With the onset of cold weather, it often turns out that the efficiency of the heating equipment in the room is insufficient. The reason is worn out radiators that should be replaced. In some cases, a discrepancy between the number of devices and the area of the room is revealed. At the same time, it is impractical to completely change serviceable batteries, you can simply add sections.
Nuances of connecting radiators

In some situations, in order to increase the efficiency of heating the premises, it is necessary to connect the heating radiators to each other. The link can be done in three ways:
- Series connection - one pipe is involved. The heating devices do not heat up evenly.
- Parallel connection involves the use of two pipes. The bimetallic radiators are connected to each other through the upper and lower taps.
- When connected through, the coolant passes through the heater system without lingering in the batteries.
The most reliable and economical way to connect two heating batteries to each other is considered to be consistent, the easiest to implement - through and through.
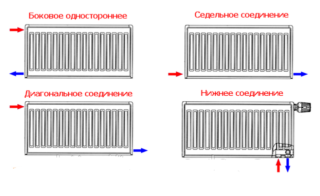
Ways to connect pipes and radiators
To maintain a comfortable temperature in a living room during the cold season, it is necessary to select and connect heating devices correctly. There is a wide selection on the market: bimetallic, aluminum, cast iron. All of them have various shapes and sizes, differ in the level of heat transfer and the type of connection.
- Side type, or one-way connection. The peculiarity of this system is that heat is supplied from the same side of the radiator from which the return line is located. This method is used in multi-storey buildings with vertical supply of a heating fluid.
- The diagonal circuit is characterized by minimal heat loss. With this type, the supply pipe is located on one side, water, having passed through all sections of the device, comes out from the other side. With this option, the coolant can enter the upper hole and exit through the lower one, or vice versa, enter the lower hole and exit through the upper one. This scheme is used in one- or two-pipe systems. It is effective when using long batteries (more than 12 sections).
- The lower one is used when it is necessary to hide pipes in the walls or mount them in the floor. With this scheme, a high heat loss occurs, which is compensated by the choice of a more powerful radiator. It is not recommended to connect batteries in the bottom way with natural circulation of the coolant
The choice of the type of connection should be approached responsibly, because improper operation will result in significant heat loss. Violation of the technology for connecting the sections can lead to uneven heating of the battery and even to the formation of leaks. Therefore, it is important to select suitable heating devices and connect them correctly.
Efficient operation of the heating system will save money on fuel costs.
Types of radiators for strapping

The type of radiators for strapping a dwelling should be thought out even at the construction stage so that the building is prepared in advance for the installation of the entire heating system. Heating appliances differ in several ways.
By the material used in their manufacture:
- Cast iron was at the peak of popularity in Soviet times and is still often found in apartments. The advantages of this type of devices include a long service life and undemandingness to the coolant - you can use any liquid in them without thinking about its quality. Among the shortcomings, it is worth noting the appearance - such batteries are difficult to fit into the modern design of the room. In addition, the cast iron radiator has a very low thermal conductivity, which significantly increases fuel costs.
- Aluminum have a variety of designs and high thermal conductivity. The only drawback is that the aluminum radiator is very sensitive to water quality. It should be well filtered before use.
- Steel can be panel and tubular. The first option belongs to the budget category, but has a high heat transfer. Such radiators are unpretentious, therefore they are widely used in residential and office premises. The second option belongs to the "premium" category. Such devices have a long service life, high thermal conductivity and an attractive appearance.
- Bimetallic ones have a long service life and a high level of heat transfer. The only drawback is that bimetal is expensive.
- Copper ones are the most resistant, they hardly wear out during operation. The design features allow the use of water and antifreeze as a heat carrier. Such batteries dissipate heat, increasing heating efficiency. The disadvantage is the very high price.
- Plastic - a budget option for those who want to save money. They are lightweight, easy to install, fairly wear-resistant and inexpensive. Disadvantage - the coolant should not heat up more than 80 degrees.
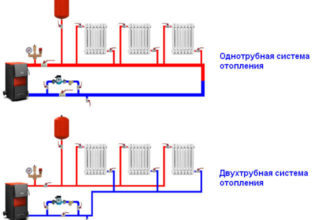
When connecting radiators to the heating system, two connection schemes are used. When choosing an unsuitable method, heat loss can reach 50%.
- The one-pipe system allows the use of a minimum number of pipes. A serious drawback is that devices connected in series do not warm up evenly. Those located closer to the boiler heat up more, while those located far from it can remain cold. This effect is observed on the first floors of multi-storey buildings, where the coolant moves from top to bottom.
- Two-pipe wiring diagram. It uses two pipes. One is the supply of the coolant, hot water from the boiler flows through it, the second is the return, the cooled coolant returns to the heating tank. With this scheme, the batteries are warmed up evenly, which reduces heat loss.
Installation of batteries has its own characteristics due to their type and wall material. For heavy cast iron radiators, you should choose massive holders made of thicker metal. For lightweight aluminum, bimetallic or steel, thinner brackets are used.
There are also corner radiators. They are mounted in the corner of the room and can have different designs and designs.
Required tools and materials for installation

Installation of radiators is not a difficult process with certain skills and a set of tools. To install devices and connect them to the heating system, you will need:
- Torque wrench. It allows you to adjust the torque of the thread on metal or plastic pipes.
- Building level. With its help, brackets are installed on the walls.
- Rotary hammer and drills for drilling holes for fasteners.
- Hammer for driving brackets into the wall.
- The radiator valve is needed for the installation of shut-off valves for heating devices.
- Fum tape for sealing threaded connections.
- Special scissors for cutting polypropylene pipes and a soldering iron for soldering them with elbows, couplings, tees, etc.
When installing heating radiators, it is necessary to observe the accuracy and tightness of all connections. Violation of the technology for installing heating devices can lead to leaks.
The principle of performing strapping with polypropylene pipes
Plastic pipes are popular due to their low price and ease of installation. Polypropylene does not rust and is therefore durable. The boiler is piped with such pipes by hot welding using a special soldering iron.
Antifreeze does not combine well with polypropylene, therefore, water is used as a coolant with such a strapping.
When choosing a piping made of plastic, the most important point is to take into account all the features of a particular building. The installation process itself is not difficult, even a beginner can handle it. The preparation of the project should be carried out by experienced professionals, since the slightest mistakes and shortcomings can lead, at best, to heat loss and an increase in fuel costs, at worst to serious accidents.








