GOST R 54860-2011 regulates the need for calculations when organizing heat supply communications. Before arranging the line, the owner must determine the required parameters of the boiler and batteries. Heating calculations are also performed to establish the energy efficiency of the equipment and the likely heat loss.
- Design parameters
- Calculations by volume of rooms
- Calculations by number of floors
- Selection of a heating boiler
- Gas modifications
- Electric models
- Combined units
- Solid fuel boilers
- Liquid fuel devices
- Features of calculating heat losses
- Hydraulic calculation
- Pipeline diameter
- Pressure parameters
- Hydraulic balancing
- Features of counting the number of radiators
- Calculation of boiler power
- How to choose heating devices
- Convection devices
- Radiator systems
- Convective radiator installations
- Installation rules for heating devices
Design parameters
The calculation technology allows you to select a heating system that is suitable in terms of power and length for a house or apartment. The calculation is performed based on several initial values:
- building area, its height from ceiling to floor, internal volume;
- the type of object and the presence of other buildings next to it;
- materials for the construction of the roof, floor and ceiling;
- the number of window and door openings;
- intended use of parts of the house;
- the duration of the heating season and the average temperature in a given period;
- features of the wind rose and the geography of the area;
- probable room temperature;
- specifics of points of connection to gas, electricity and water supply.
Insulation of doors, windows and walls must be taken into account.
Calculations by volume of rooms
The calculation for heating, made by the volume of the living space, is distinguished by the accuracy of the data. It is advisable to consider it using an example: a house of 80 m2 in the Moscow region with a ceiling height of 3 m, 6 windows and 2 doors that open outward. The algorithm of actions will be as follows:
- Calculation of the total volume of the building. The parameters of each room are summed up or the general principle is used - 80x3 = 240 m3.
- Counting the number of openings going out - 6 windows + 2 doors = 8.
- Determination of the regional coefficient for the Moscow region, which belongs to the middle zone of the Russian Federation. It will be 1.2. The value for other regions can be found in the table.
| Region | Features of the winter period | Coefficient |
| Krasnodar Territory, Black Sea coast | Warm weather with little or no cold | 0,7-0,9 |
| Middle lane and northwest | Moderate winters | 1,2 |
| Siberia | Harsh and frosty winters | 1,5 |
| Yakutia, Chukotka, Far North | Extremely cold climate | 2 |
- Counting for a country cottage. The first obtained value is multiplied by 60: 240x60 = 14,400.
- Multiplication by the regional correction. 14 400x1.2 = 17 280.
- Multiplying the number of windows by 100, doors by 200 and summing up the result: 6x100 + 2x200 = 1000.
- Adding the data obtained at stages No. 5 and No. 6: 17 280 + 1000 = 18 280.
The power of the heating system will be equal to 18,280 W without taking into account the materials of the load-bearing walls, flooring, and thermal insulation characteristics of the house. There is no correction for natural ventilation in the calculations, so the result will be approximate.
Calculations by number of floors

Residents of an apartment building pay for utilities depending on the number of storeys. The higher the house, the cheaper it is to heat it. For this reason, the calculation of the heating system is tied to the height of the ceilings:
- not more than 2.5 m - coefficient 1;
- from 3 to 3.5 m - coefficient 1.05;
- from 3.5 to 4.5 - coefficient 1.1;
- from 4.5 - coefficient 2.
You can calculate communications using the formula N = (S * H * 41) / Cwhere:
- N - the number of radiator sections;
- S is the area of the house;
- C - heat output of one battery, indicated in the passport;
- H - the height of the room;
- 41 Watt - heat consumed for heating 1 m3 (empirical value).
The calculations also take into account the floor of residence, the location of the rooms, the presence of the attic and its thermal insulation.
For premises on the first floor of a three-story building, a coefficient of 0.82 is set.
Selection of a heating boiler
Heating units, depending on the intended purpose, are single-circuit and double-circuit, can be installed wall-mounted and floor-standing. Boilers also differ in the type of fuel.
Gas modifications

