High-quality heating communications in the dwelling will reduce the risks of heat loss and ensure a comfortable temperature is maintained. When planning heating in a private house, it is necessary to select the type of system, draw up a project, and purchase materials. Self-laying of the heating main should be carried out in accordance with the recommendations of specialists and current regulations.
- Popular types of heating systems
- Steam heating
- Water main
- Open fire
- Gas communications
- Air heating
- Electric heating
- Features of DIY heating installation in a private house
- Pipeline type
- Number of radiators and sections
- Installation and wiring diagram
- Alternative heating technologies
- Heat pumps
- Solar collectors
- Hybrid systems
- Parameters for choosing the right heating system for a private house
Popular types of heating systems
Depending on the coolant used, there are several types of communications.
Steam heating
The main element of the line is a boiler, where water boils, and steam is supplied to the house along a special circuit. Moving through pipes and radiators, the coolant cools down, becomes liquid and moves back into the reservoir. The system is used to equip multi-apartment housing, industrial enterprises. Steam heating is not used in the private sector due to the risk of explosion and fire.
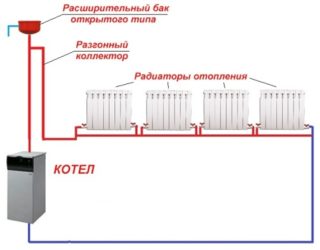
Water main
The difference between the water system is the use of natural and forced circulation of the coolant and the pressure difference of the circuits. When using forced circulation, a special pump is installed; for a natural one, a tank is needed.

The principle of operation of the line consists in heating water in a tank and its further supply through closed pipes and radiators. They heat the room. Heating of the coolant is carried out by gas, liquid or solid fuel.
The advantages of hot water heating for a private house include:
- pipes and radiator devices heat up, but do not burn when touched;
- the rooms maintain the same temperature regime;
- fuel economy;
- long operational period;
- minimum noise level;
- ease of maintenance.
When choosing a hydraulic heating, it is necessary to take into account the location of the wiring, the connection diagram of the elements and the design of the risers.
Open fire

Stove heating is characterized by autonomy, energy independence. Depending on the needs of the owners, a fireplace or stove is equipped with heating. You can cook food on the hob and dry fruits and vegetables in the oven.
Using an open flame as a heat source has several advantages:
- minimum costs for the purchase of materials for masonry and decoration;
- the ability to combine a standard stove and fireplace;
- cozy atmosphere with live fire;
- installation of a structure into a load-bearing wall;
- saving on fuel resources.
The stove method of generating heat requires space for the installation of a heating unit, which heats up for a very long time. First, the walls warm up, and then the air in the rooms.
50% of the useful heat energy is emitted through the chimney.
Gas communications

A floor-standing or wall-mounted boiler is an economical heating method if you have a country or private house. The pipeline operates on the principle of gas combustion in a combustion chamber with the release of thermal energy. It heats the liquid heat carrier through a heat exchanger. The use of a gas system eliminates the costs of arranging the chimney and ensures maximum heat retention.
Depending on the goals of the arrangement, the number of contours is selected. A single-circuit tank can only heat the dwelling, and a double-circuit one can provide hot water.
It is beneficial to use a gas unit for several reasons:
- fuel is low cost;
- efficiency of heating installations;
- the system can be fully automated;
- absence of soot and ash during boiler operation;
- many variants of the boiler.
The disadvantage of communications is the danger of maintenance and installation, the high cost of equipment and the need for a special permit for its installation.
Air heating
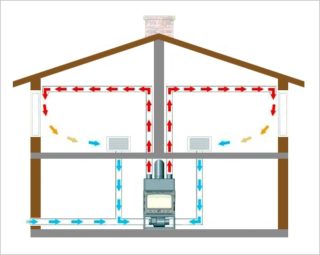
A heating system without a coolant that works by passing air through a heat generator and heating it. Air masses are directed to the rooms through special channels. Cooling down, they go down, collect in the air intakes and are brought out to the generator. The operation of the line is based on forced (air injection pump) and natural (flow temperature difference) circulation.
For a private house, you can choose the following type of communications:
- Local - an auxiliary option, implemented by special devices, fans and heat guns. Their principle of operation is air recirculation.
- Central - suitable for buildings with general ventilation. It is organized on the basis of direct flow, partial or complete recirculation.
- Thermal curtains - mounted in openings, create a barrier to cold air when the sash is opened.
Air communications reduce heat loss by 2 times.
Electric heating

