Air heating in residential buildings is a prerequisite for comfort. It is important to know how the heating scheme of a two-story house with forced circulation of a coolant is arranged already at the design stage. This will help save money and supervise the construction crew. The builder's little skills will allow you to implement the heating system yourself.
Construction principles
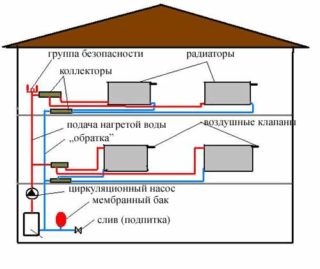
Heating schemes in two-story houses are based on common structural elements.
The composition must include:
- boiler-heat generator: electric, gas, solid or liquid fuel;
- heat exchangers-radiators;
- piping system from the boiler to the batteries;
- automation and protection scheme;
- expansion tank;
- coolant;
- adjusting equipment.
In modern gas and electric heaters, automation and an expansion tank are built into the structure. For solid-state heaters, a protective strapping is made.
Structural elements
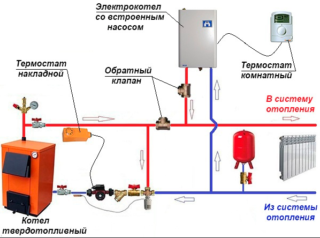
There are boilers on sale that can operate on two types of fuel - electric tubular heaters (TENs) are built into the circuits of a gas or wood heater in this case.
Automatic heaters allow restarting heating after shutdown without user intervention or in manual mode. Protection circuits promptly turn off the supply of energy in emergency operating modes (overheating of the coolant, overpressure in the system). Such devices are required in gas boilers. When disconnected, the valve closes and when the supply is resumed, gas will not enter the premises.
Pipelines are made of steel, copper, metal-plastic or polypropylene products. The latter option is preferable in terms of money costs, it saves installation time. For welding, inexpensive soldering irons are used, costing from 800 rubles. Fittings, adapters from plastic to metal threads are affordable.
The expansion tank is an indispensable element of the heating system. When heated, the water expands and the surplus goes into the reserve tank.
If the inside of the device is in communication with air, the circuit is called open. If the expansion tank rubber diaphragm is not connected to air, the circuits will be closed.
There are no high requirements for the strength of heat exchangers in a private house. The maximum pressure in the pipes does not exceed 2 - 3 atm. Even purely aluminum radiators can withstand such pressure, which can collapse in centralized heating systems, where the pressure reaches 14-15 bar.
Choice of coolant

Water or special antifreeze is chosen as the coolant. The first option is less expensive. Filling of pipes and radiators takes place through the tap from the water supply. Water as a heat carrier is justified in settlements with a constant supply of energy carrier (gas, electricity). If interruptions are frequent and prolonged, they refuse water. In the event of a shutdown for a long time in cold weather, it will freeze. Ice will destroy pipelines, radiators.
Do not pour water into the heating system of summer cottages that are rarely visited. In addition to stopping the supply of energy carriers, the boiler may stop heating water for other reasons.If the heating is not restarted in time, accidents are inevitable.
In summer, the system must not be allowed to drain - this will lead to corrosion or oxidation of the inner surface of the heat exchangers.
Antifreeze is expensive, but does not freeze in the cold, the minimum temperature is indicated on the package. Even if the antifreeze is cooled more, it turns into a kind of loose snow, which will not lead to the destruction of the radiators and the boiler. The concentrates are diluted with water in proportions according to the manufacturer's instructions.
When filling the system with non-freezing liquids, special pressure pumps are used. This is a disadvantage - it is desirable to have the device for personal use. Call the master for refueling 200 - 300 gr. the evaporated or leaked liquid is materially costly.
The antifreeze recipe includes anti-corrosion additives, which will preserve the inner surface of pipes, radiators, boiler heat exchanger.
General working principle
The scheme of operation of any heating system consists in converting the energy of burnt gas, solid (liquid) fuel or electricity into heat. Heated water (antifreeze) enters the radiators through pipes, where it gives off heat to the space.
