A two-pipe heating system is one of the most popular ways to maintain a comfortable temperature in a private house. The water option is considered the most effective and practical in difficult climatic conditions. There are various connection schemes that are selected depending on the features of the building. Before you make heating in a house with your own hands according to a two-pipe scheme, you need to familiarize yourself with its varieties and distinctive features of each type.
Features of two-pipe heating
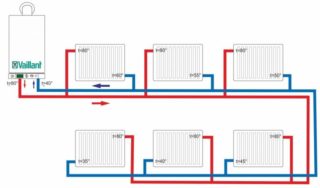
All types of heating systems powered by a liquid heat carrier (water, antifreeze) have a closed circuit. It connects all heating elements to each other: boiler, radiators.
The water moves through the heat exchanger and heats up to a high temperature. This value can be adjusted by installing special sensors and systems. After heating, the liquid enters the radiators. All heat is transferred from the heated battery to the air and to the surrounding objects. Gradually, the water cools down and returns to the circuit, where the heating cycle takes place again.
In the case of one-pipe systems, water only flows through one pipe to each radiator. The two-pipe heating method is more complicated. There are two pipes - through one water is supplied, and through the other it returns. The second is also called "return". This design avoids the main disadvantage of a one-pipe system, which consists in the flow of a colder coolant into the second, third and subsequent radiators. With a heating system with two pipes, the heat transfer of each section is practically the same.
System advantages

Two-pipe designs are more complex than using a single pipe. At the same time, they are becoming the most popular way to heat a private and apartment building. Positive features:
- The water temperature for each section of the circuit is the same.
- Each battery can be adjusted. The owner can install thermostats on different radiators and adjust the device to the desired temperature. This will not affect the heat transfer of the remaining batteries in the house.
- Minimal pressure loss. Due to this property, a low-power circulation pump can be used.
- The system continues to function even after one of the batteries fails. When carrying out renovations, you do not need to turn off the heating throughout the house.
- Can be installed in a building with any number of floors and different areas.
Of the shortcomings, only the complexity of installation and a higher cost are distinguished due to the increased number of pipes.
Varieties of schemes
The classification of two-pipe systems can be carried out according to various criteria. There are open and closed circuits, as well as with natural and artificial circulation. The connection and layout methods are also different.
Open wiring
All hydraulic heating systems have a closed circuit with an expansion vessel. It is necessary to take in excess liquid that is formed as a result of heating. If the wiring is open, choose a tank in which water communicates with the atmosphere. Part of it will evaporate, so control of the coolant level will be required.
The advantages of an open circuit include simplicity and low cost of construction. The downside is the rapid lag of the coolant in the cold season due to contact with air. In addition, only water can be used in such a wiring. Compounds of glycols and antifreeze during evaporation form harmful substances that poison the air.
Closed wiring
In such systems, a closed expansion tank is installed in which the liquid does not come into contact with the outside world. There is no need to control the water level. To protect against breakdowns, membrane tanks are installed, in which a sharp decrease or increase in pressure is compensated.
An important advantage of such a system is the ability to use any liquid as a heat carrier. This can increase the efficiency of the system and maximize savings.
Natural circulation designs
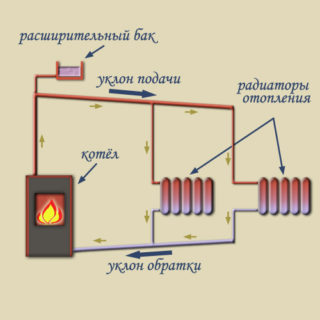
The boiler heats the liquid to high temperatures. The density of the coolant decreases, as a result of which cold water displaces hot water upward.
When heat is transferred to the radiator, the liquid cools down and increases its density. After that, it moves back to the double-circuit boiler and repeats the cycle again.
Advantages of the system:
- Excess air is not generated. He manages to go to the top point while the coolant passes along the contour.
- Duration of operation. It is associated with the absence of moving elements and complex mechanisms that can break.
Disadvantages:
- Slow work. The speed of movement also depends on many factors: the angle of inclination of the pipes, climatic conditions, the cross-section of the pipeline.
- Polypropylene pipes with an increased diameter are required.
- Complexity of design. It is imperative to observe all angles, otherwise the coolant will not be able to move freely along the contour.
- Low pressure drop.
- Different radiators receive liquid of different temperatures. The farther the battery is from the boiler, the colder the coolant gets into it.
The pumpless system is capable of self-regulation. The colder the room temperature, the faster the fluid will move through the pipe. Also, the speed is influenced by the cross-section and material of pipes, the number of turns, radii.
