External insulation of the outer wall of a brick house reduces energy leakage from the inside of a residential building, which reaches 25-35%. Insulation on the front side with a thickness of 10 cm protects against losses, similar to the one and a half meter masonry made of silicate bricks. The parameters of the facade thermal insulation are laid down at the design stage, thus saving building materials, reducing the weight of the enclosing structures.
- Advantages of external thermal insulation
- The main characteristics of thermal insulation materials
- Water absorption coefficient
- Coefficient of thermal conductivity
- Flammability
- Density
- Soundproofing level
- Environmental friendliness
- Complexity of installation
- Recommended insulation for brick walls
- Styrofoam
- Extruded polystyrene foam
- Mineral wool
- Warm plaster
- Warming methods
- Under siding
- Modern method
- Thermal insulation of the house with polystyrene foam according to the principle of "wet facade"
- How to apply warm plaster to walls
Advantages of external thermal insulation

Wall protection is installed inside and outside. Internal insulation is done if it is not possible to perform external insulation.
Advantages of front facade insulation:
- regulation of temperature fluctuations, leading to a decrease in deformations and a decrease in the risk of cracks;
- saving the internal space of rooms;
- facilitating the laying of internal communications;
- improving the appearance of the building.
The temperature at which condensation occurs is called the dew point. The phenomenon occurs in the thickness of the wall or on the inner surface - it depends on the technical characteristics of the material and the design of the fence. The position of the dew point is influenced by the difference between the internal and external microclimate. The front insulation shifts the condensate boundary to the outer plane where moisture is generated.
Thermal insulation from the front side is difficult to perform if the facade of the building rises to a great height. The installation of scaffolding is required, the labor costs of people increase for lifting materials to the workplace. Additional mechanisms and equipment are used.
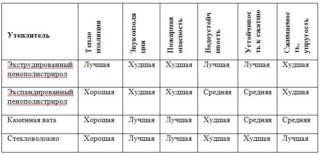
The main characteristics of thermal insulation materials
The market offers many outdoor protection materials that vary in quality. Insulation is selected according to its technical characteristics, taking into account the behavior of the insulation during humidity, frost, fire, interaction with chemicals.
Some materials are destroyed in extreme conditions, others are durable. The ecological purity of the insulation and the ability not to harm the environment are important, since toxic substances can be released when the facade is heated by the sun's rays.
Water absorption coefficient
The parameter is determined by the ratio of the volume of moisture that the material can absorb when it comes into contact with water or when it is in damp conditions, to the mass of a completely dry insulation. The ability of the insulating lining to retain the incoming fluid in the pores is important.
The structure of expanded polystyrene consists of closed pores, so the surface of the material is moistened only from the outside. Mineral wool is saturated with moisture and loses its heat-shielding properties, so it needs a ventilated space to dry. A material with a low absorbency lasts longer, as it withstands a greater number of freezes and thaws.
Coefficient of thermal conductivity
The ability of an insulating layer to transfer heat from one surface to another is called thermal conductivity.The coefficient reflects this property and is equal to the amount of energy penetrating through 1 sq. m layer 1 m thick, while the temperature on opposite sides differs by 10 наС.
According to thermal conductivity, materials are divided into classes:
- low (A) - up to 0.06 W / mK;
- medium (B) - in the range 0.06 - 0.115 W / mK;
- high (V) - 0.115-0.175 W / mK and more.
The ability of insulation for a brick house outside to conduct heat depends on the structure, density, moisture resistance and other technical characteristics.
Flammability

Fire resistance (combustibility) is the ability of a layer to restrict fire and maintain the declared qualities when heated to the boundary temperature. The property is characterized by flame spread and fire resistance.
These indicators are checked by fire testing according to the standard method and are expressed by the time interval before the appearance of the condition:
- destruction;
- temperature rise + 160˚С on the plane opposite to the flame;
- the appearance of through slots through which the flame appears or combustion products come out.
The information about the limits is used when designing the insulation of houses. For structures there are established fire resistance classes (5), the protective layer must correspond to the general characteristics of the building. Mineral wool and foam glass do not burn, extruded foam and sprayed insulation correspond to the fire resistance category G3 - G4. Polyfoam has a high degree of fire hazard, it is prohibited to use above the second floor.
Density