Gravity system
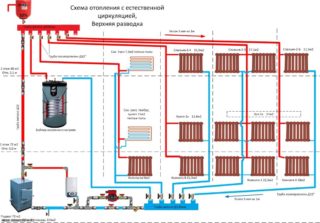
Functioning is based on the laws of physics. If the contours provide for the natural movement of water, then such a scheme is called gravitational.
It is extremely difficult to make a contour of a warm floor in gravitational systems without the use of additional pumps. A drop in pipes in the floor by several millimeters leads to airing and cessation of the movement of the coolant.
The density of a heated coolant is lower than that of a cold one. Due to the density difference, the water / antifreeze from the boiler rises up the supply riser (diameter 60 - 80 mm). An open or closed expansion tank is installed at the top of the entire system.
Along the perimeter of the premises of the second floor, the upper wiring contour is laid. A pipe with a diameter of 40-50 mm is mounted with a slope of 2-3 cm per meter of length. In places where radiators are installed, pipes with a diameter of 16 - 25 mm are welded into the wiring. Through them, the liquid flows into the radiators. Then the coolant enters the batteries on the ground floor.
At the level of the boiler or slightly lower along the perimeter of the building, a lower circuit (return) is laid, in which chilled water is collected.
It is possible to equip the gravity circuit without additional injection pumps when the height from the boiler to the upper distribution pipe is no more than 6-7 m. This is the height of a two-story house.
The circuit is used in places where the electricity needed to operate the pumps is often cut off. Gas boilers in this case are equipped with non-volatile safety devices.
The same scheme is needed for systems with solid fuel boilers. In the event of a power outage, the circulation stops and the wood / coal continues to heat the water. It is possible to stop the operation of a solid fuel boiler only by quickly removing the burning fuel, which is extremely problematic. Increased pressure arises, which can destroy pipes and radiators.
Operation of circuits with forced circulation

For the forced movement of the coolant, circulation pumps are used.
The pump is cut in at the junction of the "return" and the boiler - here the coolant is already cooled and the pump operates in a gentle mode. At the exit from the heater, the temperature of the coolant reaches 80 - 100 degrees, which sharply reduces the equipment resource. In boilers with a built-in pump, everything is connected according to the correct scheme.
The water movement pattern works according to the following algorithm:
- After power is applied, the pump turns on and sets the coolant in motion.
- The boiler heats up the water / antifreeze, and the pressure generated by the pump squeezes the coolant into the circuits.
- Hot water is supplied through pipes to radiators, where it cools, heats the air and enters the "return" pipes.
- The process goes into a cyclic state.
Different wiring schemes have been developed and are used in practice, which are optimal for different operating conditions.
According to the principle of supplying and collecting the coolant, two types of structures are distinguished: one- and two-pipe. In the first case, the system is similar to the gravitational one. Through the supply pipe, the hot coolant is supplied to the radiators. The second pipe collects the chilled water and returns it to the boiler. It is this option that is used when replacing old boilers without pumps with new automatic models. In this case, the piping diagram is not changed. The coolant is pumped through the riser to the second floor and then flows down.
Two-pipe schemes
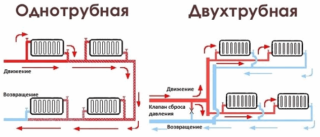
When arranging large buildings, it is the two-pipe scheme that is used. Radiators are connected in parallel. According to the location of the supply pipes, schemes with upper and lower wiring are distinguished.
Radiator connection diagrams for upper and lower wiring are indicated in the technical documentation. Incorrect connection will cause air build-up or low efficiency of the device.
Advantages of the two-pipe:
- does not require complex calculations and selection of pipe diameters;
- independent adjustment of the heat transfer of each radiator, which allows you to set the temperature in each room and save energy;
- easy setup and commissioning;
- the power of the pumps is low;
- there are no significant pressure losses at the beginning and end of the circuits;
- the temperature of the coolant is approximately the same in all radiators of the circuit;
- by shutting off the supply and drain taps, the battery can be removed for replacement or repair without turning off all the heating;
- minimum hydraulic resistance of pipelines.
The disadvantage is the increased consumption of pipes (for supply and return). Considering the cost of polypropylene pipes, ease of installation and repair, this disadvantage can be neglected.
