SNiP 2.04.05-86 in Appendix No. 10 gives instructions on the use of steam and water heating systems in industry and everyday life. Steam is used in production, water is used in housing. Steam heats heating devices to temperatures above 100 ° C, which is dangerous for residents. This document does not apply to private households. The physics of steam heating processes consists in the use of dry steam, which, when condensing, releases a lot of heat. In the process of condensation of 1 kg of steam, 2300 kJ of thermal energy is released. Water cooled by 50 ° C gives 120 kJ.
Steam heating
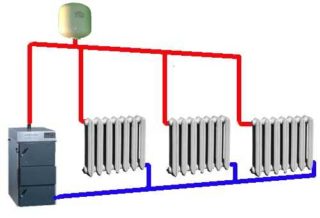
The difference in the released energy explains the advantages of steam heating:
- reduced number of radiators;
- quick warm-up of the system;
- no “defrosting” effect during breaks in work;
- significantly lower heating costs during installation and operation.
The second and third points are important for summer cottages and country houses - buildings in which residents are visiting.
According to the steam pressure used in the system, they are distinguished:
- High pressure systems (over 6 atm) - allow heating large areas with long pressure and condenser lines.
- Low pressure (1.7-6 atm) - can be used in private housing construction.
- Vacuum (pressure less than 1 atm) - an interesting opportunity to realize the boiling of water at temperatures below 100 ° C and reduce the temperature of heating devices to a safe one. They are used extremely rarely due to the need to ensure high tightness of the system.
A system communicating with the atmosphere is considered "open", not communicating - "closed".
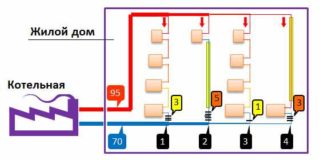
The disadvantages of steam include:
- excessive heating of pipes and radiators;
- wear of system elements due to aggressive steam;
- noises accompanying the operation of the system.
During installation, one-pipe and two-pipe wiring schemes are used. In the first case, steam and condensate move along the same pipe. Steam comes from the boiler, condensate - towards it. In a two-pipe system, steam flows through the pressure line to the radiators and, condensing in them, returns to the tank in the form of water in the form of water to collect it or directly to the boiler.
The slope when laying steam heating is taken at 1-2% in the direction of the movement of steam and condensate for two-pipe systems. The same 1-2% in the direction of the movement of condensate is taken for a one-pipe system.
Water heating
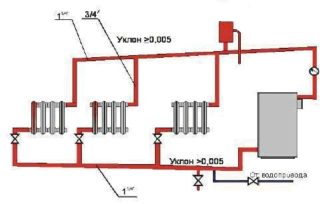
The popularity of hot water heating is due to its safety and great comfort. There are systems with natural and forced circulation. In the first, the movement of the coolant occurs due to the difference in the specific gravity of hot and cold water, in the second, it is provided by a circulation pump. One-pipe and two-pipe installation schemes are used.
With natural circulation, the slope is taken within 5-10 mm per linear meter of the pipe. The slope in the heating system is arranged in the direction of water movement, i.e. the pressure line is tilted from the boiler to the radiators, and the return line is tilted from the radiators to the boiler. The water heater must be located below the radiators, which may lead to the need to place the boiler in a pit. In a private house, this does not create problems.If a slope leads to a similar result when installing heating in an apartment, it is necessary to increase the height of the radiators and reduce the slopes of the pipes. It is necessary to decide what minimum slope in heating with natural circulation can be adopted without compromising performance. Practice suggests a value of 5 mm per running meter. For more information on the regulatory requirements, see SNiP 2.04.05.-91 *.
Pumps are used to create the movement of water in complex systems. If the pump provides a flow rate of more than 0.25 m / s, there may be no pipe slopes. It is important that the air pockets move faster than the liquid and collect near the air valves located at the top of the system. During operation, repairs are possible that require draining the coolant. Therefore, it is advisable to make the slopes of the pipes so as to ensure complete drainage of the coolant.
What is the minimum slope adopted for water heating systems depends on the specific circumstances. It should not be less than 3 mm per 1 m. The angle of inclination of the single-pipe heating line is chosen based on the same considerations.
Heating pipe characteristics

Pipes used in heating systems are divided into metal and plastic. The first are:
- steel;
- made of stainless steel;
- corrugated stainless steel;
- copper.
The listed materials are durable and have high performance properties, but they are expensive and difficult to install. Their use is justified in steam heating systems.
Plastic pipes are:
- metal-plastic;
- polypropylene;
- made of cross-linked polyethylene.
Their common advantages include ease of installation, low weight, and reasonable price.
Installation and assembly recommendations

Starting the installation, in accordance with the existing design of the heating system, determine the location of the boiler, radiators, pumps, expansion tank, etc. Further, using a level, marks are applied to the walls indicating what slope the heating system should have in all its sections. When installing heating pipelines with forced circulation, slopes can be avoided.
Post-installation system tests
After the installation is completed, the quality of the work performed is visually checked. The main task of the test is to identify leaks. As a rule, the hydrostatic method is used. The system is filled with water and the pressure is 25-50% higher than the operating pressure. Stand for 1 hour. The total length of the section to be tested should not exceed 100 m. Another method is to test with compressed air. Before filling the heating with a coolant, compressed air is fed into the system with a pressure of 1-1.5 atm higher than the operating pressure, and the pressure drop is monitored for 30 minutes. If there is no fall, the system is sealed. Otherwise, look for a leak. Determine the leak by soaping.








