The choice of thermal insulation materials on the modern market is huge. Manufacturers produce models of various structures, density, sound insulation characteristics and moisture resistance. Consumers need to know the thermal conductivity of heaters and the selection criteria. A detailed comparison of all types will help you find the ideal material for building.
- Thermal conductivity concept
- Factors influencing thermal conductivity
- Characteristics of different materials
- Styrofoam
- Extruded polystyrene foam
- Mineral wool
- Basalt wool
- Glass wool
- Foamed polyethylene
- Sprayed thermal insulation
- Table of thermal conductivity coefficients of different materials
- Other criteria for the selection of heaters
- Volume weight
- Ability to keep in shape
- Vapor permeability
- Flammability
- Soundproofing
- Practical application of the thermal conductivity coefficient
Thermal conductivity concept

Thermal conductivity is understood as the transfer of heat energy from object to object until the moment of thermal equilibrium, i.e. equalization of temperature. In relation to a private house, the speed of the process is important - the longer the alignment takes place, the less the structure cools.
In numerical form, the phenomenon is expressed through the coefficient of thermal conductivity. The indicator clearly expresses the passage of the amount of heat for a certain time through a unit of surface. The larger the value, the faster the heat energy flows away.
The heat transfer of various materials is indicated in the manufacturer's specifications on the packaging.
Factors influencing thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity depends on the density and thickness of the insulating material, so it is important to take it into account when purchasing. Density is the mass per cubic meter of materials that are classified as very light, light, medium and hard by this criterion. Lightweight porous products are used to cover internal walls, load-bearing partitions, dense ones - for external work.
Modifications with lower density are lighter in weight, but have better thermal conductivity parameters. Comparison of heaters by density is presented in the table.
| Material | Density indicator, kg / m3 |
| Minvata | 50-200 |
| Extruded polystyrene foam | 33-150 |
| Polyurethane foam | 30-80 |
| Polyurethane mastic | 1400 |
| Roofing material | 600 |
| Polyethylene | 1500 |
The higher the density, the lower the vapor barrier.
The thickness of the material also affects the degree of heat transfer. If it is excessive, the natural ventilation of the premises is disturbed. The small thickness causes cold bridges and condensation on the surface. As a result, the wall will be covered with mold and mildew. You can compare the parameters of the thickness of the materials in the table.
| Material | Thickness, mm |
| Penoplex | 20 |
| Minvata | 38 |
| Aerated concrete | 270 |
| Brick masonry | 370 |
When choosing the thickness, it is worth considering the climate of the area, the building material.
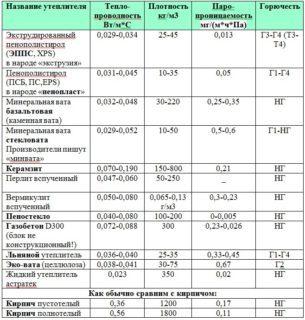
Characteristics of different materials
Before considering the thermal conductivity table of heaters, it makes sense to read a brief overview. The information will help developers understand the specifics of the material and its purpose.
Styrofoam

Board material made by foaming polystyrene. Differs in ease of cutting and installation, low thermal conductivity - in comparison with other insulators, foam is lighter. The advantages of the product are inexpensive cost, resistance to humid environment. The disadvantages of polystyrene are fragility, quick flammability.For this reason, slabs with a thickness of 20-150 mm are used for thermal insulation of light external structures - facades for plastering, walls of plinths and basements.
When the foam burns, toxic substances are released.
Extruded polystyrene foam
Extruded polystyrene foam is resistant to humid environments. The material is easy to cut, does not burn, and is easy to lay and transport. In addition to low thermal conductivity, plates have high density and compressive strength. Extruded polystyrene foam of the Technoplex and Penoplex brands is popular among Russian developers. It is used for thermal insulation of the blind area and strip foundation.
Mineral wool

