The design of any heating system begins with the calculation of its basic parameters. First of all, this concerns the optimal load on heat supply. Therefore, before purchasing the necessary equipment, you should calculate the power of the heating system: boilers, radiators, pumps, batteries.
Why do you need a heating calculation
The defining task of performing calculations is to optimize further costs. The minimum required power of the heating boiler will directly affect the consumption of the energy carrier. But the savings should be within reasonable limits.
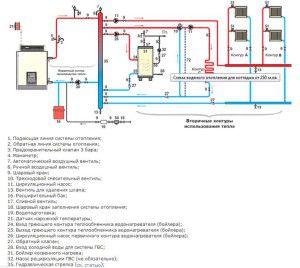
The main purpose of heat supply is to maintain a comfortable temperature level in living quarters. This is influenced by the nominal power of cast iron heating radiators, the heat loss of the building and the parameters of the boiler.
For the correct selection of equipment, you should correctly calculate its parameters. This can be done using specialized programs or independently, using certain formulas.
In addition, experts recommend calculating the power of the heating boiler and other system components for the following:
- Equipment purchase cost planning... The higher the rated power of the boiler or the heat dissipation of the battery, the higher their cost. As a result, this will affect the budget of the entire event for the arrangement of heat supply;
- Correct scheduling of system load... The correct calculation of the pump power for heating will allow you to find out the maximum and minimum load on the equipment when external factors change - the temperature outside, in the rooms of the house;
- System modernization... If heating costs are high, lowering them is a top priority to minimize maintenance. To do this, calculate the power of the heating battery and other components.
Having decided that without calculating the basic data, it is impossible to start purchasing material and components for arranging heat supply, one should choose calculation methods. First, the characteristics of each component are recognized separately - the boiler, the radiator pump. Then their parameters are entered into the heating program and checked again. The same methodology is used to calculate the heating of the greenhouse.
The type of energy carrier used affects the calculation of the power of a gas heating boiler. It is necessary to decide in advance what kind of gas will be used - main or liquefied.
Determination of heat loss at home
At the first stage, it is necessary to correctly calculate the amount of heat that will go through the outer walls, windows and doors of the building. The operation of the heat supply must compensate for these losses, and on the basis of the data obtained, a further calculation of the capacity of the circulation pump for heating, boiler and batteries will be performed.
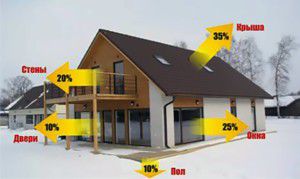
The defining parameter is the heat transfer resistance of walls and window structures. This is the inverse indicator of the thermal conductivity of materials. It is impossible to make a selection of the power of the heating boiler without knowing these values. Therefore, before starting the calculations, you should find out the thickness of the walls and the material from which they are made.
It is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the content of SNiP II-3-79, as well as SNiP 23-02-2003.These documents indicate the standard values of the heat transfer resistance for different regions of Russia. Knowing them, you can solve the question of how to calculate the power of a heating radiator. Each material has a specific heat transfer value. Data on the most common for the construction of residential buildings can be taken from standard tables.
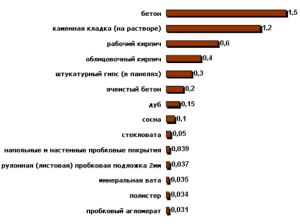
But this is not enough to further calculate the power of steel heating radiators. Additionally, you will need to know the thickness of each type of material used to build walls. The ratio of this value to the heat transfer coefficient will be the desired value:
R = D / λ
Where R - heat transfer resistance;D - material thickness;Λ - heat transfer resistance.
In the future, this will be used to calculate the required power of the heating boiler. This calculation step is recommended. Only by knowing the actual resistance of the walls can you determine the rated power of the entire heating system.
The calculation does not take into account the wind rose characteristic of each specific region. The data about it affects the calculation only for multi-storey buildings.
Features of calculating the power of various heating boilers
For the correct selection of the power of the heating boiler, they are determined in advance with its place of installation, the type of heat supply system (open, closed) and the type of fuel used. Additionally, the total area of the house and its volume are taken into account. This data will allow you to do the calculations in several ways.

The easiest method to calculate the power rating of your heating equipment is to use only the area of the house. For this, the standard ratio is taken that for heating 10 m² of the room, 1 kW of thermal energy must be consumed. This method will only work for buildings with good thermal insulation and standard ceiling heights. Its disadvantage is its large error. So, for a house with an area of 150 m², according to the calculation of the heating boiler power, you will need to choose a 15 kW model.
Additionally, a correction factor is applied, which depends on the location of the building. Then the final formula for calculating the power of a gas heating boiler will look like this:
W = (S / 10) * K
Where W - rated power of the boiler;S - the area of the house;K - correction factor.
For the central regions of Russia K = 0.13; for northern latitudes, the value ranges from 0.15 to 0.2. When selecting the power of the heat supply boiler for the southern regions, K = 0.08.
Accurate calculations can only be made after a preliminary determination of the heat transfer coefficient of the walls. This technique has been described above. To begin with, we find the temperature difference between the heated air outside and in the house - Δt. Then it is necessary to determine the heat loss. They are found by the formula:
P = Δt / R
Where R - heat loss at home;Δt - temperature difference;R - coefficient of resistance to heat transfer.
Further, to calculate the power of a gas heating boiler, it is necessary to multiply the area of the outer walls by heat losses. As an example, let's take a house with a wall area of 127 m², the coefficient of heat transfer resistance is 0.502. The optimal value of Δt should be 55. In this case, the heat loss per m2 will be equal to:
P = 55 / 0.505 = 108 W / m2
Based on this, the power of the heat supply boiler can be calculated:
W = 127 * 108 = 13.7 kW
In the following, the load on the heating system is determined at various values of Δt. It is recommended to choose a model of equipment with a small power reserve - 10-15%. This will allow expanding the heat supply without replacing the boiler and radiators.
For apartments with normal insulation, you can take the ratio of 41 W of heat per 1 m³ of room volume in a panel building and 38 W in a brick building. If the walls were insulated, you will need to make the above calculation.
Calculation of the power of radiators and heating batteries
But in addition to the boiler, the technical characteristics of other components affect the operation of the heat supply. Therefore, you need to know how to calculate the power of the heating battery. In fact, heat transfer of energy from hot water to indoor air takes place in it.