Electricity is used to heat floors, ceilings and walls. There is no need to install a boiler in a residential building, the heat is evenly distributed. Manufacturers produce several types of equipment:
- TEN and electrode. The coolant is heated by a heater or two electrodes. The differences between boiler plants are compactness and durability.
- Induction. Consists of magnetic and thermal circuits, which contributes to the rapid heating of the coolant and rooms. If necessary, the heating unit can be equipped with an automatic control.
- Combined. The electric apparatus can operate on another type of fuel, which is suitable for summer cottages and villages.
All heating options can be combined.
Features of DIY heating installation in a private house
When arranging heating in a house with your own hands, it is necessary to draw up a project. It reflects several points.
Pipeline type

Installation of the following products is allowed:
- Steel. The metal material is characterized by high thermal conductivity, strength and affordable cost. Of the minuses - a lot of weight, the complexity of bending and susceptibility to corrosion processes.
- Copper. The pipe is used for a self-contained circuit, it is characterized by flexibility under the influence of high temperature, the absence of irregularities on the internal walls. A closed circuit cannot be made of them - eddy currents will break the tightness of the route.
- Polypropylene. For the manufacture of PP-H-fittings, polypropylene is used without reinforcement, so it is not suitable for hot water. PP-B is used for systems with a coolant no more than +50 degrees.The polypropylene PPRC material has a reinforced middle layer and can withstand high heat carrier temperatures.
The minimum diameter of heating pipes is 30 mm.
Number of radiators and sections
The SNiP says that the calculation is made depending on the area of the heated room. The document regulates 100 W of heat per square meter, so the area of the room must be multiplied by 100.
The number of sections depends on the degree of heat transfer of one element. It is indicated by the manufacturer. The amount of heat must be divided by the heat transfer coefficient, and the result must be translated into radiators.
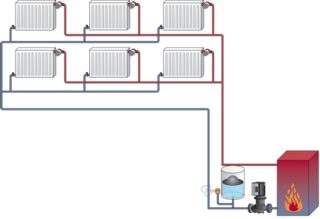
Installation and wiring diagram
The piping is laid out according to the one-pipe or two-pipe principle.
One-pipe communications are distinguished by the simplicity of self-assembly, minimal material costs. The device of the main line implies the sequential delivery of the coolant - it leaves the boiler, heading to the batteries in turn. The connection is made according to the following schemes:
- Horizontal. The connection of the radiators for the sequential movement of the heat carrier is carried out one after the other. The pipe is one-piece, not routed through the batteries. The disadvantage of the scheme is the inconsistent heating of the fittings.
- Vertical. Suitable for two-storey buildings and provides for a pipe with a heat source to the upper floor. There you will need to connect the batteries and make taps down. The disadvantage of the system is that it is warmer on the second floor than on the first.
- Compensatory. Leningradka with bypasses-jumpers that direct the coolant bypassing. The cells are located under the batteries, which ensures uniform heat distribution and temperature control.
Leningradka can be realized in a two-story and one-story building.
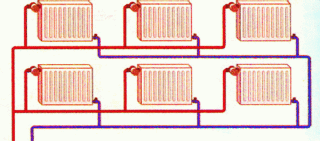
Two-pipe scheme heating is a return and supply line, between which radiators are placed. The input is connected to the supply, and the output is connected to the return. For masking communications, leveling and adjusting the temperature regime, wiring from the top and bottom is used.
When bottom wiring plastic fasteners are used for laying the supply and return lines. In the presence of radiators with side connection, the outlet is carried out from the supply pipe to the upper side cavity. The coolant intake is carried out from below. Air vents are mounted on the radiators, the expansion unit is placed at the bottom.
The battery connection is diagonal, which increases the heat transfer coefficient. The circuit is closed, the tank is completely sealed, the pressure is pumped by the circulation pump.
To heat a two-story house, pipes are installed on both floors and are fed in parallel to the boiler.
When top wiring the expansion tank is placed at the highest point - under the ceiling or in the attic. The coolant from it descends into the batteries, and after the energy is released through the return pipe, it moves into the container.
The upper system is a good method for heating high-rise buildings, eliminates the cost of downpipes and allows you to run a line with a natural type of circulation. The disadvantages are open pipes and the need for forced circulation in tall buildings.

