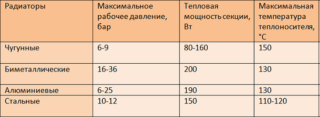
To organize heating in a private house, you can use systems that differ in the type of heat exchangers. The most popular are bimetallic radiators, which combine the properties of several types. When choosing radiators, you need to study their technical characteristics in order to correctly calculate the power and the number of sections required to heat the room.
Heat dissipation and its use

When studying the characteristics of a radiator, it is important to pay attention to heat dissipation. This concept includes the amount of heat generated by a radiator over a period of time. The heat flux or power of a device is measured in watts. For bimetallic radiators, this figure is 200 watts.
In technical documentation, heat transfer is often indicated in calories per hour, which can be converted to watts using the formula. 1 watt equals 859.8 calories per hour.
As a result of battery operation, three processes take place. This generates heat. Heating of the room is due to:
- heat exchange;
- convection;
- radiation.
For the operation of any model of heating devices, the use of all processes is characteristic. The only difference is proportions.
Sizes and capacity of sections

The popularity of bimetallic radiators is due to their compactness. Thanks to steel inserts, they look neater than cast iron. The smaller one section is in size, the less heating medium is required for heating. Therefore, the use of this type of battery will be more economical in terms of energy consumption. But very narrow pipes have their drawbacks. They quickly become clogged with debris that moves along heating networks. It is better to choose models of bimetallic radiators with thin walls, like water pipes.
The battery capacity is influenced by the distance between the axles. Heat transfer depends on the capacity of the radiator itself. For example, this parameter for a battery with a center distance of 20 cm is from 0.1 to 0.16 liters.
The main feature of bimetal radiators is a small amount of coolant. But at the same time, the power of the heat flow will be sufficient to heat the premises as efficiently as possible. For example, a device of ten 35 cm sections can heat a room of 14 square meters, but at the same time it contains only 1.6 liters.
Bimetallic batteries can be assembled independently one section at a time, or you can purchase a ready-made radiator of the required size.
Number of bimetallic radiator sections

How many kilowatts in one section of an aluminum radiator or bimetallic battery is indicated in the technical data sheet of the equipment. All calculations must be made based on the specified data. If there is no information on the characteristics in the documents, it can be found on the official website of the manufacturer. Sometimes an average value is used. Calculations are made separately for each room.
To make the correct calculations of the number of bimetal radiator sections, several factors must be taken into account.It is important how many kW in 1 section of a bimetal radiator. If you plan to replace cast iron batteries with bimetallic radiators, you need to take into account that the bimetal has a higher heat transfer rate than cast iron. Therefore, the dimensions can be left the same as they were. But it is important to take into account that over time, the quality of heating will deteriorate due to clogged pipes. Deposits will form due to the interaction of water with metal.
It is recommended to replace with the same number of sections or take a margin of one or two sections to avoid loss of heat transfer due to clogged pipes. If radiators are purchased for a new room, it is imperative to make a calculation for each room.
Types of calculations of the capacity of one section
There are two calculation methods, thanks to which it is possible to determine the power of one section of a bimetallic radiator.
Standard way
Sanitary-technical standards determine the minimum heat transfer rate of batteries for each region separately. For central Russia, there should be at least 100 watts per square meter. Calculation according to the standard scheme is carried out as follows:
- the area of the room in which the installation is made is taken;
- the resulting indicator is multiplied by 100 W;
- the result must be divided by the heat transfer of one section, this data can be found in the technical passport of the heating equipment.
This method has its drawbacks. It is recommended to use it only for rooms in which the ceiling height is no more than three meters. The calculation does not take into account the material of the walls, window structures and the degree of insulation.
Volumetric method
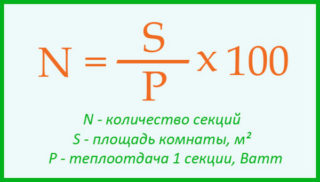
The volumetric method allows you to get an accurate calculation, which makes it possible to more efficiently select the required number of sections. The power is calculated in cubic meters. According to the norms of SNIP, a value of 41 watts is taken. The counting is done as follows:
- the area of the room is calculated;
- the resulting indicator is multiplied by the height of the room, thus the volume is obtained;
- the required power for the room is determined - the SNiP norm is multiplied by the resulting volume;
- to calculate the exact number of sections, the total power is divided by the parameter, one section at a time.
The result obtained will differ from the calculation in the standard way. The volumetric method is considered the most accurate.
Operating conditions of a bimetallic radiator

For more efficient functioning of bimetallic batteries, it is recommended:
- Before installing the radiators, cover the wall with reflective foil. Thanks to this, it will be possible to reduce heat loss.
- Disconnect radiators in the correct sequence. The supply line must be turned off first, then the return line. After that, the water is drained through the shut-off valve.
- Turn on the heating system, starting with the return flow, then the air is released and the flow part starts up.
- Install filters to keep dirt out of the radiator.
- Before the beginning of the heating season, clean the surface of the batteries with warm water and detergents. Do not use acids and alkalis, as well as products with abrasive particles.
The radiator must always be filled with coolant. Batteries can be without it for no more than two weeks a year. Every two years, the sections must be rinsed inside under a high pressure of water.
Increased heat transfer at no cost
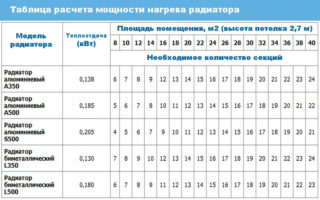
For each parameter of the heating system, its own heat transfer rate is used. The value is written in the technical passport. One of the important indicators that must be taken into account when carrying out calculations is the thermal head in the system.
Most often, the heat transfer parameter for one section is given at a thermal head of 60 degrees.This indicator corresponds to the temperature regime of water in the system at the level of 90 degrees. These parameters are typical for old houses. In modern construction, new technologies are used that do not require a high head of heat. This value for the heating system will be 40 to 50 degrees.
Since the values of the pressure prescribed in the technical passport and issued in fact differ from each other, it is necessary to recalculate the power of the sections. Most often, the indicator turns out to be lower when recalculated than the declared one. The heat transfer indicator is multiplied by the actual value of the heat head, then the resulting figure is divided by the parameter written in the document.
The power of a section of a bimetallic radiator is an important indicator that must be determined before installing a heating system. The efficiency of heating the room depends on the correctness of the calculations.








