Underfloor heating - a variant of electric space heating. The system's passport indicates its energy consumption per 1 sq. m. area. However, this value is the energy consumption in the on state, and the heating system works in cycles. How much electricity a warm floor consumes depends on how much all the nuances of installation and selection are taken into account.
- Factors Affecting Electricity Consumption of Underfloor Heating
- System type
- External factors
- Floor characteristics
- Electric floor consumption calculation
- Calculation of total power
- Amendment to work with a thermostat
- Resource cost calculation
- How to reduce resource costs
- Correct thermostat installation
- Heating of the usable area
- Multi-tariff meter
- Building insulation
- Reducing room temperature
- Nuances of power consumption of electric floors
Factors Affecting Electricity Consumption of Underfloor Heating

Electricity is an expensive source of energy, but efficient. If you choose the right heating system, you can provide the house with heat and not spend a lot of money on paying bills.
System type
There are several types of electric floor heaters:
- Heating cable - resistive or zone. The cheapest option. Accumulates some heat, after switching off the floor cools down slowly. The installation scheme is complex: the cable can only be placed in open areas, otherwise it overheats and breaks down. This modification is installed on balconies, loggias, in baths, where heating is required less often.
- Thermomats - convection and infrared. More economical and consume less electricity. Installation requires high qualifications. The thermomats are placed under a thin floor covering, placed in a screed or in a layer of tile glue.
- IR film - heating only by IR radiation. At the same time, the stage of heat transfer to the coating disappears. IR films are more efficient. It is installed in residential areas where an acceptable temperature must be maintained constantly.
- Self-regulating - due to the inclusion of carbon-polymer material, the system self-regulates. In the cold section, the resistance of the cable drops, a current of greater intensity passes through it and heats it up. When heated, the resistance of the cable increases and the current decreases. This option is designed for the industrial sector, is expensive to manufacture, but more efficient than other modifications.
Lower energy consumption and cost are not the only factors in choosing a product. It is unprofitable to install cable heaters in rooms with a low ceiling; more expensive IR films are installed here.
External factors

Factors determine the amount of heat loss. The smaller they are, the less powerful heating can be installed, and the less you pay for electricity. Consider the following:
- Number of windows and doors - metal or glass surface conducts heat well. Prevent losses by insulating doors.
- The level of resistance to heat loss - the value is the indicator of the wall material - brick, concrete, quality, thickness of the thermal insulation layer, characteristics of external and internal finishing. Insufficient thermal insulation negates the benefits of underfloor heating and leads to unnecessary costs.
- Weather conditions - in extreme cold, consumption naturally increases.
- The number of tenants - the more people live in an apartment, the less the heated floor works.
The infrared foil or heating cable can be installed not only on the floor, but also on the walls in a brick building, frame or wooden.
Floor characteristics
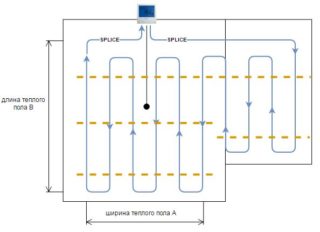
The energy consumption of any option for a warm floor is influenced by its own indicators:
- the presence of a thermostat - the more accurately the temperature is regulated, the more economical the system;
- cable laying step - the smaller it is, the more powerful the heater, the more energy it consumes;
- the thickness of the floor covering - laminate, tile, or screed - the smaller it is, the lower the electricity consumption.
Carpet or carpet will reduce the efficiency of the underfloor heater and cause it to work too hard. The material makes it difficult to dissipate heat, which can lead to overheating and damage to the cable. Only small decorative rugs are allowed.
Electric floor consumption calculation
ETP heating is efficient, but too high energy consumption makes it unprofitable. Costs are calculated, taking into account the operating mode and type of floor heater, otherwise the data will be inaccurate.
Calculation of total power
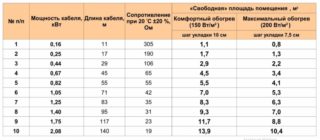
An approximate calculation is made as follows: the useful area is multiplied by the power of the electric underfloor heating per 1 square meter, indicated in the product passport. The highest possible flow rate is obtained.
However, the floor heater does not work constantly: the cable heats up for 5–20 minutes within an hour. For example, for an area of 12 sq. m. with a system power of 150 W / sq. m, the maximum consumption will be 1.8 kW per hour. But since the system works only 10 minutes per hour, and cools down for 50 minutes, the real consumption will be only 0.3 kW per hour.
Temperature influences in the same way. The maximum temperature of the cable floor is +65 C, for IR films - +60 C. Such high heating is rarely needed. The operating temperature is no more than 30–35 C, that is, the power consumption is reduced by another 40%.
The degree of insulation both increases and decreases energy consumption:
- heating of residential premises requires up to 120 W / sq. m;
- for a bathroom - 150 W / sq. m, since this room is non-residential;
- on the balcony or loggia, the insulation is the weakest; heating will require 200 W / sq. m.
Since the bathroom and the loggia are used much less often than the bedroom or kitchen, the real expense is not so great.
Amendment to work with a thermostat
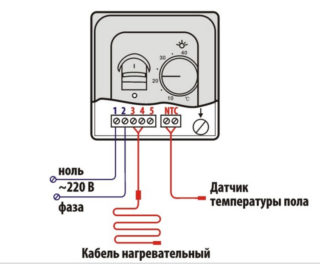
The thermostat turns on and off the heating depending on the readings of the temperature sensor. When the air temperature in the room exceeds the set value, the underfloor heating is turned off; when it falls - the thermostat turns on the heater. Cyclical operation saves energy consumption.
An electronic programmable thermostat provides an optimal heating mode. The default settings assume that in the morning, while all residents are at home, the temperature should be kept at 25 C. If the house is empty during the working day, the heating can be reduced to 15 C. In the evening, when the residents return home, the temperature is raised again. The heating intensity decreases at night.
Resource cost calculation
Calculating costs is easy. The received capacity of the system for each room and taking into account the work schedule is multiplied by the value of the tariff adopted in the region. The actual consumption may differ if some of the factors were not taken into account in the calculations or if the weather conditions turned out to be different from the expected ones.
How to reduce resource costs
It is possible to reduce the cost of electricity bills if we take into account all the nuances of the underfloor heating. With insufficient thermal insulation at home, no tricks will help.
Correct thermostat installation

