The comfort of people staying indoors, especially in the winter season, largely depends on the temperature of the air around them. Therefore, among the engineering communications, equipped in residential premises, the heating system takes the first place. In urban conditions, issues of heating apartments are most often solved in a centralized manner, however, in private houses, their owners have to equip autonomous heating systems, the main element of which is a hot water boiler. The efficiency of the entire system depends on the technical and economic characteristics of the latter.
How to calculate the power of the boiler

The power of a heating boiler is the main indicator characterizing its capabilities associated with optimal heating of premises during peak loads. The main thing here is to correctly calculate how much heat is needed to heat them. Only in this case it will be possible to choose the right boiler for heating a private house in terms of power.
To calculate the power of a boiler for a house, various methods are used, in which the area or volume of heated rooms is taken as a basis. More recently, the required power of a heating boiler was determined using the so-called house coefficients established for different types of houses within (W / m2):
- 130 ... 200 - houses without thermal insulation;
- 90 ... 110 - houses with a partially insulated facade;
- 50… 70 - houses built using technologies of the XXI century.
By multiplying the area of the house by the corresponding house coefficient, we obtained the required power of the heating boiler.
Calculation of boiler power according to the geometric dimensions of the room
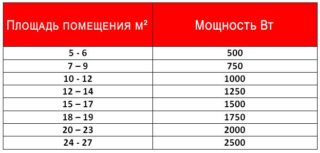
You can roughly calculate the power of the boiler for heating a house by its area. In this case, the formula is used:
Wcat = S * Wud / 10where:
- Wcat - rated power of the boiler, kW;
- S - the total area of the heated room, sq. M .;
- Wood - specific power of the boiler, which falls on every 10 sq. M. heated area.
In the general case, it is assumed that, depending on the region in which the room is located, the value of the specific power of the boiler is (kW / sq. M.):
- for the southern regions - 0.7 ... 0.9;
- for areas of the middle lane - 1.0 ... 1.2;
- for Moscow and the Moscow region - 1.2 ... 1.5;
- for the northern regions - 1.5 ... 2.0.
The above formula for calculating a boiler for heating a house by area is used in cases where the water heating unit will be used only for heating rooms with a height of not more than 2.5 m.
If it is assumed that a double-circuit boiler will be installed in the room, which, in addition to heating, must provide users with hot water, the calculated power obtained must be increased by 25%.
If the height of the heated premises exceeds 2.5 m, then the result obtained is corrected by multiplying it by the coefficient Kv. Kv = N / 2.5, where N is the actual height of the room, m.
In this case, the final formula is as follows: P = (S * Wsp / 10) * Kv
This method of calculating the required power, which a heating boiler must have, is suitable for small buildings with an insulated attic, the presence of thermal insulation of walls and windows (double glazing), etc.In other cases, the result obtained as a result of an approximate calculation may lead to the fact that the purchased boiler will not be able to operate normally. At the same time, excessive or insufficient power contributes to the appearance of a number of undesirable problems for the user:
- reduction of technical and economic indicators of the boiler;
- failure in the operation of automation systems;
- rapid wear of parts and components;
- condensation in the chimney;
- clogging of the chimney with products of incomplete combustion of fuel, etc.;
To obtain more accurate results, it is necessary to take into account the amount of actual heat loss through individual elements of buildings (windows, doors, walls, etc.).
Updated calculation of boiler capacity

The calculation of the heating system, which includes a heating boiler, must be carried out individually for each object. In addition to its geometric dimensions, it is important to take into account a number of such parameters:
- the presence of forced ventilation;
- climatic zone;
- availability of hot water supply;
- the degree of insulation of individual elements of the object;
- the presence of an attic and basement, etc.
In general, the formula for a more accurate calculation of the boiler power is as follows:
Wcat = Qt * Kzapwhere:
- Qt - heat loss of the object, kW.
- Kzap - the safety factor, by the value of which it is recommended to increase the design capacity of the object. As a rule, its value is in the range of 1.15 ... 1.20 (15-20%).