The thermal conductivity coefficient of mineral wool is 0.048 W / (m * C), which is more than foam. The material is made on the basis of rocks, slag or dolomite in the form of plates and rolls, which have a different stiffness index. For insulation of vertical surfaces, it is allowed to use rigid and semi-rigid products. It is better to insulate horizontal structures with light mineslabs.
Despite the optimal thermal conductivity index, mineral wool has little resistance to humid environments. Plates are not suitable for warming basements, steam rooms, dressing rooms.
The use of mineral wool with low thermal conductivity is allowed only in the presence of a vapor barrier and waterproofing layers.
Basalt wool
The basis for the insulation is a basalt type of rock, which swells when heated to a state of fibers. Non-toxic binders are also added during manufacture. On the Russian market, the products of the Rockwool brand, by the example of which you can consider the features of the insulation:
- does not ignite;
- it has a good indicator of heat and sound insulation;
- lack of caking and compaction during operation;
- environmentally friendly building material.
Thermal conductivity parameters allow the use of stone wool for indoor and outdoor use.
Glass wool

Glass wool insulation is made from borax, limestone, soda, sieved dolomite and sand. To save on production, cullet is used, which does not violate the properties of the material. The advantages of glass wool include high levels of heat and sound insulation, environmental friendliness and low cost. There are more cons:
- Hygroscopicity - absorbs water, as a result of which it loses its insulating characteristics. To prevent rotting and destruction of the structure, they are laid between the vapor barrier layers.
- Inconvenience of installation - fibers with increased fragility disintegrate, can cause burning and itching of the skin.
- Short-term operation - after 10 years shrinkage occurs.
- The impossibility of using for warming wet rooms.
When working with glass wool, you need to protect the skin of your hands with gloves, your face with glasses or a mask.
Foamed polyethylene

Roll polyethylene with a porous structure has an additional reflective foil layer. Advantages of Isolone and Penofol:
- small thickness - from 2 to 10 mm, which is 10 times less than conventional insulators;
- the ability to save up to 97% of useful heat;
- resistance to moisture;
- minimum thermal conductivity due to pores;
- ecological cleanliness;
- reflective effect, due to which heat energy is accumulated.
Rolled insulation is suitable for installation in wet rooms, on balconies and loggias.
Sprayed thermal insulation

If you refer to the table, you can see that the sprayed types replace 10 cm of mineral wool. They are produced in cylinders, resemble polyurethane foam and are applied using a special tool.The sprayed insulation can be of different hardness, the container also contains foaming agents - polyisocyanate and polyol. By the type of the main component, insulation is:
- PPU. Open-cell polyurethane foam is durable, heat-efficient. In the presence of closed voids in the composition, steam can pass.
- Penoizolnaya. Liquid foam based on urea-formaldehyde is characterized by vapor permeability and fire resistance. Applied by pouring. The optimum hardening temperature is from +15 degrees.
- Liquid ceramics. Ceramic components are melted to a liquid state, then mixed with polymeric substances and pigments. Evacuated cavities are obtained. External insulation protects the building for 10 years, internal insulation for 25 years.
- Ecowool. Cellulose is crushed to a state of dust, becomes sticky when water gets in. The material is suitable for working on damp wall surfaces, but is not used near chimneys, chimneys and stoves.
Sprayed insulation is distinguished by good adhesion to surfaces for which wood, brick or aerated concrete were used.
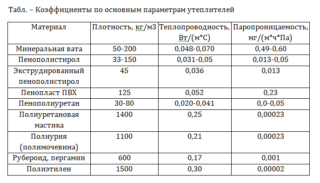
Table of thermal conductivity coefficients of different materials
Based on the table with the thermal conductivity coefficients of building materials and popular heaters, a comparative analysis can be made. It will ensure the selection of the optimal thermal insulation option for the building.
| Material | Thermal conductivity, W / m * K | Thickness, mm | Density, kg / m³ | Laying temperature, ° C | Water vapor permeability, mg / m2 * h * Pa |
| Polyurethane foam | 0,025 | 30 | 40-60 | -100 to +150 | 0,04-0,05 |
| Extruded polystyrene foam | 0,03 | 36 | 40-50 | -50 to +75 | 0,015 |
| Styrofoam | 0,05 | 60 | 40-125 | -50 to +75 | 0,23 |
| Minvata (slabs) | 0,047 | 56 | 35-150 | -60 to +180 | 0,53 |
| Fiberglass (slabs) | 0,056 | 67 | 15-100 | +60 to +480 | 0,053 |
| Basalt wool (slabs) | 0,037 | 80 | 30-190 | -190 to +700 | 0,3 |
| Reinforced concrete | 2,04 | 2500 | 0,03 | ||
| Hollow brick | 0,058 | 50 | 1400 | 0,16 | |
| Wooden beams with a cross cut | 0,18 | 15 | 40-50 | 0,06 |
For the thickness parameters, an averaged indicator was used.
Other criteria for the selection of heaters
The thermal insulation coating provides a 30-40% reduction in heat loss, increases the strength of supporting structures made of brick and metal, reduces noise levels and does not take up the useful building area. When choosing a heater, in addition to thermal conductivity, other criteria must be taken into account.
Volume weight

