Radiator - a heating device for dissipating heat in the air in the form of radiation or convection. Its characteristics determine how comfortable it will be in the house and how much the user will have to pay for it. Which is better - steel or bimetallic radiators - depends on many factors.
The device of steel radiators

By design features, there are 2 types of batteries: tubular and panel.
Tubular pipes consist of a main pipe and looped ribs soldered onto it. In appearance, they resemble standard cast iron batteries. The efficiency of the device is not very high. They cannot withstand high pressures in a central heating system.
Panel radiators are more efficient. It consists of a double sheet steel structure with horizontal and vertical collectors. The panels are welded with a continuous seam. The heat transfer of the model is increased due to the ribbing of the corrugated sheet. An air outlet grill is located on top of the device, through which heated air enters the room.
Models are produced with side and bottom eyeliners. The complete set includes a Mayevsky tap, plugs, a thermostatic valve.
The efficiency of the model is determined by the number of panels - 1, 2 or 3 rows, and the presence of ribbing. In the marking, the first number indicates the number of rows, and the second indicates the number of convective plates.
For the manufacture of panel and tubular heaters, cold-rolled steel sheets with a thickness of 0.15 to 1.4 mm are used.
Features of bimetallic radiators
This model is made of 2 metals. Steel is strong, but the level of thermal conductivity is relatively low. It is prone to corrosion and needs protection. Aluminum conducts heat better and does not lend itself to rust, but its mechanical strength is low. Joining a steel or copper core with an outer layer of aluminum allows you to combine the useful qualities of metals and get rid of the disadvantages.
The bimetallic radiator consists of threaded sections. Each section contains 2 steel pipes connected by a lintel. An aluminum body is welded to the base using a special injection molding technique. It serves as a heat exchanger. The hull shape is complex and includes multiple ducts to maximize heat dissipation.
There are models in which the core is only partially made of steel. The cost of such batteries is 20% lower, but they are less durable and are prone to leaks at the joints of steel and aluminum in the core.
Advantages and disadvantages
Each of the heaters has its own pros and cons. Steel or aluminum radiators for an apartment or office are chosen after a careful assessment of the parameters.
Steel

The steel panel heater was developed during the energy crisis. It is served by a small volume of water and meets all the requirements for energy saving. Tubular tubes are less economical and less efficient.
Advantages:
- high efficiency - a large working surface provides a quick warm-up of the room;
- easy temperature control due to the small volume of the coolant, the heating system can be equipped with automatic regulators;
- operating pressure in the system - 9–10 atm;
- laconic and austere design;
- ease of maintenance - the smooth surface is easy to wash and paint.
The disadvantages of the model include:
- low resistance to water hammer;
- draining the coolant provokes metal corrosion;
- the devices are incompatible with some polypropylene pipes.
Steel batteries are chosen when organizing an autonomous heating system. Their popularity is due to the transition to a closed heating circuit as more efficient. It is undesirable to use them in the open.
Bimetal

This option combines the positive qualities of steel and aluminum. Its heat transfer is 20% lower than that of aluminum, but almost 2 times higher than that of iron. However, it is necessary to decide which radiators are better - steel or bimetallic - after evaluating other features.
Advantages of the 2-metal model:
- high heat transfer;
- low sensitivity to impurities in water - corrosion does not threaten bimetallic radiators;
- weak thermal inertia;
- resistance to high pressure - the operating indicator is 25 atm, the battery can withstand water shocks up to 60 atm;
- the devices are lightweight, which simplifies installation;
- durability - the factory warranty for the product is 20 years.
Disadvantages:
- the cost is 15–40% higher than other heating devices;
- if oxygen enters the system, the alloy quickly rusts;
- in low-quality products, leakage is possible at the junction of aluminum and steel.
The installation of bimetallic batteries is simple, but requires great care. If the core of the instrument is strong, the aluminum case can be easily bent and damaged if handled roughly.
Comparison of characteristics of steel and bimetallic radiators

To decide whether to install a steel or aluminum radiator in a private house, compare the most important indicators of devices. The negative sides of the heaters should also be assessed.
Heat dissipation
The efficiency of a bimetallic radiator is 2 times higher than that of a steel one. With a section width of 500 mm and a coolant temperature of 70 C, the power of the combined heater reaches 199 W, and the steel one - only 85 W.
Corrosion resistant
The weak element of both designs is steel. In conditions of central heating, when the water from the batteries is drained in the spring, it makes both devices equally vulnerable.
The bimetal is more resistant to external influences: aluminum forms an oxide film in air, which protects it from corrosion. Steel products rust quickly if the paintwork is damaged. Batteries need to be painted periodically.
Life time
The service life of steel radiators is 15–20 years. In humid rooms, it is reduced to 10.
Bimetal protects the top layer of aluminum. The product serves up to 40 years, not inferior in durability to cast iron batteries.
High pressure
An important difference between steel panel radiators and bimetallic ones is pressure resistance. Although steel is stronger, the allowable working pressure is 6 atm. This is higher than that of aluminum heaters, but noticeably less than that of bimetallic ones - 25 atm.
Tubular steel devices withstand pressures up to 16 atm. They are more adapted to central heating.
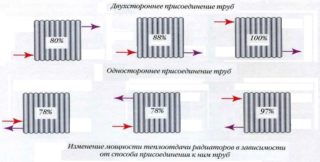
The method of connecting to pipes for batteries is the same - threaded couplings. Steel elements are attached to each other, this ensures reliable contact. However, bimetallic radiators weigh less, which makes installation easier.








