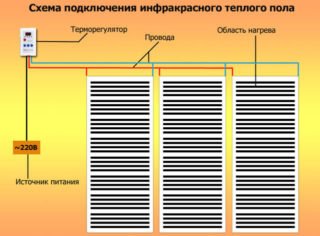
The concept of electric underfloor heating includes several designs. Their efficiency and energy consumption are different. Carbon fiber underfloor heating heats the surface more evenly and uses less energy.
Description of carbon fiber underfloor heating

The basis of the electrical system is the heating cable. When turned on, the electric current heats the wire, it transfers heat to the floor surface, and the latter gives it off to the air in the room. This option has 2 drawbacks. The resistance of the cable practically does not change with increasing temperature, therefore it is impossible to regulate the degree of heating along the length of the cable. More importantly, heat transfer occurs in 2 stages, which increases electricity consumption.
The first problem is partially solved by laying the cable in loops at regular intervals. This is not very convenient, since only modules of a certain size are received. During installation, they have to be docked with each other. The standard modification does not solve the second problem.
The construction of a carbon floor heating is devoid of these disadvantages:
- The base of the underfloor heater is made of carbon rods. Carbon is an amorphous carbon, it has a high electrical resistance - when an electric current passes, it heats up strongly and emits thermal radiation in the range of 5–20 microns. Infrared radiation transfers heat to objects and objects, not air - such a system heats the floor, furniture and people in the room, and the air heats up secondarily. To increase the efficiency of the heater, elements of graphite and silver are included.
- Carbon rods are assembled in blocks and interconnected by stranded copper cables in polymer insulation. The area of such a structure is practically unlimited.
- The role of temperature regulators is played by polymer inserts. When the air temperature reaches a threshold value - from +18 to +22 C, the material increases in volume, which leads to an increase in electrical resistance. In this case, the current decreases, and the heating temperature of the rod decreases.
Carbon heaters generate heat radiation. At the same time, the air heats up slightly and retains its natural humidity.
The main types of graphite underfloor heating
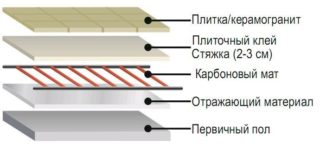
They produce 2 main types of heaters: film and rod. They also include bimetallic and amorphous floors. However, these 2 options do not include carbon elements. Although the principle of operation is the same: the radiation of infrared heat.
Rod mats
The core heat-insulated floor is a wire mat, 83 cm wide, the number of cores in 1 running meter is 10. The structure is spread on a prepared base of any area. The sections are connected to each other with connecting kits.
Rod mats are laid under any, most capricious material: tiles, laminate, wood flooring, parquet. Prerequisite: the heater is placed in a layer of concrete screed or tile adhesive. The sub floor is thermally insulated.
The advantage of the product is the possibility of self-adjustment. The core carbon fiber floor is not afraid of pressure, as its design excludes overheating of the wire. If the site is temporarily covered with furniture, the heat transfer on it decreases. At the same time, the rods reduce energy consumption and cool down.In areas where the surface cools faster, the elements get hotter.
The level of electricity consumption is determined by the heating temperature - from 110 to 180 W per linear meter.
Film mats

The design of the product is significantly different. The basis of the heating element is still carbon or a mixture of carbon and graphite. The composition is sprayed onto a base of heat-resistant polypropylene, forming conductive tracks. The base is closed on both sides with a two- or three-layer film and sealed. The material can withstand heating up to 120 C, is not afraid of water or moisture. The width of the strip is 50–100 cm. They are interconnected by copper buses.
There are several methods of applying carbon:
- Continuous film - carbon fiber is applied over the entire surface of the substrate. The heating rate of the heater is as high as possible, the energy consumption is lower. If any areas are damaged, the system's performance does not change.
- Perforated - stripes and circles are formed in a continuous coating, where there are no heating elements. The modification is designed for screed or under tiles.
- Honeycomb perforation is a variation of the previous one.
- Striped - the classic version, in which strips of different widths are formed on the substrate. The power of IR films depends on their size.
Installation of IR films is extremely simple and convenient. It is very thin - 0.23–0.47 mm; it is laid without a screed. The film can be cut into pieces of any size and heat the smallest platforms and even stair treads. If any of the sections breaks down, the rest of the floor continues to work in the same mode, and the damaged fragment can be replaced at any minute.
However, the film option has many limitations. It cannot be laid under porcelain stoneware, tiles, since "wet works" and IR-film are incompatible. The exception is the perforated modification. But its use is, rather, a forced decision. Flooring made of materials that do not conduct heat well, such as carpet, linoleum on a felt basis, is not suitable. In this case, the heat is absorbed by the coating.
Film underfloor heating can be dismantled, transported to another place and re-installed in another room.
Advantages and disadvantages