Forced circulation
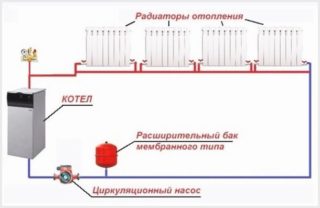
The main difference from systems with natural water movement is the presence of a pump. It forces the coolant to move along a closed heating circuit. In the case of using a pump, the design of the system is simplified, since external factors will not affect the normal movement of the coolant. Pump circuits are used most often.
Benefits:
- High speed of work.
- Reliability and stability.
- The most uniform heating of the batteries due to the flow of a coolant of the same temperature into them. It is possible to adjust a separate radiator in each wing of the building.
- Possibility of installing a membrane tank in a closed version.
- Installation is simplified, since strict adherence to the angle of installation of pipes is not required.
- Possibility of making edits to the design.
- Profitability.
An important disadvantage is energy dependence. The pump will not work without an electrical connection. For work in the country and with frequent problems with the power supply, a device with a battery may be required. You also need to take into account the costs of the pump itself and the fittings necessary for its operation.
Horizontal and vertical layout
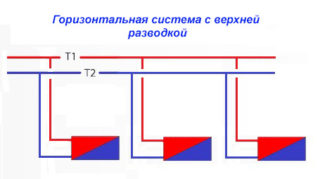
The way of connecting to the backbone is horizontal and vertical. The number of vertical lines is minimal. In the case of horizontal installation, the treatment pipes can be placed under the floor.Such a scheme cannot work without a circulation pump. Installed in one- and two-story houses.
If connected to vertical risers, there will be no air pockets. Such a system is installed in multi-storey residential buildings. The cost of a vertical system is higher than a horizontal one.
Top routing
The upper collector system is distinguished by the laying of supply pipes along the upper part of the room, and return pipes along the lower part.
Benefits:
- High line pressure.
- It is possible to install pipes of the same diameter even in the case of natural circulation.
- A circulation pump can be installed to improve efficiency.
- High speed of movement of the coolant.
- There is no airing of the line.
- Possibility of installation in one-storey and multi-storey buildings.
Disadvantages:
- The design involves the installation of an expansion tank at the top of the house. This is usually an unheated attic, which can cause efficiency problems. Polypropylene insulation may be required.
- Unaesthetic appearance of a room with pipes running under the ceiling.
- High consumption of pipes and accessories.
- Does not allow heating large areas.
- Difficulty placing the expansion tank.
For the system to be effective, all calculations must be done in advance. To avoid mistakes, you may need the help of a professional who will take into account all the features of the room.
Bottom wiring
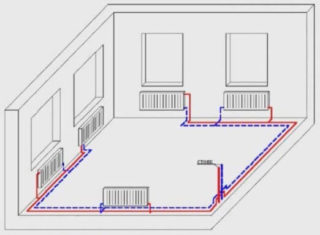
A system with a bottom wiring assumes the placement of pipes for supplying and removing water from the bottom of the batteries. In this case, the movement of the coolant changes. First, it moves from the bottom up, enters the batteries and goes through the return to the heating boiler. The circuit can have several circuits, as well as associated fluid movement.
Excessive airing is noted in the system. To get rid of it, Mayevsky's taps are installed. If the dacha has several floors, such a system should be installed on each radiator. To avoid this, it is recommended to install special overhead lines. They will collect excess air and direct it to the central riser. From it, air masses move into the expansion tank and are removed from there.
Systems with a bottom distribution and natural circulation of the coolant are practically not used. This is due to application restrictions. For this reason, forced circulation of the coolant through the heating circuit is most often used.
The main positive qualities of a system with a lower wiring:
- Lack of highways laid in plain sight. Such a system does not spoil the appearance of the room.
- Compactness of placement of the system control area. It can be installed in the basement of a private house.
- Heat loss is minimized as much as possible. This is possible thanks to the lower line routing.
- Such a system can work even during construction and repair work. When building a multi-storey building, you can heat the first floor while work is underway on the second.
- Profitability. Heat can be distributed in the required volume to different rooms, so there will be no extra spending on heating an underutilized room.
Of the minuses, we can note the need to purchase a large number of pipes and accessories. This increases the budget for installation work. Also, the circuit has a low coolant pressure in the supply line.
The system must be monitored and air removed through the Mayevsky taps, otherwise the efficiency of functioning will drop.










