The heating main of an apartment building is a network of several elements that perform the functions of heating, compensation for heat losses, and maintaining a normal microclimate. During the construction process, they are guided by the popular wiring diagrams of heating systems in multi-storey buildings. Understanding the principle of their work and types of connection will help you choose the best type of communication.
- Types of heating for high-rise buildings
- Individual system
- Autonomous heating main
- Central heating
- The principle of operation of the heating system
- How the water goes
- Wiring diagrams
- One-pipe communications
- Two-pipe communications
- Specificity of connecting radiators
- Bottom connection
- Diagonal connection
- One-way way
Types of heating for high-rise buildings
Depending on the location of the boiler room and the installation site of the generator in an apartment building, there are several options for floor heating.
Individual system
A high-rise building or apartment building is equipped with its own mini-boiler room. It contains equipment that, according to individual wiring, supplies water or gas to each apartment. The owners independently set the temperature in the system, regulate the power of the radiators, and determine when to turn on and off the heating.
Autonomous heating main
The circuit provides heat supply from a separate boiler in the apartment. It is compatible with existing communications, can be supplemented with other circuits with parallel or series connection.
Residents for the construction of an autonomous highway are required to obtain permission from the local administration or the housing office. This point is specified in Art. 26 and 27 ZhK, Resolution No. 307 and FZ No. 190.
Central heating

Provides for the sequential supply of the coolant to several buildings or quarters from one boiler room. The centralized system consists of the following elements:
- a distributor that supplies water or gas to the mains;
- pipelines for transporting the coolant to consumers;
- control and regulation equipment, which takes into account the quantity and quality of the coolant, changes its characteristics for certain factors.
Central heating is used in old houses, panel, brick five and nine-storey buildings with a typical layout.
The principle of operation of the heating system
The principle of operation of the heating system in an apartment building depends on autonomy. It is advisable to consider it using the example of centralized communications.
The heat carrier comes from the central point (boiler room) to the heating unit and is directed to the apartments. The flow rate is regulated in the boiler room using circulation pumps (independent method). If there is a dependent system in the house, the coolant is supplied without distribution from the CHP to the batteries or hot water supply. The peculiarity of communications is the lack of hot water in the summer.
How the water goes
The specificity of the direction of heating - from top to bottom or from bottom to top - depends on the number of floors. The upper method is used for buildings from 7 floors. The coolant enters the upper apartments or the attic through the main riser. From there, it is directed along single-pipe risers to the distribution pipes and goes down, passing sequentially through each heating device.
The high-rise type of housing stock (from 12 floors) provides for a breakdown of the structure into separate units (2-3 pcs.). Separate coolant distribution units are mounted on vertical communications.The upper floor is allocated for wiring, but it can be organized in apartments.
Wiring diagrams
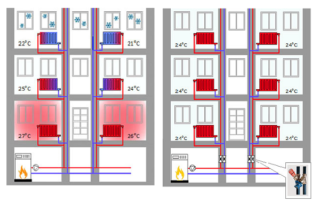
To select a system for heating a high-rise building, it is necessary to take into account the parameters:
- Pressure. For buildings with a height of up to 5 floors, the normal indicator is from 2 to 4 atm. In houses from 5 to 9 floors - 5-7 atm. The difference is explained by the pressure of the coolant at the time of supply.
- Temperatures. In living quarters it varies from +18 to +22 degrees, on stairs and in utility rooms it can reach +15 degrees.
After establishing the optimal values, you can choose the layout.
One-pipe communications
The single-pipe Leningrad line is suitable for Khrushchev houses and consists of several distribution stations to which consumers are connected. The coolant circulates along one circuit. Installation work practically does not require investments, because there is no return line. The Leningrad woman has several disadvantages:
- The apartment warms up unevenly. The heat in the room is determined by the distance from the collector unit. For this reason, some residents feel warm in their apartment, while others feel cold.
- Without a bypass on each battery, it is difficult to adjust the heating intensity.
- Balancing requires temperature controllers and shut-off valves.
- With slight fluctuations in pressure and temperature, interruptions in operation are observed.
- The costs of installing metering devices in each apartment.
In the presence of a one-pipe system, it is problematic to take into account the individual flow rate of the coolant.
Two-pipe communications
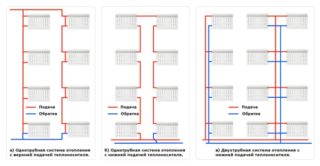
The scheme of a two-pipe heating system in a multi-storey building is characterized by the presence of a second circuit - a return. The design of the line also includes distribution pipes, radiators and a boiler. The coolant in a heated state moves through the batteries, and then, having cooled down, is sent to the return pipes. The water is collected and recycled to the boiler or CHP plant for heating. The features of the two-pipe system include:
- the presence of mixing devices for the convenience of adjusting the temperature range;
- overlapping during repair work of one circuit, and not the entire line;
- minimal inertia - water immediately enters the radiators;
- installation of pumping stations to reduce the load.
The optimal pressure indicator in a two-pipe system is 3-5 atm.
Specificity of connecting radiators
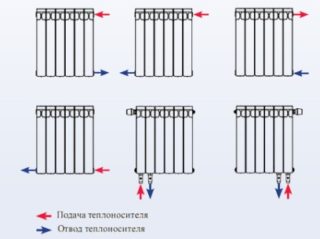
Batteries can be connected to the heating system in several ways.
Bottom connection
The pipes supplying and removing the coolant are led to the bottom of the radiator. This technology allows you to mask the pipeline. If a sectional product is installed with the lower method, the supply pipe goes to one side, and the return pipe goes to the other at the bottom. Changing sides reduces the heating efficiency of heaters by 15-20%.
Diagonal connection
The supply line is located on one side of the battery at the top, and the return on the other at the bottom. The technology is justified in the presence of a sectional device of more than 12 elements and a panel length of 120 cm. The diagonal line excludes uneven heating.
One-way way
The supply and return pipes are located on the same part of the battery. The system will work with maximum heat output. The heat transfer rate of the battery is also fully utilized. The peculiarity of the connection is the location of the supply at the top, and the return flow at the bottom. Using special fittings, you can put the branch pipes from below, but it will turn out to heat only 70-80% of the area.
When choosing a scheme for housing in an apartment building, consider the type of heating system and the number of pipes. In addition to the characteristics of the line, you will need to pay attention to the method of connecting the radiators.








