Climatic conditions in most of Russia require a reliable and efficient heating system for comfortable living in a house or apartment. Despite the variety of alternative ways to heat a room, for example, using a warm baseboard or infrared heaters, traditional heating radiators that are installed under windows remain the most popular. In order for heat transfer to meet the needs of consumers and provide a normal temperature in winter, it is necessary to calculate the number of heating radiator sections, taking into account a number of specific criteria, including the area of the room and heat loss.
Calculation recommendations and basic requirements

You should not buy radiators with a large margin or at random. If they are not powerful enough, it will not be possible to maintain a comfortable temperature in the room in winter, too powerful will lead to high heating costs.
Main things to consider:
- area and height of the room;
- the material from which the radiator is made;
- maximum number of sections;
- heat transfer of one section.
One section of a cast-iron radiator provides a heat transfer of 160 W, if this is not enough, the amount can be increased. They are durable, do not corrode, keep warm. However, they are fragile, do not withstand sharp point impacts.
The heat dissipation of aluminum radiators is about 200 watts, they can withstand temperatures of about 100 ° C and pressures from 6 to 16 atm, but are susceptible to oxygen corrosion. This problem is solved by anodized oxidation.
The bimetallic ones are made of steel on the inside, and aluminum on the top, due to which they combine the positive properties of both metals: high wear resistance and heat transfer.
Steel - the most affordable, lightweight and quite attractive in design. However, they quickly cool down, rust and cannot withstand water hammer.
Summary data for different types of radiators are presented in the table:
| Cast iron | Steel (panel) | Aluminum | Anodized aluminum | Bimetal | |
| Power of one section at coolant temperature - 70 and height - 50 cm, W | 160 | 120 | 175-200 | 216,3 | 200 |
| Maximum coolant temperature, ° C | 130 | 110-120 | 110 | 110 | 110-130 |
| Pressure, atm | 9 | 8-12 | 6-16 | 6-16 | 16-35 |
When choosing a radiator, be sure to take into account what material it is made of. This parameter has a significant impact on the calculations. In addition, you need to pay attention to the minimum heat transfer rates, since maximum heat transfer is possible only at the maximum temperature of the coolant, and this happens extremely rarely.
How to calculate the number of heating radiator sections
The basic value for calculating the required power of radiators is the area of the room or its volume. But simple formulas are used to calculate when the room has no peculiarities. In other cases, the formula becomes much more complicated.
Per square meter
If the room has a standard ceiling height of 2.7 m, and also does not differ in architectural features - a large glazing area, high ceilings, - you can use a simple formula that takes into account only the area:
Q = S × 100.
S in this formula - the area of the room, which is usually known in advance from documents. If there is no such data, it is easy to calculate it by multiplying the length of the room by the width. 100 - the number of watts required to heat 1 m2 of the room. Q - heat transfer - the value obtained as a result of multiplication.
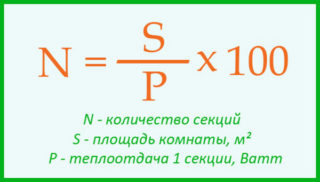
The power of the non-separable radiator is indicated in the documents. You should choose a device whose power is slightly higher than the calculated one. This formula is suitable if the radiator power is calculated for a room in a multi-storey building with a ceiling height of 2.65. Let the area of this room be 20 m2, then the battery power is 20 × 100 or 2000 W. If the room has a balcony, the value is increased by another 20%.
If you want to know how many battery sections are needed per square meter, the resulting value is divided by the power of one section and the required number of sections is obtained for efficient heating of a particular room. Using the already calculated value to determine the number of sections of the cast-iron radiator, you get 2000/160 = 12.5 sections. The number is usually rounded up, which means that a 13-section cast-iron radiator is needed.
In rooms where heat loss is not great, it is permissible to round down. In the kitchen, for example, there is a stove, which will be an additional means of heating.