This characteristic is related to thermal conductivity and depends on the type of material:
- Mineral wool products have a density of 30-200 kg / m3, therefore they are suitable for all surfaces of the building.
- Foamed polyethylene has a thickness of 8-10 mm. The density without foil is 25 kg / m3 with a reflective base - about 55 kg / m3.
- Foam plastic differs in specific gravity from 80 to 160 kg / m3, and extruded polystyrene foam - from 28 to 35 kg / m3. The latter material is one of the lightest.
- Semi-liquid sprayed foam insulation with a density of 10 kg / m3 requires preliminary plastering of the surface.
- Foam glass has a density associated with its structure. The foamed version is characterized by a volumetric weight of 200 to 400 kg / m3. Cellular glass heat insulator - from 100 to 200 m3, which makes it possible to use it on facade surfaces.
The lower the volumetric weight, the less material is consumed.
Ability to keep in shape

Manufacturers do not indicate dimensional stability on the packaging, but you can focus on Poisson's and friction ratios, bending and compressive strengths. The stability of the shape is judged on the crease or change in the parameters of the heat-insulating layer. In the event of deformation, there is a risk of 40% heat leakage through cracks and cold bridges.
The form stability of building materials depends on the type of insulation:
- Cotton wool (mineral, basalt, eco) when laid between the rafters is straightened. Deformation is eliminated due to rigid fibers.
- Foam species keep their shape at the level of hard stone wool.
The ability of a product to keep its shape is also determined by its elastic characteristics.
Vapor permeability
According to the degree of vapor permeability, two types of insulation are distinguished:
- Foams are products for the production of which the foaming technology is used. The product does not allow condensate to pass through at all
- Cotton wool - thermal insulation based on mineral or organic fibers. Materials can leak condensation.
When installing vapor-permeable wool, a film vapor barrier is additionally laid.
Flammability
- NG - non-combustible: stone and basalt wool.
- G - flammable. Materials of category G1 (polyurethane foam) are distinguished by low flammability, category G4 (expanded polystyrene, including extruded) - highly combustible.
- B - flammable: chipboard plates, roofing felt.
- D - smoke generating (PVC).
- T - toxic (the minimum level is for paper).
The best option for private construction is self-extinguishing materials.
Soundproofing
Characteristic related to vapor permeability and density. Cotton wool excludes the penetration of extraneous noise in the room, more noise penetrates through the foam.
Dense materials have better sound insulation properties, but installation is complicated by thickness and weight. The best option for independent thermal insulation work would be stone wool with high sound absorption. Similar indicators are for light glass wool or basalt insulation with twisted long thin fibers.
The normal indicator of sound insulation is density from 50 kg / m3.
Practical application of the thermal conductivity coefficient
After a theoretical comparison of materials, it is necessary to take into account their division into heat-insulating and structural groups. Structural raw materials have the highest heat transfer indices, so they are suitable for the construction of floors, fences or walls.
Without the use of raw materials with the properties of insulation, you will need to lay a thick layer of thermal insulation. Referring to the thermal conductivity table, one can determine that low heat transfer of reinforced concrete structures will be only with their thickness of 6 m.The finished house will be cumbersome, it can sink under the soil, and the construction costs will not pay off even after 50 years.
The sufficient thickness of the heat-insulating layer is 50 cm.
The use of thermal insulation materials reduces construction costs and reduces overpayments for energy in winter. When buying a heater, you need to take into account the thermal conductivity parameters, the main characteristics, the cost and convenience of self-assembly.