintain the volume of the coolant during temperature fluctuations;
- restore the volume of fluid in case of leakage;
- when the system overflows, they discharge excess water into the sewer;
- limit hydraulic pressure;
- remove air from the system.
The disadvantage of these devices is their large size. They are prone to internal corrosion of heating devices. Due to these shortcomings, open-type tanks are very rarely used in heating systems.
Closed

Closed expansion tanks are the best option for heating with natural and forced circulation. Thanks to the appearance of such devices, it became possible to operate the heating system without contact with the atmosphere. During the circulation of the coolant, impurities will not be released, due to which corrosion will form.
The use of such a system extends the life of pipes and equipment. The closed heating circuit can be operated under high pressure. In this case, additional recharge will not be needed.
Closed expansion tanks are installed in boiler rooms. They can be used all year round without fear of freezing.
Requirements when choosing an expansion tank
The expansion tank in the heating system is one of the important elements that affects the quality and safety of work. Therefore, when choosing, you need to pay attention to certain points:
- It is recommended to select a device with a safety valve. Most modern tanks are equipped with it. If not, it's best to purchase it separately.If the valve operates frequently, then the volume calculations are incorrect. To remedy the situation, you can purchase additional equipment that is installed in parallel with the old one.
- The smallest volume of capacity should be at least 10% of the total volume of the system.
- The structure must be solid, without mechanical damage.
Experts do not recommend purchasing very cheap devices. It is better to give preference to trusted manufacturers. Only in this case will a long service life be guaranteed.
The quality of the equipment must be documented. It must meet hygienic requirements and have international certificates.
Tank size calculation methods
General selection method
The volume of the tank can be selected at the rate of 10% of the total internal size of the heating complex.
Calculation by formulas
The most common method for calculating the volume of an expansion tank for closed-type heating is the formula: A = Bx / KwhereIN - the volume of the coolant, FROM - parameters of thermal expansion of the coolant, TO - parameters of the membrane tank efficiency.
Calculation of the volume of the coolant
Geometric
Mathematical calculation is performed by summing all the elements. This will require:
- Boiler capacity, which is specified in the passport.
- The volume of water, which is calculated depending on the number of sections in the radiator. All information about the volume of one section is spelled out in the documentation with technical characteristics.
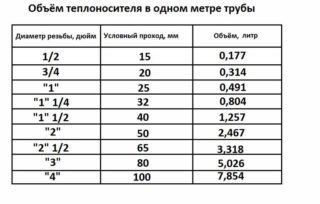
- The amount of water in the pipeline is calculated by measuring all lengths.
All elements are added, as a result, the total volume of the coolant is obtained.
When filling the system
The most accurate calculation methods include filling the system with water. A water meter is used to control the volume. If it is not there, you can pour water into buckets and thus calculate the volume obtained.
Generalized method
For 1 kW of boiler heat power, 15 liters from the total volume of the system are taken. Depending on the types of heating devices, the generalized method will have a more precise modification.
If radiators are used, the amount of water should be at least 11 liters, in convectors - at least 7 liters. For underfloor heating, the volume should be 18 liters.
In the technical passport of the equipment, the manufacturer prescribes the volume of the heat exchanger. The amount of water in the pipeline can be calculated independently. To do this, you need to calculate their length and internal volume. All indicators, including the boiler, pipes and appliances, must be summed up. The result will be the total volume of the heating complex.
Consequences of incorrect calculations

If the volume of the expansion tank is calculated correctly, the pressure during operation will always be stable. All excess water that forms during the expansion process will be collected in a special reservoir.
When the calculations are not done correctly, there will be constant pressure drops in the system. If in a closed heating system, excess hot water is not discharged anywhere, an accident will occur. Pipes may burst, connections may be depressurized.
Pressure drops in the system can provoke:
- stopping the operation of the entire heating system;
- freezing, if the boiler shutdown occurred during the winter period.
If the volume of the tank is insufficient, the circuit needs to be replenished with water. Most often, owners of a boiler with a built-in tank face such a situation.
It is recommended to purchase an expansion tank with a volume margin.If the stock is not included in the calculation, this will negatively affect the operation of the entire system.
In order for the entire area of the house to be fully heated, it is necessary to correctly calculate all the parameters of the equipment. Selection errors can lead to complete failure of the heating system.