The indicator is determined by the ratio of the weight of the material to the volume it occupies, expressed in kg / m3. The characteristic depends on the structure and shape of the pores and changes when moistened, heated or cooled. Dense materials are hygroscopic, more durable, porous better vapor and air permeability.
Expanded clay insulation has the highest density, followed by sawdust, foam glass and mineral wool. Foam and cotton wool have the lowest density. The correct insulation is chosen taking into account this characteristic.
Tight insulation weighs more and creates additional stress on the structure. It is better to choose materials with an average value.
Soundproofing level
Protective layers are characterized by the way they reduce noise coming into the room from the outside. The quantitative measure of sound insulation is measured in decibels and depends on the properties of the insulation. Porous layers with a cellular structure or randomly placed fibers are good noise absorbers. An example is basalt wool, foamed types of polymers, felt, vermiculite.
The use of different materials in the same structure leads to improved sound insulation. For example, insulation for the walls of a house outside under a brick can consist of two layers, which will increase the absorption of noise from the street. The science of building acoustics distinguishes between shock and air backgrounds. Air is retained by the insulating layer, since it is transmitted in the atmosphere. Vibration and impact sound are transmitted through the supporting structures.
Environmental friendliness
The concept means the ability of the insulating layer to ensure the safety of the surrounding space during operation. Non-ecological materials contain substances that are harmful to health. Some of them begin to stand out from old layers, others are activated by heating or interaction with chemical reagents.

Harmful fillers and additives:
- formaldehyde;
- styrene, polystyrene, styrene monomers;
- borax fire retardant;
- lime;
- polyol, pentane, dust, bromine.
Mineral wool belongs to environmentally friendly insulators, since it is made on the basis of basalt.Extruded polystyrene foam is conditionally environmentally friendly, produced by a chemical method, it is recommended to insulate the outer walls. Polyfoam contains volatile conglomerates, is not used for interior work.
For external insulation, all types of insulation are used, since they do not come into contact with people and are closed from heating by the sun with finishing layers: a simple plaster is performed or in the form of a fur coat, siding is placed.
Complexity of installation
The difficulty of installation, the use of an additional frame for installation determines the choice of insulation. What matters is the ability to perform external protection with your own hands by a person without much experience. Making the base from slats or profiles adds to the total cost of the insulating layer.
Styrofoam, expanded polystyrene, polystyrene foam are glued to the wall surface and do not require a bulky frame. Mineral and basalt wool, roll materials require air supply, therefore, a frame is made with a ventilation gap.
Recommended insulation for brick walls
Materials are organic, the category includes gas-filled plastics and products from woodworking industry waste (sawdust, reeds, straw). The second group is inorganic insulation, the layers are made of mineral wool, slabs, glass wool, foam glass, foam concrete, expanded perlite. The third category includes mixed materials.
Styrofoam

Foamed polystyrene foam is produced in bulk granular mass and in the form of plates. Specific density of panels in the range of 10 - 50 kg / cu. m defines the scope of insulation. Material with low rates is used to insulate the walls of change houses, garages, high-density slabs are used for shops, residential buildings, refrigerators, industrial buildings.
Plates are produced with a thickness of 20 - 120 mm, the thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.042 W / mK. During the day, the material absorbs 2.5 - 3% moisture by volume.
Extruded polystyrene foam
The insulation shows low thermal conductivity coefficients, is resistant to the action of chemicals. Expanded polystyrene is produced in several types, but all are characterized by strength, absorb little moisture and pass air well.
Mold and fungus do not appear in the layers, rodents do not live. The material protects the walls of the structure from the harmful effects of the environment. Plates with special edges are produced with a thickness of 20 - 100 mm, coeff. thermal conductivity - at the level of 0.03 W / mK, absorbs 0.2 - 0.45% of water by volume.
Mineral wool

