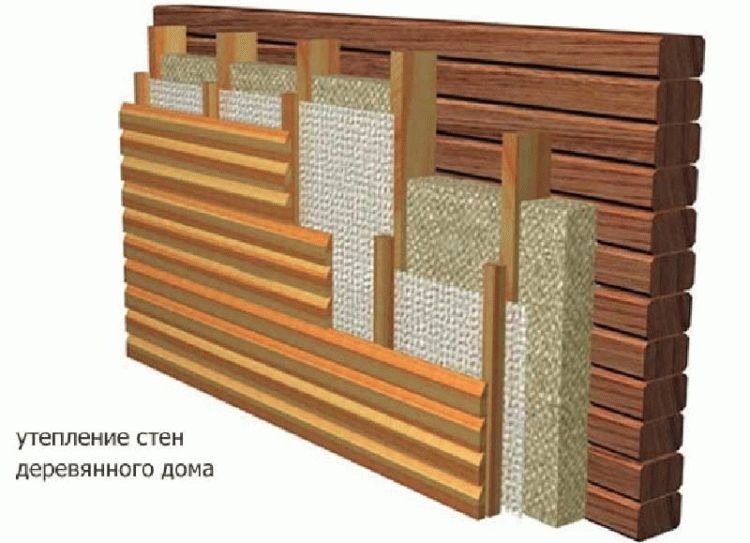
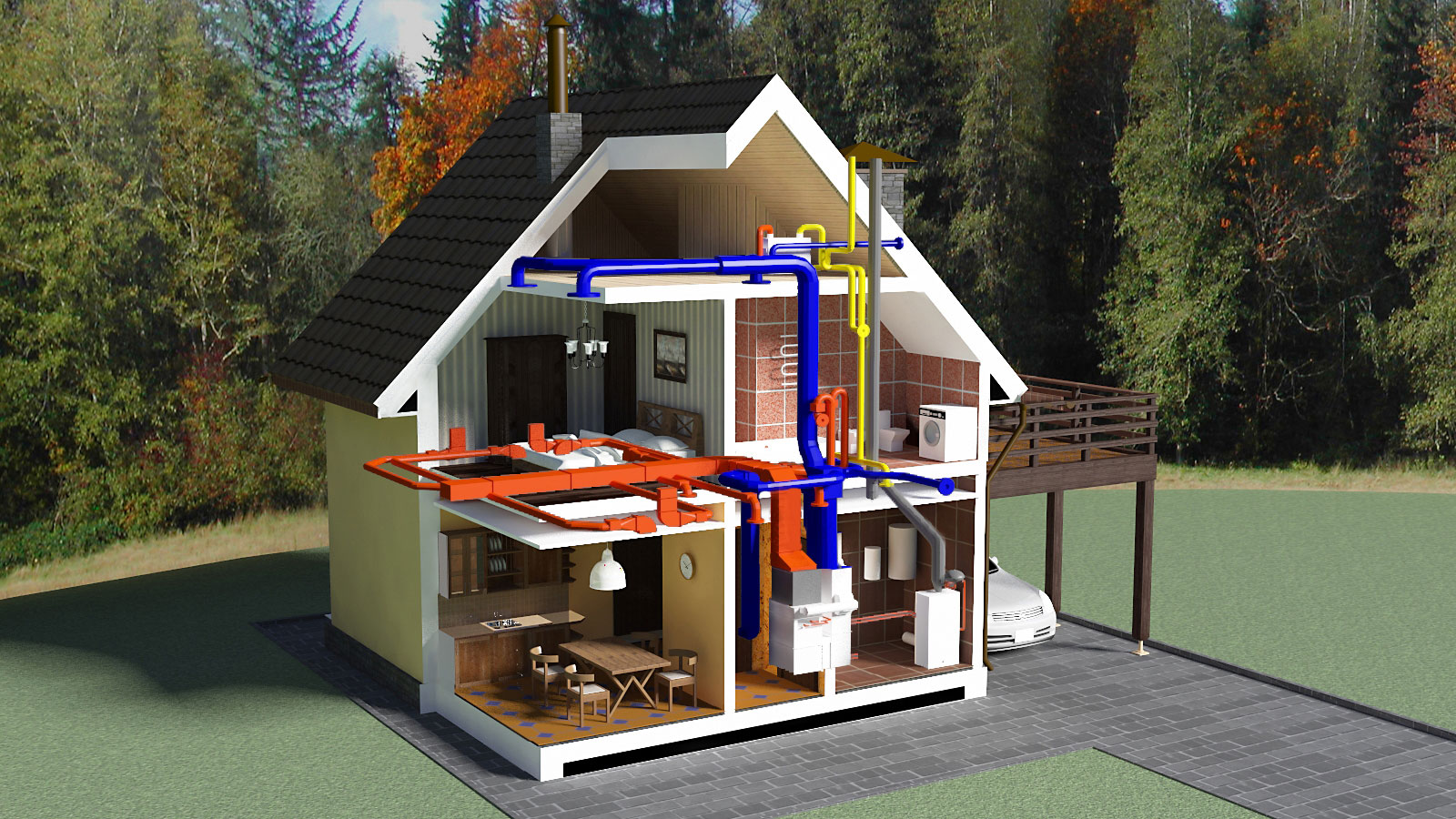
Today manufacturers offer a wide selection of heating radiators: cast iron, steel, bimetallic, aluminum. In many respects, the choice of this or that system will be determined by what kind of heating system works in your house, because water, having passed many kilometers of the central heating system, significantly loses its quality: it becomes chemically aggressive and rather dirty.
