How to optimize heating costs? This task is solved only by an integrated approach that takes into account all the parameters of the system, buildings and climatic features of the region. In this case, the most important component is the heat load on heating: the calculation of hourly and annual indicators is included in the system for calculating the efficiency of the system.
Why you need to know this parameter
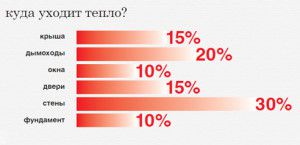
What is the calculation of the heat load for heating? It determines the optimal amount of heat energy for each room and the building as a whole. Variables are the power of heating equipment - boiler, radiators and pipelines. The heat losses of the house are also taken into account.
Ideally, the heat output of the heating system should compensate for all heat losses and at the same time maintain a comfortable temperature level. Therefore, before calculating the annual heating load, you need to determine the main factors that affect it:
- Characteristics of the structural elements of the house. External walls, windows, doors, ventilation system affect the level of heat losses;
- House dimensions. It is logical to assume that the larger the room, the more intensively the heating system should work. An important factor in this is not only the total volume of each room, but also the area of the outer walls and window structures;
- The climate in the region. With relatively small drops in temperature outside, a small amount of energy is needed to compensate for heat losses. Those. the maximum hourly heating load directly depends on the degree of temperature drop in a certain period of time and the average annual value for the heating season.
Taking these factors into account, the optimal thermal mode of operation of the heating system is compiled. Summarizing all of the above, we can say that the determination of the heat load on heating is necessary to reduce energy consumption and maintain the optimal level of heating in the premises of the house.
To calculate the optimal heating load based on aggregated indicators, you need to know the exact volume of the building. It is important to remember that this technique was developed for large structures, so the calculation error will be large.
Choice of calculation method
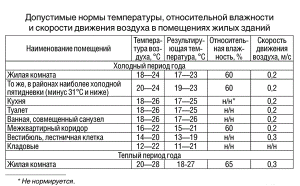
Before calculating the heating load according to enlarged indicators or with a higher accuracy, it is necessary to find out the recommended temperature conditions for a residential building.
When calculating the heating characteristics, one must be guided by the norms of SanPiN 2.1.2.2645-10. Based on the data in the table, in each room of the house it is necessary to ensure the optimal temperature mode of heating.
The methods by which the calculation of the hourly heating load is carried out can have varying degrees of accuracy. In some cases, it is recommended to use rather complex calculations, as a result of which the error will be minimal. If the optimization of energy costs is not a priority in the design of heating, less accurate schemes can be used.
When calculating the hourly heating load, the daily change in outdoor temperature must be taken into account. To improve the accuracy of the calculation, you need to know the technical characteristics of the building.
Simple Ways to Calculate Heat Load
Any calculation of the heat load is needed to optimize the parameters of the heating system or improve the thermal insulation characteristics of the house. After its completion, certain methods of regulating the heating heat load are selected. Consider the easy-to-use methods for calculating this parameter of the heating system.
Dependence of heating power on the area
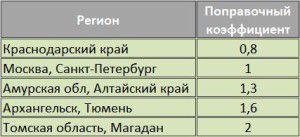
For a house with standard room sizes, ceiling heights and good thermal insulation, a known ratio of room area to required heat output can be applied. In this case, 10 m² will need to generate 1 kW of heat. To the result obtained, you need to apply a correction factor depending on the climatic zone.
Let's assume that the house is located in the Moscow region. Its total area is 150 m². In this case, the hourly heat load for heating will be equal to:
15 * 1 = 15 kW / hour
The main disadvantage of this method is its large error. The calculation does not take into account changes in weather factors, as well as building features - heat transfer resistance of walls, windows. Therefore, it is not recommended to use it in practice.
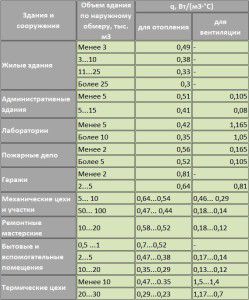
Aggregated calculation of the thermal load of a building
The enlarged calculation of the heating load is characterized by more accurate results. Initially, it was used to preliminary calculate this parameter when it was impossible to determine the exact characteristics of the building. The general formula for determining the heat load for heating is presented below:
Where q ° - specific thermal characteristics of the structure. The values must be taken from the corresponding table,but - the correction factor mentioned above,Vн - the outer volume of the building, m³,TVn and Tnro - temperature values inside the house and outside.
Suppose you want to calculate the maximum hourly heating load in a house with a volume of 480 m³ along the outer walls (area 160 m², two-storey house). In this case, the thermal characteristic will be equal to 0.49 W / m³ * C. Correction factor a = 1 (for the Moscow region). The optimum temperature inside the dwelling (Tvn) should be + 22 ° C. The temperature outside will be -15 ° C. Let's use the formula to calculate the hourly heating load:
Q = 0.49 * 1 * 480 (22 + 15) = 9.408 kW
Compared to the previous calculation, the resulting value is less. However, it takes into account important factors - the temperature inside the room, outside, the total volume of the building. Similar calculations can be done for each room. The method of calculating the heating load according to the enlarged indicators makes it possible to determine the optimal power for each radiator in a separate room. For a more accurate calculation, you need to know the average temperature values for a particular region.
This calculation method can be used to calculate the hourly heat load for heating. However, the results obtained will not give an optimally accurate value of the building's heat loss.