Manufacturers produce various devices, so when choosing, you should pay attention to the following factors:
- The purpose of the installation of heating communications. Single-circuit options are used for heating, double-circuit options with a built-in boiler for 150-180 liters can provide a house with hot water and heat it.
- The number of heat exchangers in a dual-circuit model. The only bithermal element heats water as a heat carrier and a hot water supply resource at the same time. In versions with two, the heating primary is used for heating, the secondary is used for heating the DHW system.
- Heat exchanger material. Cast iron accumulates heat for a long time and does not corrode, steel is practically insensitive to temperature fluctuations.
- Combustion chamber type. The open chamber works on natural draft, therefore the boiler needs a separate room with good ventilation. The closed unit removes the combustion products through a coaxial horizontal chimney.
- Features of ignition. In the electric ignition mode, the wick will burn constantly, but the equipment needs electricity to operate. Models with piezo ignition are independent, but manually switched on.
Condensing gas units with a water economizer differ in performance, but the fuel fee is almost doubled.
Electric models

The devices are distinguished by almost silent operation, compactness and safe operation. Owners of houses and summer cottages can purchase modifications:
- On tubular heating elements. Devices with heating elements are suitable for wall mounting, automated, but often break down due to scale.
- On the electrodes. Small devices connected to a circuit of two or more batteries. The boiler is efficient, equipped with temperature settings, but is sensitive to the coolant.
- Induction. Equipped with an overheating protection system, they quickly heat up the coolant, have an efficiency of 97%.
Induction boilers are expensive equipment.
Combined units

They heat any area, they can operate in a universal mode and on two or three types of fuel. The type of power supply is selected by the user:
- solid fuel + gas;
- solid fuel + electricity;
- gas + electricity;
- gas + diesel.
One type of fuel resources is the main one, the second is auxiliary, which does not heat the house, but only maintains a normal temperature regime.
Solid fuel boilers
They work on wood, sawdust, coal, coke, special briquettes, are distinguished by safety and ease of use. For a private house, you can pick up units:
- Classic. They function according to the principle of direct combustion; the furnace must be filled every 5-6 hours.
- Pyrolysis. They work on the principle of afterburning residual gases in a special chamber. Fuel is loaded every 12-14 hours.
The devices require a chimney with good draft and are installed in a separate room. The user must periodically clean the combustion chamber from soot and tar.
Liquid fuel devices
They run on diesel fuel, therefore they are placed in a separate room. The boiler room is equipped with an exhaust hood and a high-quality ventilation system. Heavy oil is stored in sealed containers in a separate room. All liquid-fuel devices are automated, productive, and have great power.
Features of calculating heat losses