The table shows ready-made values for standard rooms of various sizes:
| Area, m2 | 5-6 | 7-9 | 10-12 | 12-14 | 15-17 | 18-19 | 20-23 | 24-27 |
| Power, W | 500 | 750 | 1000 | 1250 | 1500 | 1750 | 2000 | 2500 |
By volume
If the ceilings are significantly higher than 2.7 m, for example 3.5 m, a formula should be used in the calculations that takes this indicator into account in addition to the area of the room. It is determined that 34 W is required for heating 1 m3 in a panel house, and 41 W in a brick house, so the formula takes the following form:
Q = S × h × 41 (34)
Instead h substitute the height of the ceilings in meters, instead of S - area, similar to the previous formula. Q - the required power of the heating radiator. Suppose you need to perform a calculation for a room of 20 m2 with a ceiling height of 3.5 m in a panel house. We get: 20 × 3.5 × 34 = 2380 W. We divide the power of 160 W to calculate the number of heating radiator sections: 2380/160 = 14.875. Requires 15 cell battery.
Non-standard room

More complex calculations, taking into account secondary parameters, are necessary if the walls of the room are in contact with the street, the windows face the north side, or the walls are not well insulated. Also, many other parameters are taken into account by a formula of the form:
Q = S × 100 × A × B × C × D × E × F × G × H × I × J
The basis remains the same, it is S × 100... Other components of the formula are increasing and decreasing correction factors, depending on a number of features of the room.
BUT allows you to take into account heat loss in the presence of street walls:
- if there is only one outer wall (this is a wall with a window) - k = 1;
- two outer walls (corner room) - k = 1.2;
- three walls contact the street - k = 1.3;
- four walls - k = 1.4.
B used to calculate thermal energy, depending on which side of the world the windows of the room face. When the window opening is located on the north side, the sun does not look into the windows at all, the east room receives less solar energy, because the rays at sunrise are not yet active enough. In these cases k = 1.1... For western and southern rooms, this coefficient is not taken into account or it is considered equal to one.
FROM takes into account the ability of walls to retain heat. Walls of two bricks with a surface insulation are taken as a unit, which can be, for example, polystyrene plates. For walls, the thermal insulation properties of which, according to the calculations above, are used k = 0.85, for walls without insulation k = 1.27.
D allows you to calculate the power of the radiator taking into account the climate. The average temperature of the coldest decade of January is taken into account when calculating:
- the temperature drops below -35 ° C, k = 1.5;
- ranges from -35 ° C to -25 ° C - k = 1.3;
- if it drops to -20 ° C and not lower - k = 1.1;
- not colder than -15 ° C - k = 0.9;
- not lower than -10 ° C - k = 0.7.
E Is the height of the ceilings. For rooms with ceiling heights up to 2.7 m k = 1, i.e. it does not affect the result at all.Other values are presented in the table:
| Ceiling height, m | 2,8-3 | 3,1-3,5 | 3,6-4 | >4,1 |
| k (E) | 1,05 | 1,1 | 1,15 | 1,2 |
F - a coefficient that allows you to take into account the type of room located on top in the calculations:
- unheated attic or any other room without heating - k = 1;
- insulated attic or roof - k = 0.9;
- room with heating - k = 0.8.
G changes the total value according to the type of glazing:
- standard wooden double frames - k = 1.27;
- standard glass unit - k = 1;
- double glazing - k = 0.85.
H - takes into account the glazing area. If the windows are large, more sun penetrates through them, it heats objects and the air in the room more intensely. You must first divide S windows on S rooms. The resulting value should be evaluated according to the table:
| S-windows / S-rooms | <0,1 | 0,11-0,2 | 0,21-0,3 | 0,41-0,5 |
| k (H) | 0,8 | 0,9 | 1 | 1,2 |
I determined according to the radiator connection diagram.
Diagonal connection:
- the inlet of the hot coolant from above, the outlet of the cooled coolant from the bottom - k-1;
- entrance from below and exit from above - k = 1.25.
One side:
- hot coolant from above, cooled down - from below - k = 1.03;
- hot - from below, cooled - from above - k = 1.28;
- hot and cold from below - k = 1.28.
On two sides: hot and cooled coolant from below - 1,1.
J - must be used if the radiator is partially or completely hidden by a window sill or screen:
- completely open - k = 0.9;
- a window sill on top - k = 1;
- in a concrete or brick niche - k = 1.07;
- there is a window sill on top, and on the front of the screen - k = 1.12;
- covered by a screen on all sides - k = 1.2.
It remains to substitute all the numbers in the formula and calculate the result.
Suppose you want to calculate the radiator power for a room:
- on the second floor of a two-storey building with an insulated attic on top;
- an area of 23 m2;
- glazing area 11.2 m2;
- with double glazing;
- with completely open mounting of the radiator;
- with two outer walls;
- with windows facing east;
- with a ceiling height of 3.5 m;
- with walls of two bricks without insulation;
- with one-sided bottom connection for radiators;
- the average temperature of the coldest decade of January is from -25 ° C to -35 ° C.
Substituting values into a formula 23 x 100 x 1.2 x 1.1 x 1.27 x 1.3 x 1.1 x 0.9 x 0.85 x 1.2 x 1.28 x 0.9 = 5830.91 W. Let's calculate the number of sections 5831/160=36,44... It is better to divide this number into two or three batteries, making sure to place at least one on the outer wall, even if there is no window.
How to take effective power into account
Effective and rated power are not the same thing. Even if the calculations are correct, the heat dissipation may be lower. This is due to the weak temperature difference. The assigned power declared by the manufacturer is usually indicated for a temperature head of 60 ° C, but in reality it is often 30-50 ° C. This is due to the low temperature of the coolant in the circuit. To determine the effective power of the battery, it is necessary to multiply its heat transfer by the temperature difference in the system, and then divide by the nameplate value.
The temperature head is determined by the formula T = 1/2 × (Tn + Tk) -Tvnwhere
- Tn - temperature of the coolant at the supply;
- TC - temperature of the coolant at the outlet;
- Tvn - temperature in the room.
Manufacturer for Tn accepts 90 ° C; per TC - 70 ° C, for Tvn - 20 ° C. Actual values may differ greatly from the original ones. In case of extremely low temperatures, it is necessary to add 10-15% of the power.
It is recommended to provide for the possibility of manual or automatic adjustment of the coolant supply to each radiator. This will allow you to regulate the temperature in all rooms without wasting excess heat energy.
Calculation correction methods
The resulting value of the required battery power can and should be adjusted up or down, since heat loss can increase due to the presence of a balcony, natural ventilation, a basement below and compensated for by the installed underfloor heating system, warm baseboard, stove or heated towel rail.
Exact calculation method
A fairly accurate calculation method, taking into account most of the significant parameters, is made according to the formula presented above. However, you can calculate the power of the radiator even more accurately using a specialized calculator. It is enough to substitute the known values.
Approximate calculation

With approximate calculations, the heat loss will be:
- through the heating system and natural ventilation - 20-25%;
- through the ceiling adjacent to the roof - 25-30%;
- through walls - 10-15%;
- through abutments - 10-15%;
- through the basement - 10-15%;
- through windows - 10-15%.
Autonomous heating operating in cottages and private houses is more efficient than centralized heating.
The efficiency of the system also depends on its features. A two-pipe system is more efficient than a one-pipe one, since in the latter, each subsequent radiator receives more and more cooled coolant. For example, if there are six batteries in the system, the estimated number of sections for the last one will need to be increased by 20%.
Exact calculations, taking into account the requirements of SNiP, are performed by professionals. Simplified calculation options can be performed independently and this is quite enough to determine the required power of heating batteries in a cottage or a separate apartment. It is only important to carefully check all the data in order to avoid mistakes.