Accurate heat load calculations
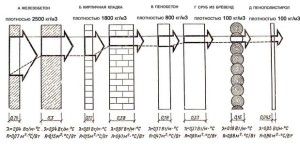
But still, this calculation of the optimal heat load for heating does not give the required calculation accuracy. It does not take into account the most important parameter - the characteristics of the building. The main one is the resistance to heat transfer, the material for the manufacture of individual elements of the house - walls, windows, ceiling and floor. It is they who determine the degree of conservation of thermal energy received from the heat carrier of the heating system.
What is heat transfer resistance (R)? This is the reciprocal of the thermal conductivity (λ) - the ability of the material structure to transfer thermal energy. Those. the higher the value of thermal conductivity, the higher the heat loss. To calculate the annual heating load, you cannot use this value, since it does not take into account the thickness of the material (d). Therefore, experts use the parameter heat transfer resistance, which is calculated using the following formula:
R = d / λ
Calculation for walls and windows
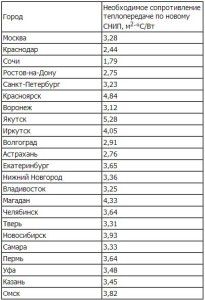
There are normalized values of the heat transfer resistance of walls, which directly depend on the region where the house is located.
In contrast to the aggregated heating load calculation, you first need to calculate the heat transfer resistance for the outer walls, windows, ground floor and attic floor. Let's take the following characteristics of the house as a basis:
- Wall area - 280 m²... It includes windows - 40 m²;
- Wall material - solid brick (λ = 0.56). External wall thickness - 0.36 m... Based on this, we calculate the resistance of the TV transmission - R = 0.36 / 0.56 = 0.64 m2 * С / W;
- To improve the thermal insulation properties, an external insulation was installed - expanded polystyrene with a thickness 100 mm... For him λ = 0.036... Respectively R = 0.1 / 0.036 = 2.72 m2 * C / W;
- Total value R for external walls is 0,64+2,72= 3,36 which is a very good indicator of the thermal insulation of a house;
- Heat transfer resistance of windows - 0.75 m² * С / W (double glazing with argon filling).
In fact, heat losses through the walls will be:
(1 / 3.36) * 240 + (1 / 0.75) * 40 = 124 W at a temperature difference of 1 ° C
We take the temperature indicators the same as for the aggregated calculation of the heating load + 22 ° С indoors and -15 ° С outdoors. Further calculation must be done according to the following formula:
124 * (22 + 15) = 4.96 kWh
Ventilation calculation
Then it is necessary to calculate the ventilation losses. The total air volume in the building is 480 m³. Moreover, its density is approximately equal to 1.24 kg / m³. Those. its mass is 595 kg. On average, the air is renewed five times per day (24 hours). In this case, to calculate the maximum hourly load for heating, you need to calculate the heat losses for ventilation:
(480 * 40 * 5) / 24 = 4000 kJ or 1.11 kW / hour
Summing up all the indicators obtained, you can find the total heat loss of the house:
4.96 + 1.11 = 6.07 kWh
In this way, the exact maximum heating load is determined. The resulting value directly depends on the temperature outside. Therefore, to calculate the annual load on the heating system, it is necessary to take into account changes in weather conditions. If the average temperature during the heating season is -7 ° C, then the total heating load will be equal to:
(124 * (22 + 7) + ((480 * (22 + 7) * 5) / 24)) / 3600) * 24 * 150 (days of the heating season) = 15843 kW
By changing the temperature values, you can make an accurate calculation of the heat load for any heating system.
To the results obtained, you need to add the value of heat losses through the roof and floor. This can be done with a correction factor of 1.2 - 6.07 * 1.2 = 7.3 kWh.
The resulting value indicates the actual costs of the energy carrier during the operation of the system. There are several ways to regulate the heating load. The most effective of these is to reduce the temperature in rooms where there is no constant presence of residents. This can be done using thermostats and installed temperature sensors. At the same time, a two-pipe heating system must be installed in the building.
To calculate the exact value of heat loss, you can use the specialized Valtec software. The video material shows an example of working with it.









Dear Olga! Thank you very much for the video and comments. But, if possible, a few clarifications: In the example of calculating the infiltration coefficient for Omsk, figure 273 appears, which is the duration of the heating period or something else. And one more thing: this site provides a formula for the aggregated calculation of the heat load, which is different from yours, as well as a table of specific thermal characteristics of buildings (residential) that does not correspond to the Methodology, and a table of correction factors for climatic zones of the Russian Federation. If possible, please provide information on the legal basis of these tables and whether they can be used officially. I will look forward to it.
Best regards, Anatoly
Dear Olga! Sorry to address you again. According to your formulas, I get an incredible heat load:
Cyrus = 0.01 * (2 * 9.8 * 21.6 * (1-0.83) +12.25) = 0.84
Qot = 1.626 * 25600 * 0.37 * ((22 - (- 6)) * 1.84 * 0.000001 = 0.793 Gcal / hour
According to the enlarged formula given above, only 0.149 Gcal / hour is obtained. Can't figure out what's the matter? Explain, please! Excuse for troubling. Anatoly.
Perhaps in the first two comments I went to the wrong address. I contacted the author of the video. If you made a mistake, please excuse me. I am making the same request to the site ihousetop.decorexpro.com/en/. I would like to ask you to inform the legal source of tables of specific thermal characteristics of buildings and coefficients for climatic zones. I need this in order to present it to a heat supply organization that unreasonably and repeatedly overestimates the parameters for supplying heat for heating, and, accordingly, payment for it. Your calculations are very convincing, and I want to use them.
Best regards, Anatoly, pensioner.