To calculate the power of heating batteries, it is necessary to actually determine their heat transfer. This is the name of the process of transferring heat from a heated body to air into the room. There are several factors that affect this figure. The main one is the material of manufacture. The lower the heat transfer resistance of the battery, the lower the heat loss. However, along with this, the effect of energy storage must be taken into account. This is observed in cast iron structures. Since to calculate the power of the heating battery, it is necessary to know the level of its filling with hot water, the total area of the structure should be calculated. The total heat transfer also depends on this.
For calculations, it is necessary to determine Δt according to the following formula:
Δt = ((Tpod-Tobr) / 2) -Tpom
Where Tpod, Tobr and TPom - temperatures in the flow, return pipes and in the room.
To calculate the power of cast-iron heating radiators, you will need the thermal conductivity coefficient of a particular material and the total area of \ u200b \ u200bthe structures. The first can be taken from standard tables. For bimetallic models, the steel cores of the pipelines and the aluminum heating surface are taken into account when calculating the power of the heating radiator.
The calculation is performed according to the following formula:
Q = Δt * k * S
Where Q - specific heat capacity of the radiator;TO - coefficient of thermal conductivity;S - the total area of the structure.
In this way, the power of the heating battery can be calculated. However, in practice, this is difficult, since several factors remain unknown - the actual wall thickness, additional elements used in the manufacture. Also, in calculating the power of the heat supply battery, heat losses in the room are not taken into account.
Most manufacturers indicate the rated power in the radiator passport. But this is done only for one thermal mode of heating operation. Therefore, taking as a basis the passport data of the product, you can accurately calculate the power of the heat supply radiator.
The actual heat dissipation of the battery depends on the correct installation. When calculating the power of steel heating radiators, their location relative to the window sill, floor and walls in the room is not taken into account.
Calculation of the power of the circulation pump
In closed heat supply systems, fluid circulation is forced. Before calculating the power of the pump for heating, it is necessary to draw up a heat supply diagram. Only then can you start calculating.

There are several parameters that determine the main characteristics of this heating component. The operation of the pump is aimed at increasing the speed of movement of the coolant in the system. In addition, it should not create excessive hydraulic loads and increase noise. That is why it is so important to correctly calculate the pump power for heating.
To perform calculations, you will need to know the following characteristics of the equipment:
- Performance... It characterizes the amount of heat transferred per unit of time through pipelines using a circulation pump;
- Hydraulic resistance... This is the pressure loss in the lines due to the friction of water against the inner surface of the heat supply components. When calculating the power of a pump for heating, this indicator is one of the determining ones, since the flow rate of the coolant depends on it;
- Power consumption... Specified by the manufacturer in the device passport. It is determined by the characteristics of the electric motor connected to the pump rotor.
At the first stage of calculating the power of the circulation pump for heating, the capacity should be calculated.To do this, you will need to find out the required thermal power of the heat supply system. Performance calculations are performed using the following formula:
Q = (0.86 * R) / (Tpod-Tob)
Where Q - device performance;R - calculated thermal power, W;Tpod and Tob - the temperature of the water in the flow and return pipes of the heating.
The main factor affecting pump performance is the thermal capacity of the system. It is best to calculate it as accurately as possible in order to avoid buying a device with inappropriate parameters. Also, the characteristics of the heat carrier affect the calculation of the pump power for heat supply. In the case of using antifreezes, the nominal indicator must be increased by 10-15%, since their density is much higher than that of distilled water.
The hydraulic resistance of the circulation pump is determined by the following formula:
H = 1.3 * (R1 * L1 + R2 * L2 + ... Z1 + Z2) / 10000
Where R1 andR2 - loss of pressure in the supply and return sections of the line;L1 and L2 - length of pipelines;Z1 and Z2 - hydraulic resistance of system components.
The last indicator for calculating the power of the pump for heat supply can be taken from the device's passport. If there is none, it is recommended to use the data from the table.
Heating component | Hydraulic resistance, Pa |
| Boiler | 1000 to 2000 |
| Thermostatic valve | 5000 to 10000 |
| Mixer | 2000 to 4000 |
| temperature sensor | 1000 to 1500 |
Manufacturers indicate hydraulic resistance in terms of the value of the water column. Those. this is an indicator of the power that is able to raise water in a vertical pipe to a certain level.
When calculating the power of a circulation pump for heat supply, the presence of several speed modes is not taken into account. Although in practice, using this function of the device, it is possible to optimize the speed of movement of the coolant, thereby balancing the entire system.
Is it difficult to make an accurate calculation of the heating of a house or greenhouse on your own? In addition to the above methods, it is recommended to use specialized programs for heat supply. This will allow you to check the results and achieve the maximum accuracy of the calculations.
The video material shows an example of calculating heating power using a specialized program:








