Cost, versatility and ease of installation are the main parameters when choosing building and finishing materials. PSB insulation is suitable for each of the requirements. It is important to know the characteristics and methods of work when insulating houses and other structures.
Terms and GOSTs

For all materials used in construction, legislation sets standards. Until 2014, GOST 15588-86 was in force. Foam sheets produced according to the parameters were assigned a conventional designation, for example, "PSB-S-15-900x500x50 GOST 15588-86".
The decryption means the following:
- P - plate;
- C - from suspension polystyrene;
- B - made without a press;
- C - self-extinguishing, does not support combustion for more than 4 seconds when the exposure to open fire is stopped;
- 15 - density grade;
- 900x500x50 - geometric dimensions.
To impart incombustibility, fire retardants are added to the foam, which is denoted by the letter "C".
The density grade corresponded approximately to the mass of 1 m3 of foam. For civil construction, products with a specific gravity of up to 15, 25 and 35 kg / m3 were produced.
The 1986 standard provided for the indication in the name of the maximum mass of the material. From January 1, 2014, instead of the outdated document, a new GOST 15588-2014 began to operate.
Important amendments for the consumer were made:
- the plates were named PPS (self-extinguishing polystyrene plates);
- the specific gravity should now be no less than that indicated in the name.
Some enterprises manufacture products according to the old GOST and call boards PSB, the new foam plastic is called PPS.
An example of the current designation is PPS16F-R-B-1000x500x120 GOST 15588−2014.
- PPS is a polystyrene plate obtained by a pressureless method from a suspension.
- P - cut from large blocks.
- B - with a side edge selected in a quarter (A - with a rectangular edge).
- 1000x500x120 - the geometrical dimensions of the slab in mm.
The reasons why manufacturers produce part of their products according to the old standards:
- not all production equipment has been replaced;
- less stringent product requirements that satisfy private developers;
- economy of materials - for example, PSB-S-15 can have a mass of 12 to 15 kg / m3, and PSB-15 is only higher than this value.
The critical technical characteristics of “old” and “new” cookers do not differ significantly.
Physical and technical properties
The popularity of polystyrene is directly influenced by technical characteristics:
- thermal conductivity
- density - measured in kg / m3 and indicated in the marking;
- geometrical dimensions are reflected in the marking;
- water absorption;
- compressive strength.
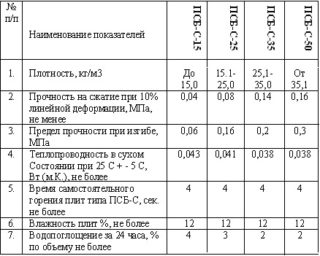
Thermal conductivity of thermal insulation boards at a temperature of +10 degrees is in the range from 0.036 W / m * K for PSB-S-35 polystyrene to 0.041 for lightweight PSB-S-15 products. When the air warms up to 25 degrees, the indicators change slightly - by 1%.
A deviation of the geometrical dimensions by 2–5 mm is allowed.Tolerances do not affect the quality of insulation, since with such parameters the seams are small, they can be easily eliminated with polyurethane foam.
Water absorption is understood to mean an increase in the mass of the foam when it is in water for 24 hours. During this period of time, the foam will absorb from 2 (PSB-35) to 4 (PSB-15)% of the liquid from its mass. Thus, polystyrene boards are moisture-proof material.
The compressive strength will determine the scope of application of a particular brand of foam, for example, PSB-15 does not withstand loads, you can carefully walk on polystyrene foam 35.
The service life of the foam is limited only by the operating conditions - if the sheets are protected from adverse influences, 50 years is not the limit of use.
Benefits and important limitations of use

The positive properties of the material are due to the composition and structure of the foam.
In construction, the following are important:
- low weight;
- shape and size stability with temperature fluctuations;
- ease of installation and production of sheets of the required sizes;
- versatility of use;
- long service life;
- resistance to decay and mold, not susceptible to infestation by parasites;
- lack of reaction to a slightly alkaline medium (cement);
- incombustibility;
- low thermal conductivity - 5 cm of foam retain heat in about the same way as 70 cm of brickwork or 30 cm of a wooden bar;
- environmental safety - in the composition of finished boards, the styrene content is about 0.02%, which is released only after heating the foam above 80 ° C;
- windproof.
Disadvantages are caused by:
- low stability when exposed to substances with an acidic reaction;
- destruction from sunlight;
- susceptibility to colonization by rodents.
Polystyrene grades PSB and PPS should be used strictly for the intended purpose and technology, in this case, the durability of the insulation is ensured.
Production technology

In the process of manufacturing plates, a minimum of components are used:
- polystyrene granules obtained in the oil refining process;
- pentane - natural gas condensate associated with the granule substance;
- flame retardant additives that make the material non-combustible;
- water vapor.
The production algorithm includes several stages:
- Foaming of raw materials - under the influence of water vapor and pressure, pentane expands in granules, increasing their volume by 20–70 times. The operation is stopped after the foam balls reach the required diameter.
- Hot air drying.
- Stabilization (soaking) for 4-24 hours. During this time, the balls completely cool down and acquire their final dimensions. The pentane remaining in the granules is replaced by air.
- Hot steam baking - the balls are baked into a single product with a volume of several cubic meters.
- Maturation (maturation) lasts from one day to 30 days. During this time, the moisture completely evaporates, and the internal stresses in the product are stabilized.
- Cut to size.
Waste after cutting is ground to individual balls and reused, being introduced at the stage of stabilization.
In the final version, the manufacturer receives expanded propylene sheets, consisting of 98% air and 2% polypropylene.
Violations of technology do not allow obtaining high quality material.
Equipment for the production of polystyrene can be placed in small workshops. Small firms often produce low-quality products. Parameters are not checked by laboratory methods. You cannot be guided by a low price when buying.
How to use