Beam collector wiring: each heating system is equipped with its own main line and two collectors for supply and return. Individual straight pipes are led from them to the batteries. The beam scheme has several advantages:
- compatibility with the warm floor system;
- masking of the pipeline in the wall and floor surfaces;
- convenience of self-execution;
- remote adjustment of each circuit;
- the minimum number of joints;
- high-quality heat distribution.
Collector wiring is problematic to implement in a constructed dwelling, equipment and installation require large financial investments.
Alternative heating technologies

Alternative heating, as auxiliary or completely autonomous, can be installed by hand. Depending on the power supply of the area and financial possibilities, several options are selected.
Heat pumps
An electrical device transforms the energy of natural resources and directs it for heating. Manufacturers release the following modifications:
- Soil - immersed in the ground and completely heated into the house. The devices pay off in 10-15 years and provide for the initial investment. For installation, you will need a soil collection system.
- Air - replace traditional heating, but ineffective at sub-zero temperatures. Air vents are suitable for off-season operation.
Two-tariff meters are compatible with heat pumps.
Solar collectors

Ancillary equipment, the effectiveness of which depends on the length of daylight hours. They are used to heat water in the summer, spring and autumn seasons. In winter, the heating of the coolant is maintained by transferring the accumulated heat to a special reservoir.
Hybrid systems
Combine traditional and alternative options to save on heating costs. The most common are:
- Boiler + solar collector. The solid fuel unit and the solar panel maintain a comfortable microclimate and hot water supply. The boiler is turned on when there is a lack of solar energy. The option is convenient for large houses with warm floors.
- Boiler + heat pump. The system is represented by an external ground geothermal circuit with an internal block (evaporator, condenser, compressor) and a storage tank. The pump circuit absorbs heat from the soil at a level of 2.5 m and more, transfers heat energy to the evaporator. The refrigerant absorbs heat by transferring it to the water.
- Heating station + solar system. Heating of air masses comes from warm floors and francoil units. Hot water is heated in a heat accumulator. Heat from the geothermal circuit is supplied through a buffer or an evaporator-compressor-condenser chain.
Hybrid systems will only pay off after 10-20 years and are not suitable for areas with cold climates.
Parameters for choosing the right heating system for a private house
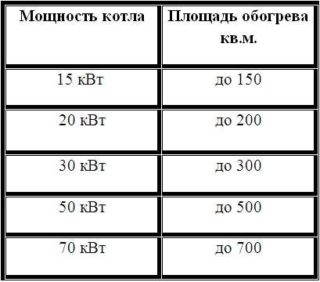
When selecting heating communications, you need to consider:
- Heat distribution level. The indicator depends on the room. In the bedroom, it is optimal + 22-25 degrees, in the hallway - +12 degrees. The total temperature should be + 20-24 degrees.
- Heat loss. Most of the heat energy flows out through windows and doors, so they should be insulated.
- Place for mounting batteries. To reduce heat leakage through the openings, it is better to place them under the window.
- Boiler power. For calculations, you will need to sum up the battery power indicators, multiply the value by 1.4 and divide by the power factor and efficiency of the unit.
- Fuel resources. For a stove and a special boiler, solid is suitable - coal, firewood, briquettes. The system also operates on electricity, gas, liquid fuel, alternative sources.
Any shortcomings will reduce the quality of heating and the efficiency of the line.
In a private country house and in the country, it is easy to implement any heating system. The owner needs to choose an option with maximum practicality, payback, in accordance with financial capabilities.