The predicted heat losses are determined by the formulas:
Qt = V * ΔT * Kp / 860, V = S * H; Where:
- V - the volume of the room, cubic meters;
- ΔT - difference between outside and inside air temperature, ° С;
- Cr - coefficient of dissipation, depending on the degree of thermal insulation of the object.
The dissipation factor is selected based on the type of building and the degree of its thermal insulation.
- Objects without thermal insulation: hangars, wooden barracks, corrugated iron structures, etc. - Cr = 3.0 ... 4.0.
- Buildings with a low level of thermal insulation: walls in one brick, wooden windows, slate or iron roof - Kr is taken equal in the range of 2.0 ... 2.9.
- Houses with an average degree of thermal insulation: walls of two bricks, a small number of windows, a standard roof, etc. - Cr is 1.0 ... 1.9.
- Modern, well-insulated buildings: underfloor heating, double-glazed windows, etc. - Cr is in the range of 0.6 ... 0.9.
To make it easier for the consumer to find a heating boiler, many manufacturers place special calculators on their websites and dealer websites. With their help, by entering the necessary information in the appropriate fields, it is possible with a high degree of probability to determine for what area, for example, a 24 kW boiler is designed.
As a rule, such a calculator calculates according to the following data:
- the average value of the outdoor temperature in the coldest week in the winter season;
- air temperature inside the object;
- the presence or absence of hot water supply;
- data on the thickness of external walls and floors;
- materials from which floors and external walls are made;
- ceiling height;
- geometric dimensions of all external walls;
- the number of windows, their sizes and a detailed description;
- information on the presence or absence of forced ventilation.
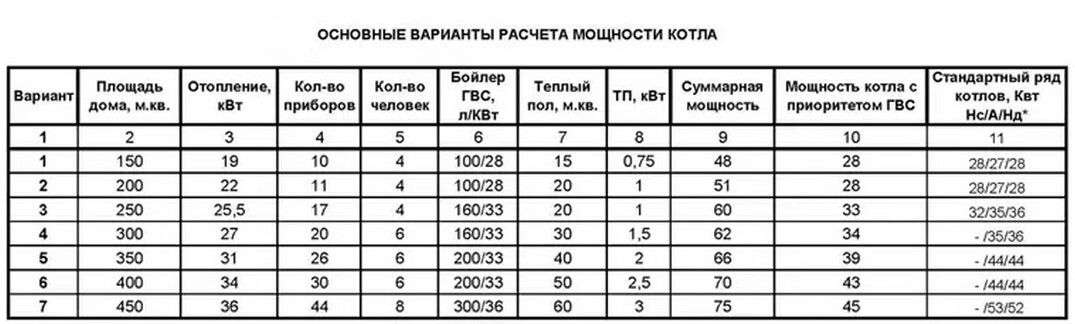
After processing the obtained data, the calculator will give the customer the required power of the heating boiler, and also indicate the type and brand of the unit that meets the request. An example of calculating a line of gas boilers designed to heat houses of different sizes is shown in the table:
Note for column 11: Нс - suspended atmospheric boiler, А - floor-standing boiler, Нд - wall-mounted turbocharged boiler.
According to the above methods, the power of the gas boiler is calculated. However, they can also be used to calculate the power characteristics of water heating units operating on other types of fuel.
Heat loss accounting

When starting to develop an autonomous heating system, it is necessary first of all to find out how much heat goes out into the street during the most severe frosts through the so-called enclosing structures. These include walls, windows, floor and roof. Only by determining the amount of heat loss, it will be possible to attend to the selection of a heat source of appropriate power. It should be borne in mind that the loss of heat by the building in the winter season occurs not only through the enclosing structures. A significant part of the generated heat (up to 30%) is spent on heating cold air coming from the street due to natural ventilation.
The total amount of heat required to heat the room is determined by the formula:
Q = Qconstruct + Qairwhere:
- Qconstruct - the amount of heat lost through a structure of the same type, W;
- Qair - the amount of heat consumed for heating the air coming from the street, W.
Summing up the values obtained as a result of calculations, they determine the total heat load on the heating system of the entire building.