Popular insulation is produced in the form of stitched rolls, mats, plates of various hardness. The material does not burn, but melts and withstands heating up to + 1000˚С, does not collapse in frost down to -185˚С.
Minvata is produced in three types:
- Glass wool. Elastic fibrous structure, brittle, damaged during installation and releases fine glass particles. Used in industrial insulation.
- Slagged. It is made from blast furnace waste (slag). It has low thermal conductivity, but does not tolerate bending during installation. It is used to a limited extent, because absorbs moisture from the atmosphere and destroys metal when touched.
- Basalt (stone) wool. It has less negative characteristics, is used for curved planes, does not collapse during installation.
Produced with mats 50 - 100 mm thick, shows a thermal conductivity of 0.03 - 0.05 W / mK.
Warm plaster

It is produced in the form of a dry mix, packaged in bags. There is no sand in the composition, it is replaced by heat-insulating components. Portland cement acts as a binding element.
Warm plasters contain fillers:
- volcanic rocks such as vermiculite or perlite;
- expanded clay crumb;
- sawdust;
- pumice stone in the form of powder or crumb;
- polystyrene foam in the form of grains;
- cork crumb.
Warm plaster has a division into a mixture for external and internal use, depending on the main component and modifiers. For strength, water repellents and reinforcing threads are added. The cost depends on the amount of supplements.
Warming methods
Which method to use is determined by the type of material and its properties. External insulation is done at an air temperature of at least 0˚C, otherwise the compositions for wet works may become unusable.
Under siding

Insulation as part of a ventilated facade is one of the common options, despite the complexity of the work. Heat loss through the walls is minimized due to the fact that the finishing layer of the siding additionally protects from the wind. Waterproofing as part of the structure protects the surface from moisture and the insulation performs its functions, regardless of humidity.
Insulation on the frame is used in most buildings; with the help of siding, the appearance of complex and curved facades is improved. The frame is made of a metal profile, which additionally presses the insulating layer. The use of a wooden lath in the decoration of the facade is not allowed.
Modern method
Sometimes a protective layer is placed on the outer surface to be plastered. If foam, basalt insulation in slabs is used, the material is glued to a plane and additionally fastened with dowels with large heads (mushrooms). From above, the surface of the insulation is pasted over with a reinforcing mesh made of metal or plastic, plaster is applied over the mesh. The interlayer is glued with the strips overlapping each other by 15 cm.
If a soft material in the form of rolls is used, the insulator is made of a frame from a profile and sheets of chipboard, OSB are placed on top, which are treated with a primer and plastered along the mesh. Wall treatment is carried out before gluing the insulator sheets, the surface is leveled and primed.
Thermal insulation of the house with polystyrene foam according to the principle of "wet facade"

Manufacturers produce systems for performing works like a wet facade. Extruded polystyrene foam with a density of 35 - 50 kg / cubic meter is used. m. Durable insulation acts as a reliable waterproofing and vapor barrier.
The wet facade system includes materials and components:
- wall primer to enhance adhesion;
- glue for fixing the heat insulator;
- hardware for fixing the insulating layer on the plane of the wall;
- reinforced mesh with a mesh of about 5 mm;
- dry plaster mix for outdoor use;
- paint on the facade.
The installation of such a system is cheaper than the implementation of a ventilated facade, but in the process of operation, regular repairs will be required. The wet facade is intended for private buildings, and the ventilated options are suitable for multi-storey buildings.
How to apply warm plaster to walls
The work process has some peculiarities, for example, before applying the composition, it is not necessary to level the plane of the vertical fences. The application itself is no different from working with wet mixes for outdoor use. Warm renders adhere well to the surface, but reinforcing materials are used to give extra strength.
After drying, the composition allows an air stream to pass through, so steam and moisture do not accumulate in the mass, but are discharged outside. Acrylic paints can be applied over warm plaster after drying. The insulation layer retains its properties longer than mineral wool, belongs to the category of environmentally friendly products.