General advantages of rod mat and IR film:
- Efficiency close to 100 is not an exaggeration. Carbon generates infrared radiation. It heats the floor, objects and people, not the air. The elimination of the intermediate stage of heat transfer makes the carbon floor much more efficient.
- The systems do not emit electromagnetic radiation.
- The air heating temperature during the operation of the IR heater is low. It stays humid and the room climate is pleasant.
- The film and core mat are very lightweight. They do not load the floor and do not require installation equipment.
- Both systems are fireproof. However, at temperatures above 120 ° C, polymer parts melt.
- They are not afraid of water, moisture, condensation, steam. The carbon floor is laid for heating bathrooms, kitchens, saunas.
- The heating area is not limited: from a staircase to a hall of 100 sq.m.
- If the material is damaged in one area, the performance of the heater in other areas does not change. Repairs are performed at any time.
There is a common disadvantage: high operating costs.
Each modification has its own design advantages and disadvantages. A core carbon floor is placed under any surface - from parquet to porcelain stoneware. High humidity or poor insulation of the room is not a hindrance. The system is self-regulating, so that overheating of the elements and excessive consumption of electricity are excluded.
At the same time, the core mats are laid under the screed - installation involves wet work. The system cannot be dismantled and moved to another location.
IR film is even thinner than mats, so it is placed directly under the finish coat.It can be dismantled, reused. IR film is more economical, consumes 30% less electricity than standard heating cable.
Infrared film is not pressure-resistant, so furniture cannot be placed on such a floor. It is selective in relation to the coating material: it is not recommended to put it under tiles or porcelain stoneware.
Main characteristics
The characteristics of the carbon core warm floor and the film depend to some extent on the manufacturer. Average values are shown in the table.
| Parameters | Rod | Film |
| Thickness, mm | 3,5–5 | 0,23–0,47 |
| Power consumption, W / sq. m. | 125-170 | 130 |
| Energy consumption per 1 sq. m, W / h | 20-50 | 25–33 |
| Heating temperature, С | 60 | 33 |
| Roll length, m | 25 | 50 |
| Roll width, cm | 83 | 50–100 |
Power consumption is indicated at maximum heating temperature. For IR film, this parameter varies. The power of the rod mat depends on the nature of the heating elements. The inclusion of silver with graphite increases system efficiency and reduces energy consumption.
Features of installing a carbon underfloor heating
The installation of different types of underfloor heaters is somewhat different. Mounting the rod mat is more difficult. The technology must be followed exactly.
- Prepare a warm floor for laying: check the integrity of the rods, heat-laying tubes, wires. Calculate the stacking area. Rod mats can be mounted under furniture, but if it is a stationary wardrobe or a piano, it is unreasonable to do so, since this area does not need heating.
- The base surface is cleaned and leveled.
- Heat-reflecting material is laid. It is better to choose an insulator with a melting point of at least 100 C - isolon, for example. The heat reflector reduces electricity consumption for heating by 30–40%, so it cannot be neglected. Lay the material over the entire area of the room or just under the carbon floor.
- The operation of the heater depends on the readings of the temperature sensor. Install the device as close to the floor as possible, then its data reflects the actual heating temperature.
- The web is cut into modules of the required size. The cut falls on the connecting wire. When stacking, the modules are connected in series or in parallel, depending on the installation scheme. The rods should not intersect with each other. The mats are fixed with tape or a dowel bar.
- A thermostat is installed, connected to a warm floor and to the network. Use the scheme given in the instructions. If the power of the heater exceeds 2 kW, it is connected via an automatic machine.
- Check the working capacity of the floor. Only after that a screed 2-3 cm thick is placed.
Concrete hardens in 28 days; earlier it is impossible to turn on the warm floor.
Main manufacturers

The manufacturers ranking in 2019 is topped by the following companies:
- Unimat Boos introduces mats with minimal bar spacing.
K-Techologies is a trademark of GTMat, RHE (Russia). - GT is a South Korean firm that produces high performance carbon rod floors.
- Devi is a Danish company. Offers all types of film floors.
- CalorIQue LLC is an American trademark known for its high security requirements.
When choosing an underfloor heater from any company, you need to evaluate its characteristics. Power ratings and system design are more important than brand.