GOST provides for the use of foam sheets for thermal insulation:
- external walls of buildings and structures in operation and newly constructed ones;
- separate premises and industrial equipment, in the absence of contact between the plates and the volume of the interior;
- refrigerating chambers at temperatures from –100 to + 80оС;
Styrofoam is suitable for wet facade systems. It is used as a middle layer in panel constructions.
Appendix A to GOST indicates the areas of application of foam grades depending on density. PSB-S-15 or PPS grades from 10 to 15 are recommended for unloaded thermal insulation in three-layer structures made using ventilated facade technology. PSB-S-25, PPS 16-20 are suitable for external walls for finishing with cement and composite plasters. The material of this brand is suitable for insulating floors under a screed, ceilings, roofs. PSB-S-35, or grade PPS 20 and higher, is used for an insulating layer under a cement screed, for surfaces under the influence of significant loads - paths, blind areas, foundations and basements of buildings for various purposes.
Methods for working with foam

When choosing the method and technology of insulation, the requirements of GOST and common sense are taken into account:
- The foam must be protected from ultraviolet radiation - direct sunlight.
- Shock loads on the surface are excluded, it must be protected from physical impact.
- Sheets should not be open in the interior space due to possible damage and styrene fumes.
Foam insulation in private construction is carried out according to the technologies of a ventilated facade, a "wet" facade under plaster, laying between layers of enclosing material.
Plaster finishing procedure

For work, choose PSB-S-25, or PPS-16F. It is impossible to use foam with a lower density, since it will not withstand the mass of the cement mortar. Buying expanded polystyrene plates with a specific gravity of 35 kg / m3 does not make sense - the material in all respects is not inferior to models 15 and 25, but it costs much more.
Warming algorithm:
- Walls made of bricks or expanded clay concrete (foam concrete) blocks are cleaned of dust and dirt spots.
- The surface is leveled, knocking down the influx of masonry mortar. Plaster if necessary - it is important that there are no drops of more than 1 cm per linear meter of the wall.
- A solution is prepared from a special adhesive for cement-based polystyrene.
- The glue is applied to the slab with a layer of 0.5–1 cm, leveled with a notched trowel.
- PSB is glued to the wall, laying the sheets in a checkerboard pattern. Another option is to use foam mounting glue.
- For reliable fastening, after 3-4 hours, the polystyrene plates are additionally reinforced with dowels with wide caps at the rate of 5 dowels per m2. Seal the joints with polyurethane foam.
- The first layer of plaster is applied, for which the same glue is used that was used in paragraph 4. The plaster mesh is pressed into the layer of plaster, the surface is leveled.
- After drying, they carry out the main plaster and putty or use decorative mixtures, for example, bark beetle.
- The surface is painted.
Wet facade technology is rarely used for wooden houses. It is believed that the foam does not allow air to pass through and the house ceases to "breathe", fungus and mold appear on the inner surface of the walls. The issue can be solved by properly organized ventilation of the premises.
Insulation of hollow brick walls

The technology is simple. Between the internal load-bearing walls and the external finishing brick, cavities are left, into which, as the masonry is being erected, sheets of polystyrene are laid.
They use the cheapest version of PSB-15 foam. There is no load in the wall cavity completely, and the characteristics of the material are not inferior to foam with a higher density.
When filling hollow walls, it is more profitable to use foam chips - it is cheaper and allows you to completely fill the internal space between the bricks.The material is sold in kraft bags with a volume of 1 m3.
Frame houses and polystyrene
Foamed polystyrene is a popular insulation material for the construction of frame houses.
Styrofoam is mounted between the inner and outer skin. The gaps between the PSB and the beams are sealed with polyurethane foam, this will eliminate "cold bridges" and will not allow the wind to blow through the structure.
It is important to leave ventilation gaps between the foam and the wall cladding so that moisture does not accumulate inside.
Ventilated facades
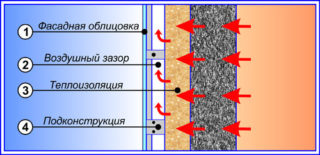
Houses finished according to the "ventilated facade" technology perfectly retain heat, prevent the appearance of mold and mildew, and are attractive in appearance.
You can do the work yourself.
The method involves the creation of several layers. Warming procedure:
- To the wall, keeping the level, a lathing of wooden bars or a galvanized profile is nailed. The bars are treated with an antiseptic with additives of a fire retardant. The cross-section of the crate is equal to the thickness of the foam. The distance between the lags should be 0.5–1 cm less than the size of the PSB so that the foam fits tightly.
- Polystyrene plates are mounted using dowels-fungi.
- The gaps are sealed with polyurethane foam.
- On the crate, a waterproofing membrane is reinforced, which protects against external moisture.
- On top of the waterproofing, a counter-lattice with a thickness of 10-15 mm is nailed or screwed on with self-tapping screws.
- An outer layer is mounted, which is used as various types of materials suitable for external use.
A counter grill and a gap are needed so that moisture does not accumulate between the insulation and the outer layer, the space is freely blown (ventilated) with air.
Expanded polystyrene is a universal insulation suitable for use in all climatic zones. Working with the material is available for any user. Its use will increase the comfort for residents and save money on energy costs.








