Polyethylene foam is a modern material with a bubble structure. It is very lightweight, elastic and does not allow moisture to pass through. Insulation materials are made from it in various forms, including sealing cords.
Properties and characteristics

Foamed polyethylene bundles are synthetic profile products, which are long cords of various thicknesses with a porous fine-mesh structure. When you touch them, you feel warm and soft. Such harnesses are considered good insulation at the joints, an excellent lock for the stable position of individual parts.
Exceptional characteristics are:
- Density - 24 - 50 kg / m3, depending on the type of used polyethylene, the technological method of production.
- The permissible operating range is -80 ° C to +95 ° C.
- The minimum thermal conductivity is about 0.035 W / m * K, allowing the temperature to be kept to the maximum.
- Water absorption - 2.5-3% of the total mass.
- Dielectric constant - about 1.16 (at a current frequency of 10 Hz).
- Chemical inertness towards acids, alkalis.
- The decomposition period in natural conditions is not less than 100 years.
- The permanent deformation after 50% compression is approximately 15%.
Polyethylene foam harnesses are considered environmentally friendly and safe for people, since they do not emit harmful substances. They are compatible with other building materials (wood, cement, gypsum, lime, concrete) and respond well to sealants.
Advantages and disadvantages

Insulation bundles made of foamed polyethylene have many positive properties that distinguish them favorably from their counterparts:
- low thermal conductivity;
- resistance to mechanical stress, return to its original position after damage;
- resistance to chemical attack;
- low hydrophobicity extending service life;
- elementary and easy installation;
- low cost;
- environmental Safety.
All products made of polyethylene foam are not prone to the growth of microorganisms and bacteria. For this reason, they have an indefinite decay guarantee.
The disadvantages include only one characteristic that narrows the scope of application of sealing harnesses - high flammability. Sealing material is not recommended for use in areas with a high risk of fire.
The combination of all the features, as well as the use of wear-saving innovative production technologies, guarantee that the PPE cord will have a long period of operation with full preservation of quality characteristics. Transportation, as well as storage of such products does not cause great difficulties.
Dimensions of seals

Depending on the area of application, foamed polyethylene bundles differ in length and thickness.
Polyethylene foam cords are usually produced:
- sliced (3 m);
- in bays (500 m).
Foamed polyethylene harnesses are made:
- solid round sections with a diameter of 0.8 - 12 cm;
- solid rectangular sections with a width of 9 - 12 cm, a thickness of 2-2.5 cm;
- round with a longitudinal hole in the middle.
Since the plastic tourniquet is very light, it adheres well to the water, so it can be used to teach young children to swim.
Scope of application

High insulating characteristics of PPE cords of various types allow them to be widely used in order to protect against excessive moisture, high noise, heat losses. They can protect parts of most building structures from condensation, corrosion, and save money on heating a residential building.
PPE cords of different thicknesses have the following purposes:
- diameter 6 - 12 mm is suitable for the arrangement of industrial floor coverings in order to fill expansion joints;
- a diameter of 2 - 20 mm is often used for thermal insulation of joints, cracks in window frames, balconies and external doors;
- a diameter of 20 - 60 mm is used during the construction of building walls in order to fill the joints between panels, as well as the gaps between logs in wooden buildings.

Construction, repair, reconstruction of premises:
- for reliable insulation of joints of individual parts of building structures;
- sound insulation of various types of walls, floors;
- as a sealant during the installation of windows, doors.
In factory mass production:
- devices, apparatus;
- ventilation, refrigeration units;
- cars;
- sports equipment, rescue equipment;
- shoe, orthopedic products;
- leather goods, upholstered furniture (for surface upholstery), etc.
In a domestic environment for fixation and insulation:
- when packing goods to protect them from external mechanical damage during transportation;
- as a reliable seal during the installation of household air conditioners;
- when designing private underground communication devices;
- for insulation of windows and doors (sealing of individual elements) for the cold winter period;
- decoration of interiors of premises.
Regardless of the area of use of the sealing cords, the application technology is the same:
- The tourniquet is placed in a separate seam. Mechanical compression averages 30%. It is important to ensure that the part of the joint remaining for filling with sealant is equal to its width or is related to it in a ratio of 1: 2.
- The sealing of the cord is carried out in an even layer, without the formation of gaps, bubbles. To make the appearance of the object flawless, masking tape is first placed on the edges of the seam. It is removed immediately after leveling the sealant.
If the amount of work required is significant, it is recommended to use a special smoothing agent instead of masking tape, which will speed up and simplify the workflow.
Comparison with other materials
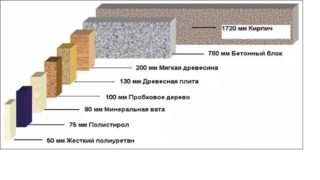
Polyethylene tow has thermal insulation properties that far exceed the capabilities of other popular building materials.
A strip with a diameter of 10 mm will replace:
- 10 cm of wood;
- 3 cm of mineral wool;
- 15 cm of brick and concrete layer;
- 1.7 cm of PVC-1 foam;
- 2cm fiberglass slab.
The sealing strand does not rot, does not get wet under the influence of moisture, and rust does not appear on it. Unlike other materials with a natural base, it is not affected by the fungus.
Foamed polyethylene cord is the most acceptable option among the materials used to protect building structures from damage and negative influences.