Many radiators, when using such a coolant, quickly fail.
Cast iron radiators
Usually manufacturers indicate the service life of a cast-iron radiator in the range of 10-30 years, however, under normal operating conditions, such a battery will last all 50 years. However, cast-iron batteries are not without their drawbacks, one of which is their very large weight. One section of such a heater weighs about 6 kg, hence problems arise during transportation and installation of a heating radiator. Also among the disadvantages should be noted their high thermal inertia. Cast iron radiators heat up more slowly and cool down more slowly.
Aluminum radiators
Aluminum radiators are able to warm up any room very quickly, but the main problem that arises during the operation of these batteries is their insufficient mechanical strength. Such heating devices may not be able to withstand the high pressure drops of the central heating system, therefore, it is recommended to use aluminum radiators only in autonomous heating systems. In addition, the alkali used for flushing heating networks dissolves the oxide aluminum film, as a result of which the metal reacts even with water, which once again speaks in favor of the fact that aluminum radiators and the domestic heating plant are completely incompatible.
It should also be borne in mind that aluminum is capable of reacting even with copper, therefore, in autonomous heating systems, where the wiring is made of copper pipes, it is unacceptable to install aluminum heating radiators. Due to the fact that aluminum reacts with water, releasing hydrogen, excess pressure will constantly build up in the system, which must be released in order to avoid destruction of the radiator.
Steel radiators
Bimetallic radiators
This type of heating devices is a frame of their strong steel pipes covered with an aluminum sheath.Steel tubes are designed to ensure the strength of the heater, which allows it to be used in a central heating system, withstand large drops and operate at pressures up to 40 atm. The aluminum shell improves heat dissipation. Thus, bimetallic radiators combine the advantages of steel and aluminum batteries. However, it should be borne in mind that the coefficient of thermal expansion for these metals is different, therefore, during operation, such heating devices can crackle, make unpleasant sounds and even deform.
Heat transfer methods of heating radiators
Cast iron batteries just have this drawback - these heating devices transmit about 70% of thermal energy by radiation, the rest by convection. Consequently, insufficient efficiency is added to the large weight of cast-iron radiators, which led to the massive abandonment of these batteries, which we are seeing today.
For aluminum radiators, the ratio of convective heat transfer and radiation is approximately 60:50, for bimetallic radiators - 50:50. Sometimes preference is given to "clean" convectors, in which heat exchange is carried out only by convection, for example, steel panel radiators.
Tips for choosing heating radiators
Regardless of the type of heating radiators, when purchasing them, it is necessary to focus, first of all, on the thermal power of the heating device. It is generally accepted that for heating 10 sq. m of the room requires a heating device with a power of 1 kW. However, if the room has excellent thermal insulation and plastic double-glazed windows are installed, you can subtract 200 W from the total power, and if the heated room is corner, then on the contrary, it is necessary to add about 20% to the received power.
Heating radiators, of course, should be installed under the window, creating an obstacle to the cold air. In this case, it is necessary to focus not on the width of the opening, but on the calculated parameters, which we have already spoken about. Otherwise, when the room overheats, oxygen begins to actively burn in it, worsening the well-being of the residents, moreover, the high ambient temperature negatively affects the condition of the furniture and flooring.