Insulated Swedish slab is a slab foundation often used in the CIS countries. For the first time such a foundation was laid in Scandinavia. Within a few years, the device gained popularity in other parts of the world. The spread is due to the moisture resistance of the base and thermal insulation parameters. It is necessary to figure out what other properties the mentioned structure has.
The structure of the insulated Swedish plate
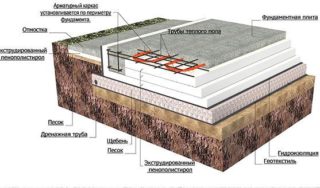
Insulated slab - slab base, which is equipped with moisture-resistant insulating materials and engineering networks. A distinctive characteristic of the USHP (insulated Swedish plate) is the shallow depth.
There are several known options for arranging the foundation. Basic elements:
- Substrate with drainage system.
- Geotextile backing.
- A cushion of sand and gravel with space for leading sewer pipes and communications.
- Heat insulating layer.
- Waterproofing - to protect against the effects of high humidity.
- TechnoNIKOL, or Carbon - a means for insulating flooring.
- Reinforcement piping and heating system.
- Concrete slab with an average thickness of 100 mm.
- Final finishing of the floor.
The drainage layer acts as a damper that compensates for fluctuations in the soil during sudden temperature fluctuations.
The frame is formed by welding thick steel blanks. Engineering communications are laid before pouring the monolith.
The structure seems cumbersome and difficult to build. Correct work in accordance with national and international standards provides a solid foundation.
Advantages and disadvantages

Positive aspects of the foundation scheme:
- there is no need for additional insulation;
- protection against groundwater;
- versatility - it can be erected on any soil (except rocky);
- savings - reduction of heating costs due to the provided function "warm floor";
- quick laying - takes no more than fourteen days;
- a sufficient level of resistance to mechanical damage and stress.
There is no need to use heavy and bulky equipment in the technological process.
Despite the abundance of advantages, disadvantages are noted in the characteristics of the insulated foundation slab:
- it is impossible to equip the basement and basement;
- the need for backup communications;
- high manufacturing cost;
- it is difficult to correct mistakes during construction;
- the presence of limits on the weight of future objects.
Mistakes can be avoided if all work is entrusted to professionals. However, with skilled workers hired, the financial benefit is diminished. Therefore, the owner of the site needs to decide which is more important: monetary savings or quality.
Step-by-step installation instructions

The beginning of the workflow is associated with the involvement of engineers. Technologists calculate the bearing capacity of the soil, determine the probability of formation shifts. Based on the results obtained, it is necessary to think over the necessary drainage possibilities.
Preparation of the base
Do not lay the foundation on a fertile soil layer. Then everything follows the standard instructions:
- Pulling out a deep pit (no more than two or three bayonets with a shovel).
- Geosynthetic coating.
- Launch the underlay on the walls from the side.
The outer boundaries of the pit should be at a distance of 1 m from the walls of the future structure.
Drainage
In order not to worry about the dryness of the base, a storm sewer and a system for the outflow of groundwater are carried out. For such purposes, a layer of crushed stone is used. Pipes of an underground reservoir run to it.
For the correct laying of the drainage system, trenches are built around the perimeter of the funnel. The devices tilt towards the main well.
Engineering communications
The layout of the water supply channels and the sewerage system is the next stage in the arrangement of the insulated Swedish stove. The hydrographic network deepens below ground level, which freezes over in winter.
In the project of the future house, the estimated places for the risers are stipulated in advance.
We must not forget about the flaws of the investigated foundation type. It is recommended to make a dubbing of communications - in case of unforeseen circumstances, a backup system will be available.
At this stage, a sand cushion is created. Everything is rammed with a special ramming machine.
Thermal insulation

Insulation for USHP is a defining element. The thermal insulation layer consists of two parts:
- Expanded polystyrene completely covers the perimeter of the pit.
- The second layer recedes from all sides by about 0.4 m inward.
This distribution is necessary for the installation of L-shaped modules.
Reinforcement
This stage is characterized by the layout of the underfloor heating system. Collectors are immediately installed and pipes are temporarily pressed.
A manifold is a technical part that mixes media from different parallel branches and distributes backward along the branches.
The reinforcing belt is made from reinforcement, the diameter of which reaches 12-16 mm. The recommended grid spacing is a 15 by 15 cm square.
Formwork manufacturing
There are two options for working. The first concerns the previously mentioned L-shaped polystyrene foam modules. The devices are additionally reinforced with boards and struts to prevent deformation under the concrete mass.
The second is classic. The frame is knocked together from durable plywood materials. The height of the formwork is calculated based on two indicators: the thickness of the insulation taken and the slab base.
Fill

Pouring an insulated slab from a monolithic one is no different. The concrete mixture is fed inward without interruption, avoiding the formation of joints.
Deep vibrators provide uniform filling.
Only after three days can the formwork be removed. If the construction process falls in the summer heat, you need to cover the slab with burlap or polyethylene film.
The final stage is grinding. It is carried out so as not to spend money on a leveling screed for the floor.
The use of insulated Swedish plate
The use of the described technology of shallow slab foundations is regulated by a number of regulatory documents. The main GOSTs include:
- R 12.4.026-2001;
- R 21.1101-2009;
- 12.0.004-90;
- 7076-99;
- 8267-93;
- 15588-86;
- 17177-94;
- 25898-83;
- 30244-94.
The following types of soils are suitable for laying:
- sand;
- sandy loam;
- clay;
- loam;
- peat, etc.
It is impossible to erect the USHP on muddy soil.
The technology is used most often in areas with high levels of humidity and elevation changes. Suitable for the construction of houses from logs, timbers, SIP panels and frame structures.
Do-it-yourself insulated plate

To make a USB with your own hands, you will need the following materials:
- extruded polystyrene foam for the foundation (from 0.3 cubic meters per 1 square meter);
- steel reinforcement with a diameter of 10 and 12 mm for the formation of grillages;
- wire;
- supports for a reinforced plastic belt;
- polyethylene film;
- geotextile cloth;
- boards and boards for equipping the formwork system;
- sand;
- crushed stone of the middle fraction;
- concrete mix.
Before direct construction, the site must be cleared of debris and weeds, mark the area for the future foundation using levels or levels. Then everything happens according to the described instructions.
UWB is a great option for mansions, warehouses and small construction sites. The high cost of work and the slightly complicated design are the only significant design flaws. But underfloor heating and savings in heating costs in the future completely cover these disadvantages.