How much energy is consumed by the warm floor depends on the type and method of installation of the control device. The recommendations are as follows:
- The settings of the electronic device are precise: the temperature can be set up to 1 degree. This is a more economical mode of operation.
- A programmable thermal sensor lowers the temperature when the inhabitants of the dwelling are not at home. In this way, energy can be saved up to 30%.
- Mount the device in the coolest place.
- A thermostat is installed in every room, since the comfortable temperature in the bathroom and bedroom is different. If heating in different rooms is controlled by only one device, all rooms will be heated in the same way, and this leads to excessive consumption.
The thermostat is adjusted using a floor sensor. Programmable can be configured to operate from 2 sensors. In this case, the floor heating is regulated depending on the air sensor indicator, and the floor sensor serves as a limiter and does not allow the temperature to rise above 28-30 C.
Heating of the usable area
There is no need to heat the floor under furniture or equipment. Cables or IR foil should be laid only on open areas of the floor, where a person comes into contact with the coating. This area is called useful or active.
Heating elements are mounted at a distance of at least 20 cm from the wall - the size of the usable area is also reduced by observing the limitation.
Multi-tariff meter

A two- and three-tariff meter takes into account the amount of electricity consumed depending on the time of the day: during the day, at night, during the morning peak. The cost of electricity differs at different times of the day. 1 kW of nighttime energy costs 50–70% less than daytime energy. In the morning and in the evening, the price is the highest.
The multi-tariff meter in combination with the programmed operation of the temperature sensor reduces the cost of night heating by accounting for a different tariff and by reducing the temperature.
Building insulation
Thermal insulation is the main condition for lower consumption. All elements of the structure are subject to insulation:
- poorly designed walls allow up to 30% through;
- 20% of heat is lost through the non-insulated foundation;
- a cold roof, even taking into account the attic, allows up to 25%;
- a window in an old wooden frame loses up to 25%;
- another 5% disappears through the entry points of external communications;
- ventilation provides 15% of losses.
A poorly insulated building saves no more than 30% of heat. Under these conditions, the heating costs are enormous. On the contrary, reliable thermal insulation keeps you warm, like a thermos of hot tea. In mid-latitudes, during warm winters, an underfloor heater can replace the standard water system while operating in auxiliary heating mode.
Reducing room temperature
The maximum permissible floor heating temperature is high - at the outlet, the air sensor can show 30 C. This is a lot. According to statistics, the temperature is more often set in the range from 23-25 C. In fact, a comfortable environment remains at lower rates - 21-22 C. A decrease in heating by only 1 degree reduces costs by 5%.
Nuances of power consumption of electric floors
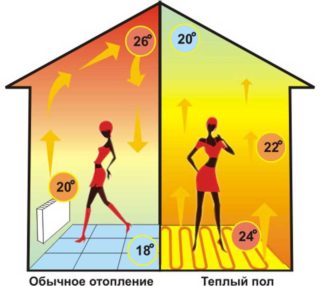
The floor surface in the system acts as a radiant panel, and the warm floor acts as heating elements. Electricity is supplied to the cables and film, which is converted into heat energy. The efficiency of all variants of the heater is close to 100%.
With the same indicators of power and energy consumption, the actual consumption of electricity is different.
Cable floors work according to the same principle: current flows through the cable, heating it, and the latter transfers heat to the floor. Since concrete is an excellent conductor of heat, it is more convenient and profitable to install cables in the thickness of the concrete screed.
The efficiency of the film heater is higher. When current flows, the elements generate infrared radiation. In this case, it is not so much the floor that heats up, but the objects and objects in the room - furniture and people. The actual temperature in such a room may be lower than with a conventional form of heating, but people feel as comfortable as at a higher temperature.This allows you to set a lower heating level and save electricity.
When installing electric underfloor heating, sensors are duplicated, reducing the likelihood of a sudden system failure.