Most often, the heat depends on the material of the floor, ceiling surface, walls, the number of openings, and the characteristics of insulation. It is possible to calculate autonomous heating taking into account heat loss in a private house using the example of a corner room with an area of 18 m2 and a volume of 24.3 m3. It is located on the 1st floor, has ceilings of 2.75 m, as well as 2 external walls made of 18 cm thick timber with plasterboard sheathing and wallpaper. The room has 2 windows with dimensions 1.6x1.1 m. The floor is made of wood, insulated, with an underground floor.
Calculation of surface area:
- External wall without windows - S1 = (6 + 3) x 2.7 - 2 × 1.1 × 1.6 = 20.78 m2.
- Windows - S2 = 2 × 1.1 × 1.6 = 3.52 m2.
- Floor - S3 = 6 × 3 = 18 m2.
- Ceiling - S4 = 6 × 3 = 18 m2.
Calculation of heat loss of surfaces, Q1:
- Outer wall - S1 x 62 = 20.78 x 62 = 1289 W.
- Windows - S2 x 135 = 3 × 135 = 405 W.
- Ceiling - Q4 = S4 x 27 = 18 × 27 = 486 W.
Calculation of the total heat loss by summing the data. Q5 = Q + Q2 + Q3 + Q4 = 2810 W.
The total heat loss of one room on a cold day is -2.81 kW, that is, the same amount of heat is supplied additionally.
Hydraulic calculation
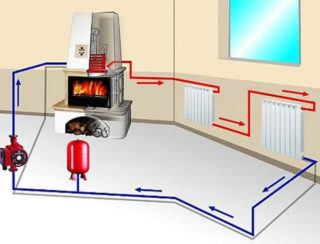
You can calculate the hydraulics for heating laid in a private house if you know:
- line configuration, type of pipeline and fittings;
- the diameter of the pipes in the main sections;
- pressure parameters in different zones;
- loss of pressure by the heat carrier;
- method of hydraulic connection of heating mains elements.
For example, you can use a gravitational two-pipe line with the following parameters:
- calculated heat load - 133 kW;
- temperatures - tg = 750 degrees, tо = 600 degrees;
- design flow rate of the coolant - 7.6 cubic meters per hour;
- method of connection to the boiler - hydraulic horizontal distributor;
- constant temperature maintained by automation throughout the year - 800 degrees;
- the presence of a pressure regulator - at the input of each of the distributors;
- type of pipeline - metal-plastic distribution, steel for heat supply.
For the convenience of calculations, you can use several online programs or a special calculator. HERZ C.O. 3.5 counts according to the linear pressure loss method, DanfossCO is suitable for natural circulation systems. When calculating, you need to choose the parameters for the temperature - degrees Kelvin or Celsius.
Pipeline diameter
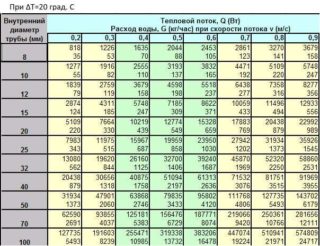
The difference between the temperature of the cooled and hot coolant in a two-pipe system is 20 degrees. The area of the room is 18 squares, the ceilings are 2.7 m high, the circulation of the forced-type heating main. The calculations are done like this:
- Determination of the average data. The power consumption is 1 kW per 30 m3, the thermal power reserve is 20%.
- Calculation of the volume of the room. 18 x 2.7 = 48.6 m³.
- Determination of power costs. 48.6 / 30 = 1.62 kW.
- Finding power reserves in cold weather. 1.62x20% = 0.324 kW.
- Calculation of the total power. 1.62 + 0.324 = 1.944 kW.
The suitable pipe diameter can be found in the table.
| Total power | Coolant movement speed | Pipe diameter |
| 1226 | 0,3 | 8 |
| 1635 | 0,4 | 10 |
| 2044 | 0,5 | 12 |
| 2564 | 0,6 | 15 |
| 2861 | 0,7 | 20 |
The value of the total power must be chosen as close as possible to the result of the calculation.
Pressure parameters
The total pressure loss is the pressure loss in each section. This value is calculated as the sum of friction losses of the moving heat carrier and local resistance. Counting Algorithm:
- Search for local pressure at the site using the Darcy-Weisbach formula.
- Search for the coefficient of hydraulic friction using the Alshutl formula.
- Using tabular data taking into account the pipe material.
| Outside diameter, mm | Friction loss coefficient | Coolant movement speed, kg / h | Local losses, kg / h |
Steel pipe | |||
| 13,5 | 5,095 | 229,04 | 0,0093 |
| 17 | 3,392 | 439,1 | 0,0025 |
| 21,3 | 2,576 | 681,74 | 0,0010 |
Electrowelded pipe | |||
| 57 | 0,563 | 7193,82 | 0,0000094 |
| 76 | 0,379 | 13 552,38 | 0,0000026 |
Polyethylene pipe | |||
| 14 | 2,328 | 276,58 | 0,0063 |
| 16 | 1,853 | 398,27 | 0,0030 |
| 18 | 1,528 | 542,1 | 0,0016 |
| 20 | 1,293 | 708,04 | 0,00097 |
Kilograms per hour can be converted to liters per minute.
Hydraulic balancing
Hydraulic balancing is a necessary step in balancing water losses. Calculations are made based on the design load, resistivity and technical parameters of pipes, local resistance of sections. You will also need to consider the installation characteristics of the valves.
Algorithm for calculating the resistance characteristics technology:
- Calculation of pressure losses per 1 kg / h of the coolant. They are measured in ∆P, Pa and are proportional to the square of the water flow in the section G, kg / h.
- Using the coefficient of local resistance and the summation of all parameters.
Information and dynamic pipe pressure can be found in the manufacturer's instructions.
Features of counting the number of radiators
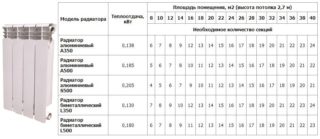
To calculate the number of radiator elements, it is necessary to take into account the volume of the building, its design features, wall material and the type of batteries. For example: a panel house with a heat flux of 0.041 kW. You need to calculate the number of batteries for a 6x4x2.5 m room.
Calculation algorithm:
- Determination of the volume of the room. 6x4x2.5 = 60 m3.
- Multiplying the area of the room by the heat flux to calculate the optimal amount of heat energy Q. 60 × 0, 041 = 2.46 kW.
- Search for the number of sections N. Divide the result of stage 2 by the heat flux of one radiator. 2.46 / 0.16 = 15.375 = 16 sections.
- Selection of radiator parameters from the table.
| Material | Power of one section, W | Working pressure, MPa |
| cast iron | 110 | 6-9 |
| aluminum | 175-199 | 10-20 |
| tubular steel | 85 | 6-12 |
| bimetal | 199 | 35 |
The longest service life of a cast iron line is 10 years.
Calculation of boiler power
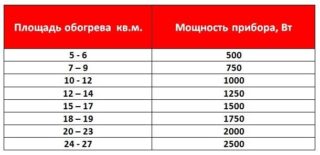
The calculation of the useful heat for heating each room involves the calculation of the power of the heating installation. Having learned it, you can create the optimal temperature regime. Boiler power is calculated by the formula W = S x Wud / 10where:
- S - indicator of the area of the room;
- Wood - parameters of specific power per 10 cubic meters of room.
The specific power indicator depends on the region of residence. It can be found in the table:
| Region | Specific power, W |
| Central | 1,25-1,55 |
| Northern | 1,54-2,1 |
| Southern | 0,75-0,94 |
An example of calculating the heat output of a boiler connected to the heating system for a room of 100 square meters in the Central Region will be as follows: 100x1.25 / 10 = 12 kW.
An approximate calculation is often used: a 10 kW boiler will heat 100 m2.
How to choose heating devices
In terms of external design, heating devices are similar, but during selection, design features must be taken into account.
Convection devices

