Underfloor heating in a wooden house is a set of control devices and heating elements located between the bottom floor slab and the finish. Depending on the type of devices and materials used in construction, these structures can be part of a general heating system or perform this function independently. With a competent approach to design and correct installation, underfloor heaters effectively cope with maintaining a comfortable microclimate in all areas of the building.
Is it possible to make a warm floor in a wooden house

The owner of a private building is free to equip any type of main and auxiliary heating. Restrictions apply to water circuits in multi-storey buildings where several families live and there are common communications. The reasons for the ban are that the pipes filled with water, together with the filled screed, are heavy, creating an unacceptable load on the walls and floor slabs. In addition, the likelihood of leaks due to rupture of the pipe walls or wear of the cushioning material at the joints is not excluded. Even in a one-story building, this is dangerous. It lies in the fact that water can wash away the foundation and damage communications located at the basement level. Another factor is the heat loss that occurs in the riser due to a circuit built into one of the apartments. Having passed through it, the water cools down and gets to the neighbors from below in a chilled state, which adversely affects the microclimate in their homes.
If the dwelling is private, its owners are responsible for their own safety. There are no restrictions on the arrangement of additional heating, since the interests of the state, the management company and neighbors are not affected.
But this does not mean that you can approach this event superficially. Own funds should be invested thoughtfully and as efficiently as possible. Otherwise, bills will rise and the comfort level will not change.
Which type to choose

When building a house from solid wood, lightweight reinforced concrete slabs or beams can be used as floors between floors. Both materials have their pros and cons. Hollow core slabs are heavier, but stronger and hold their shape better. The beam is lightweight and can be laid by hand, but it tends to bend under its own weight and the impact of people and furniture. In most cases, the floor slab is finished with wood in the form of boards, parquet, plywood or laminate.
When choosing the type of underfloor heater, the following features of wood should be taken into account:
- Low thermal conductivity. If you place heat sources under the boards, it will be almost completely absorbed by them. An exception may be wood varieties with a high density: oak, larch, cedar. They conduct heat well, but are so expensive that not everyone can afford it.
- Susceptibility to deformation. With constant heating, moisture comes out of the material, it loses volume and becomes covered with cracks. If the heat supply is interrupted, the wood absorbs moisture, expands and bends.
One of the options for a universal topcoat can be engineered board or wood-polymer composite. These materials are highly conductive, lightweight and waterproof. Moreover, their cost is quite affordable even for budget construction.
There are two types of underfloor heating that are identical in purpose, but different in principle of operation - water and electric.
Water floor
The structures are closed loops of a spiral or serpentine configuration. The water in the pipes moves under pressure, which is created by a centrifugal pump.
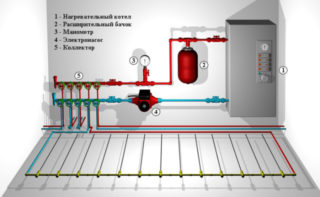
A water heat-insulated floor in a wooden house has the following device:
- Pipes through which fluid moves. Depending on how the structure is used, ordinary water or antifreeze is used. The contour is made from metal fragments, polypropylene sections or special flexible plastic pipes.
- Collector. The product is used to connect and regulate the pressure in several circuits when arranging a large area.
- Boiler. It can be gas, electric or solid fuel. It is a source of energy that heats the coolant.
- Mixer. It is used to regulate the temperature of the liquid that is supplied to the pipes. To determine the desired value, a hand is applied to the nozzle, after which the tap is turned.
- Thermostat. It is used in automatic systems that operate without human intervention, including in remote access mode. Maintains the temperature of the liquid within the specified parameters.
- Fitting. Depending on the design of the system, shut-off and drain valves, relays and automatic stops are installed.
A feature of water systems is the need to fill the screed, which receives and distributes heat over the surface, while protecting the contours from mechanical damage. You can make a screed from any heat-conducting material - cement mortar, polymer or epoxy resin. The same requirements are imposed on the finish - it must conduct heat well. To achieve the desired effect, ceramic tiles should be laid on the base or a decorative liquid mass should be poured.
Electric floors

