There are different types of heating that allow you to keep the temperature in your living quarters at a suitable level even on the coldest winter days. Owners of private and apartment buildings need to choose the optimal energy carrier, taking into account financial capabilities and the area of the heated space.
Types of heating by type of energy carrier

An important parameter of any heating system is the fuel used. Various energy sources are used, each of which has certain advantages and disadvantages.
Gas heating
In an apartment building, a spacious cottage or a small one-story mansion, this option will be optimal. Gas as an energy carrier has many advantages:
- low cost;
- no waste;
- simplicity of equipment operation.
If gas heating is used, you can install several temperature sensors in the rooms and connect them to the boiler so that the temperature in the house is always automatically maintained at the required level.
One of the drawbacks is the need to locate the house near the gas pipeline. You also need to take care of good ventilation - if gas leaks due to improper installation or accidental damage to the hoses, an explosion may occur. Good ventilation will eliminate the risk.
Liquid fuel

The energy efficiency of such heating boilers is almost not inferior to gas ones; very little waste remains during the combustion of diesel fuel. However, fuel prices have skyrocketed, so the popularity of liquid fuel boilers has plummeted.
In some cases, this option becomes the most appropriate. It is much easier to store several tons of diesel fuel than dozens of cubic meters of gas. At the same time, the risk of explosion is completely excluded - diesel fuel vapors are not so explosive.
If it is not possible to connect to the gas pipeline, it is quite possible to consider diesel fuel as the main energy source for heating a house.
Solid fuel

Not the most convenient, but quite popular form of heating in private houses. The main advantage is versatility. Solid fuel boilers work on everything that can burn: firewood, coke, coal, peat, cardboard and paper.
In addition to versatility, safety is a plus - fuel cannot explode. Storing coal or firewood is easier than storing gas and diesel - any dry room or suitable shed will do.
When the fuel is burned, a lot of ash remains, especially if it is fired with coal. Several times a week you will have to clean the furnace from accumulated waste.
Electrical

This energy carrier has only two serious advantages. The first is ease of use. There is no need to connect to the gas pipeline, load fuel into the furnace, store fuel somewhere and dispose of ash. Electricity is consumed completely and without waste. The second is the compactness of the boiler. It is much smaller than gas or solid fuel of similar power, and much easier to install.
The main disadvantage is the high cost of electricity. This energy carrier is the most expensive.
An additional disadvantage is that it is not possible to install an electric boiler everywhere.It consumes a lot of electricity - a weak network may well not withstand the additional load.
Combined

A convenient option is a boiler that runs on several types of fuel. For example, one device can run on gas and diesel fuel - you just need to reconfigure it, which can be done by any home craftsman. Others can run on gas, electricity, or solid fuels.
Such heating is suitable in regions where there are gas interruptions in winter - the pressure drops or it freezes in the pipes. In such a situation, you can always switch to pre-stored fuel - diesel fuel, wood or peat.
The disadvantage of combined boilers is the higher cost compared to standard heating systems.
Heat transfer principles
Convective heating
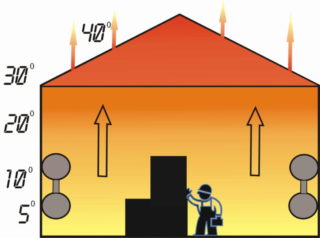
This is the name of systems in which special elements are heated and transfer heat to the surrounding air. According to the laws of physics, it rises up, and it is replaced by a cold one - in this way the room gradually warms up evenly. Almost all radiators and underfloor heating operate on this principle.
The advantage is simplicity and reliability. The disadvantage is significant thermal inertia. By increasing or decreasing the heating power, changes can only be noticed after a few hours. The top of the room will always be noticeably warmer than the bottom.
Infrared

Most often, infrared heating is a lamp, the wattage and size of which can vary significantly. They act on the same principle as the sun.
The lamp spreads infrared rays around itself, in contact with any objects, they heat them. The entire area of the room is evenly warmed up, and not the air in its upper part. It is enough to turn on a powerful lamp to make the room noticeably warmer in a few minutes.
The disadvantage of IR heat supply is a relatively low power. It is suitable only as an additional one, or for warm regions where there are no severe frosts.
Heating types by type of heating element
Three types of heating elements are common:
- classic radiators,
- warm floor,
- infrared lamps.
The radiators are reliable and durable, but their installation is rather difficult. However, it is quite easy to replace or repair them if necessary. Can be used with all types of heating boilers.
Installation of underfloor heating is even more difficult, in case of a breakdown, you will have to open the entire floor surface in order to carry out repairs. In this case, heat is distributed more evenly. It can work with water as a heat carrier and with electricity - the cable laid in the floor simply heats up and heats the room.