Heaters quickly generate heat by circulating air currents. At the bottom of the convectors there are openings for air intake, inside the body there is a heating element that heats the streams. Convection equipment is:
- Gas - connected to the mains of the house or a cylinder. The units are energy efficient, but their installation must be coordinated with the regulatory authorities.
- Water - connected by the bottom or side way, heats up quickly. The devices are not suitable for rooms with high ceilings.
- Electric - connected to the network, have an efficiency of up to 95%, low noise. The downside is the high power consumption.
Heating 10 m2 of area with convectors requires 1 kWh of energy.
Radiator systems
They are connected to heating mains in the lower, lateral or universal way. Manufactured from the following materials:
- Aluminum is lightweight, heats up quickly, heat-consuming.The threaded connection of the upper inlet valve is of poor quality.
- Bimetal - equipped with a steel core and aluminum body. They can withstand high pressure, but are expensive.
- Cast iron - have a high heat capacity and long cooling. The disadvantages of devices include slow heating and heavy weight.
Aluminum batteries cannot withstand pressure fluctuations and are not suitable for apartments.
Convective radiator installations
They are implemented by connecting a water heated floor and radiators, and are used in country houses in server regions. Effective for heating corner or glazed rooms. Sectional (4-16 cells) or panel (one-piece) batteries can be installed under the windows. Warm floors on the first floor are covered with ceramic tiles, on the second - with any material.
Installation rules for heating devices

The regulatory requirements for installation are spelled out in several SNiPs and provide for:
- Radiator temperature safety control - no more than 70 degrees.
- Removal of batteries 10 cm from the side of the wall, 6 cm from the floor, 5 cm from the bottom of the wall, 2.5 cm from the plaster.
- The presence of a nominal heat flux is 60 W less than the calculated one.
- Making connections within the same room.
- Availability of automatic adjusting valves in living quarters and manual adjustments in bathrooms, bathrooms, dressing rooms, closets.
- Compliance with the slope of the liner along the movement of the coolant by 5-10 mm.
- Threaded connection of aluminum and copper devices.
- Constant filling of the system with a coolant.
The documents also noted the need for preventive inspection and cleaning of devices from dust before the start of the heating period and once every 3-4 months during operation.
Heat calculation for heating communications is carried out on an individual basis. Energy efficiency, safety and ease of use of the system depend on the accuracy and accuracy of calculations.