Electrical systems do not have the same risks that are inherent in water-based counterparts. The structures are lightweight, easy to install and do not require any maintenance. It should be borne in mind that there is always a possibility of fire in the event of a critical increase in temperature or a short circuit on the line.
There are such types of electrical appliances for floor heating:
- Cable. Products are wires enclosed in flexible insulation, which are evenly heated along their entire length under the influence of current. Stacked in molds, on a metal mesh or between turning beacons. They have a thickness of 6-15 mm, a power of 20-40 W / r.m. After laying, they are poured with cement mortar.
- Mats. Made in the form of thin wires fused into a flexible plastic mesh. They are in the form of strips up to 200 cm long and with a power of 120-250 W / m². The thickness of 2-3 mm allows you not to make a screed, but to immediately close the mats with an adhesive at the same time as laying the tiles on the floor.
- Film. Inside the flexible strips 0.5-0.8 mm thick, there are copper cores covered with carbon fiber, giving infrared radiation under voltage. A feature of the film is that there is no need for a screed, since radiation passes through all materials. The strips can be glued to the substrate and then covered with tiles, linoleum and all types of wood flooring. The power of the products varies within the range of 100-200 W / m².
The choice of an underfloor heating system is made based on the characteristics of the room, the state of the finish and the advisability of interfering with the floor covering.
Underfloor heating device in a private house
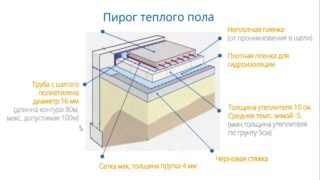
In a private house, the insulated floor consists of the following layers (from bottom to top):
- Rough flooring. It is laid on bars or columnar supports made of bricks. Serves as the basis for subsequent designs. It is made of boards treated with antiseptic preparations against microorganisms and insects.
- Membrane insulation. Diffuse membranes and films are used that remove moisture from the premises in one direction. Distinguish between insulation for floors, equipped above the basement and on the ground.
- Insulation. As a filler, synthetic and natural materials are used - mineral wool, foam insulation, ecowool, expanded clay, peat, felt, straw, wood chips.
- Vapor barrier. The films and fabrics of the membrane type are used, fixed on the frame.
- Finishing floor. It is a base that is made of slabs, boards or boards. Depending on the quality of the materials, it is used as a topcoat or as a base for laying a finish.
If a concrete slab is laid on the basement, waterproof materials can be used for its insulation - polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam.
How to install
Installation of underfloor heating of all types begins with drawing up a diagram, making calculations and purchasing building materials. The next step is the arrangement of the base.
- The finish is removed. If you plan to use it again, dismantling must be done very carefully.
- The base is cleaned of debris, dust and protruding fragments. Narrow slots are widened and sealed with a sealing material.
- The base plate is treated with a primer for the appropriate purpose.
- Depending on the type of floor, layers of waterproofing and insulation are laid.
After that, the laying of the heating elements begins. This is done in accordance with their configuration:
- The cable is laid in pre-prepared forms. In this case, the minimum bending radius must be observed in order to prevent it from kinking. After checking the strength of the fastening, the screed is poured.
- Mats are attached with glue or double-sided tape. They should be placed 20 cm from the walls, they can be cut to the desired shape. An object with a low bottom should not be allowed above the elements, as this contributes to overheating of the wire.
- The film is glued to the board with construction tape. To prevent its damage by finishing elements, a special protective cloth is laid on top of the film.
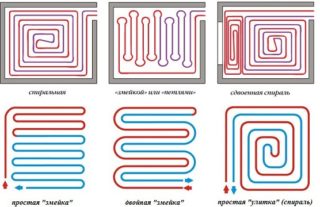
- Water pipes are laid in a snake or spiral. When choosing the shape of the snake, it is better to use shaped foam blocks with grooves.
After installation, a functional test is carried out. If everything is functioning properly, the screed is poured and finished.
Pros and cons

In order not to be mistaken in the choice, you should consider the pros and cons of each type of warm floor.
Water devices:
- low start-up and operating costs, inertness of heating and cooling;
- difficult to install, there is a risk of a line break;
- covered only with a screed.
Cables:
- ease of installation and operation;
- loss in height, high electricity consumption.
Mats:
- ease of installation, insignificant thickness, cost-effectiveness;
- high cost of elements.
IR film:
- reasonable price, economy and versatility;
- fragility, easily torn and broken.
When arranging a home, it is better not to dwell on one type of warm floor, but to select it individually for each room.