Popular wiring diagrams for two-pipe heating systems: dead-end and Tichelman.
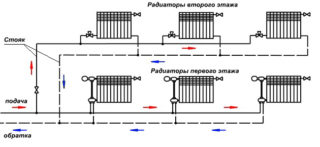
The dead-end scheme has a different name - with the oncoming movement of the coolant. The scheme is divided into sections. The heated coolant flows through the pipe from the boiler to the farthest battery, which returns to the boiler through the return pipe. The popularity is given by the simplicity of understanding, but a competent calculation and configuration of the system is required. The farther from the boiler, the thinner the pipes should be. After starting, each radiator is adjusted with shut-off valves. Incorrect adjustment can lead to this. That all the coolant will pass through one radiator, the rest will remain cold.
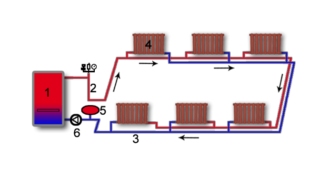
The Tichelman loop works with the passing movement of the coolant. Wiring is carried out with pipes of the same diameter. The pressure and temperature of the coolant in each of the radiators are the same, which simplifies balancing. Regulators can accurately set the temperature in each individual room.
Scheme requirements:
- Contour length up to 35 m.
- In extended areas, pipes of large diameters (40 - 60 mm) are used and thermostats are not installed, since they become useless.
- The perimeter over 30 m long is divided into several zones and the beam wiring is mounted. It is also called collector. The cost of more pipes is offset by their smaller diameter. A 16 mm pipe is enough to "feed" one radiator.
Each radiator in this version is easy to adjust for the desired heat transfer.
One-pipe schemes
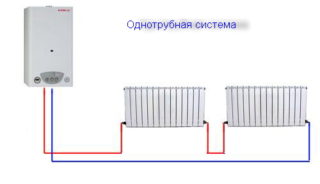
Single-pipe heating schemes are optimal for one- and two-storey buildings with up to 5 radiators in one circuit. A larger number will require fine tuning.Branches can reduce the pressure in the pipes and some radiators will not receive enough heat to heat the coolant.
The diagrams allow for top or bottom connection. In the second case, the pipeline can be hidden under the floor. It is taken into account that this will slightly reduce the heat transfer of the radiators, as part of the energy is spent on heating the screed.
One-pipe options are made with an open or closed expansion tank.
The disadvantages of the circuit include difficulties in replacing radiators. To maintain operability, a jumper must be installed immediately in place of the removed battery, otherwise the system setting will be violated. For the same reason, between the inlet and outlet of the heat exchanger, bypasses from pipes of a smaller diameter are mounted.
One of the most popular schemes is "Leningrad". For connection, use a diagonal (cross) or side (one-sided) scheme.
When choosing radiators, they clarify how the outputs for connection are made - for the bottom or side. Corner adapters are purchased if necessary. It is important to follow the manufacturer's recommendations.
Equipment stages and operation

If a decision is made to make a two-story heating scheme for a house with your own hands, they strictly follow the sequence of work.
- Calculation of the need for heat output from radiators for each individual room and the total power. Information is needed to select a boiler and the number of batteries. They take into account the location of doors and windows relative to the cardinal points, the area and degree of insulation of the floor, walls, floors.
- Drawing up a project - general and floor-by-floor, coordination of the installation sites of gas equipment with the supplying organization. Allocation of the required electrical power if electricity is used.
- Selection and purchase of a boiler, pipes, heat exchangers, components for the assembly of a single system.
- Layout of pipelines.
- Assembling a single circuit, crimping.
- First start-up and setup, elimination of leaks.
During further operation in operating mode, the following types of work are performed:
- cleaning all components from dust and dirt;
- timely elimination of leaks;
- deflation of radiators when the temperature of individual devices drops;
- pressure check, timely top-up of the coolant;
- maintaining the liquid level in the system throughout the year, including during the interfuel period.
Knowledge of the possible schemes for the equipment of a two-story house with heating will help to make the right choice, monitor the progress of installation work and in the future, correctly respond to any malfunctions that have arisen.








