An air-to-air heat pump is required to heat the heat carrier, which is installed in houses with converter heating. This approach is in increasing demand every year, since households do not freeze in their homes with the arrival of cold weather and use hot water in unlimited quantities.
Equipment characteristics

The air-to-air heat pump for home heating belongs to the equipment belonging to the field of alternative energy. The task of such a heat pump is to take heat from the air masses on the street and heat residential and non-residential premises with it. For efficient and trouble-free operation, you need to use some kind of combustible fuel.
Visually, the heat pump resembles an inverter air conditioner or a split system consisting of an indoor and outdoor unit. The principle of operation is more like a refrigerator, only with the opposite effect.
Principle of operation and device
The development of the equipment was based on the physical phenomenon of thermodynamics - during evaporation, the liquid cools the surface on which it scatters.
Refrigerators work according to this principle. The inner cavity is equipped with pipes through which refrigerant circulates under high pressure. It absorbs heat from the cavity of the freezer, while heating itself a little. The collected heat is released into the room.
For cooling, the refrigerant is compressed in the compressor. Freon in each working cycle changes its state of aggregation from gaseous to liquid and vice versa.
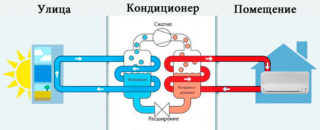
An air-to-air heat pump works on a similar principle, only it absorbs heat not from a closed freezer, but from the street. Even if the temperature outside the window is below zero, the atmosphere contains thermal energy.
The equipment includes the following segments:
- fan and condenser for supplying heated air to the room;
- compressor;
- copper tubes for transporting freon between the house and the street;
- evaporator with forced blower fan;
- expansion valve.
Compressor, expansion valve and evaporator with forced air blower are included in the outdoor unit, the rest of the parts are for the interior.
Advantages and disadvantages
Air heat pumps, like any other type of equipment, have advantages and disadvantages.
The main benefits include:
- Versatility of use. With the help of this type of equipment, it is possible to heat and cool rooms.
- Ease of use. To operate the system, it is enough to set the required temperature regime. This can be done remotely using the remote control or directly on the display.
- Environmental friendliness. Thanks to such systems, a person has the opportunity to completely abandon the burning of wood, coal, natural gas and other types of fuel that pollute the environment with combustion products.
- Acceptable cost. The pricing policy allows almost everyone to purchase a heat pump. You can even build it yourself.
- Profitability. Air-to-air heat pumps have a high heat transfer coefficient with minimal energy consumption.The equipment produces 4-5 kW of heat for each consumed 1 kW of electricity.
- Fire safety. There is no need to use flammable or fire hazardous compounds to generate heat. Even system malfunctions are not capable of causing a fire.
The owners of split systems highlight the following disadvantages:
- in the absence of power supply, the system will not work; if the resource supply is unstable, it is recommended to additionally install a generator;
- dust will hang in the air during the entire operation time of the fans;
- with a cold snap, an increase in power consumption is observed;
- the efficiency of the system depends on the temperature outside;
- insignificant, but still the same background noise.
Air-to-air heat pumps work efficiently as long as the air temperature does not drop below -10 degrees. If the country house is built in a region with a cold climate, you will additionally need to install a fireplace or boiler.
The pumps are controlled by built-in automation. You do not need to pay special attention to the setup and operation of the equipment. It is only important to regularly and efficiently clean the air filters and, if necessary, change them.
Differences from the air conditioner

Visually, the heat pump and air conditioner are similar, but the technical and design characteristics are different.
An external heat pump is used to heat rooms all year round. The air conditioner is mainly used to cool the room in the heat.
The main task of the heat pump is heating, but many models are also capable of cooling the air. However, in terms of energy efficiency, such systems are significantly inferior to air conditioners.
Air conditioners can also heat the air in rooms, but in this case they consume a large amount of electricity, which can “hit your pocket hard” at the end of the month.
Selection and calculation of heat pump power
Heating equipment "air-to-air" will be effective if it is selected correctly. It is necessary to first calculate the optimal power of the equipment, taking into account the area of the room.

When carrying out calculations, the energy efficiency coefficient - COP (the ratio of the heat pump power to the consumed energy) is used. For simple models, this indicator reaches no more than 5 points, and for expensive ones - 8. When the air temperature outside drops to -15 - -20 degrees, this coefficient will decrease equally for all models.
When calculating, it is important to consider the following nuances:
- general climatic conditions in which the house is located;
- the number of people living in a private house;
- squaring of rooms;
- insolation and thermal insulation of premises.
As a rule, for every 10 sq. about 0.7 kW of heat pump power is required. But this indicator is rather arbitrary. For example, if the ceiling height is more than 2.7 m or the windows and walls are not insulated, more heat will be required to heat the premises.
It is recommended to purchase equipment from authorized representatives of trusted manufacturers or in large household appliances stores, where the buyer will be provided with all quality certificates.