All measurements are carried out on the outside of the building, capturing its corners without fail. Otherwise, the calculation of heat loss will be inaccurate.
There are other ways of heat leakage in rooms, for example, through a kitchen hood, open doors and windows, cracks in structures, etc. However, the amount of heat lost for these reasons practically does not exceed 5% of the total heat loss and therefore is not taken into account in the calculations. ...
Calculation of heat loss through enclosing structures
The complexity of the calculation lies in the fact that it must be carried out for each room separately, carefully examining, measuring and assessing the state of each of its elements adjacent to the environment. Only in this case it is possible to take into account all the heat leaving the house.
Based on the results of the measurements, the area S of each element of the enclosing structures is determined, which is then inserted into the basic formula for calculating the amount of lost thermal energy:
Qconstr = 1 / R * (Tv-Tn) * S * (1 + Σβ), R = δ / λ; Where:
- R - thermal resistance of the construction material, sq. M. ° С / W;
- δ - thermal conductivity of the construction material, W / m ° С);
- λ - thickness of the construction material, m;
- S - the area of the outer fence, sq. M .;
- TV - indoor air temperature, ° С;
- Tn - the lowest air temperature in the winter season, ° С;
- β - heat loss, which depends on the orientation of the building.
If the structure consists of several materials, for example, a brick wall with insulation, the value of thermal resistance R is calculated separately for each of these materials and then summed up.
- to the north side - β = 0.1;
- to the west or southeast - β = 0.05;
- to the south or southwest - β = 0.
The calculation of heat losses through the elements of the enclosing structures is carried out for each room in the building, and then summing them up, the predicted value of the total heat losses in it is obtained. After that, they proceed to the calculation in the next room. As a result of the work carried out, the home owner will be able to identify the ways of maximum heat leakage and eliminate the causes of their occurrence.
Calculation of heat consumed for heating ventilation air
The amount of heat that is consumed for heating the ventilation air in some cases reaches 30% of the total heat energy losses. This is a large enough value, which is impractical to ignore. To calculate the amount of heat that will be forced to be spent on heating the supply air, the following formula is used:
Qair = c * m * (Tv-Tn)where:
- c - the heat capacity of the air mixture, the value of which is 0.28 W / kg ° C;
- m - mass flow rate of air entering the room from the street, kg.
The mass flow rate of air entering the room from the outside is determined by assuming that the air is renewed throughout the house 1 time per hour.In this case, adding the volumes of all rooms, the volumetric value of the air flow is obtained. Then, using the value of the density of air, its volume is converted to mass. Here you need to take into account the fact that the density of air depends on its temperature.
| Supply air temperature ºС | — 25 | — 20 | — 15 | — 10 | -5 | 0 | + 5 | + 10 |
| Density, kg / m3 | 1,422 | 1,394 | 1,367 | 1,341 | 1,316 | 1,290 | 1,269 | 1,247 |
Substituting all known values in the above formula, the amount of heat required to heat the supply air is determined.
Common mistakes
Calculation of an autonomous heating system is a complex process consisting of several interrelated, step-by-step procedures:
- Calculation of heat losses of the object.
- Determination of the temperature regime of individual rooms and the building as a whole.
- Calculation of the power of heating radiator batteries.
- Hydraulic calculation of the heating system.
- Calculation of the power of the heating boiler.
- Determination of the total volume of the autonomous heating system.
The thermal calculation of a heating system is not a theoretical study, but an accurate and reasonable result, the practical implementation of which will allow you to correctly select all the necessary components and equip an effective heating system that has been functioning without problems for many years.
The main mistake that many owners of private houses make is ignoring some stages of the calculation. They believe that in order to resolve the issue, it is enough to choose a more powerful boiler, focusing only on the data of an approximate calculation of its power over the area of the room. This approach threatens with unnecessary operating costs and often leads to the fact that the boiler will work constantly, the radiator batteries will be hot, and the room will be cold. In this case, it is necessary to return to the original state and make a complete calculation of the heating system. Only then can one begin to eliminate the shortcomings caused by critical errors in the calculations.