Universal insulation foam is the most popular insulation material. It is used in apartment renovation, construction of private houses, garages, residential and office buildings. Technical characteristics allow it to be used on various parts of the structure - from the foundation to the roof.
The structure and composition of the foam

Foam production began in Germany in the 40s of the XX century. Gas-filled plastics have a closed-cell structure. A significant part of the volume of the material is air, it accounts for 98%. The remaining 2% is polystyrene. During the production process, polymer granules are foamed and treated with steam. After drying and pressing, the material is cut into slabs.
Heating costs depend on the thickness of the foam for wall insulation. Manufacturers offer slabs with a parameter from 10 to 100 mm. The thicker the material, the less heat loss. For the insulation of houses in the middle lane, 40 and 50 mm expanded polystyrene is used, in cold regions - 100 mm. It is impractical to use the thickest insulation, it is much more expensive than medium-sized products.
Foam plastics and polystyrene foam for house insulation are made from the same raw material - polystyrene, but using different technologies. Expanded polystyrene is obtained by steam treatment of granules. Its structure is porous, with many voids. Penoplex is made by extrusion. The slabs are dense and durable. The material wins in some technical characteristics, but the low cost of the foam plays a decisive role in many cases.
Specifications

The performance characteristics of a material determine its properties and application. Insulation features:
- Thermal conductivity. Air capsules provide reliable insulation, thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.037-0.044 W / m * K.
- Soundproofing and windproof. The cellular structure of the material provides excellent sound insulation. When using expanded polystyrene, no additional wind protection is required.
- Water absorption. The indicator is 1% during the day. Insulation absorbs moisture poorly.
- Biological inertness. The heat insulator is not susceptible to mold and mildew.
- Resistant to chemical attack. Alkalis, lime, bitumen, acids do not affect the foam. Protect the material from oils, solvents and petroleum products.
- Flammability. Expanded polystyrene belongs to the G3 flammability class. This is a moderately flammable insulation that has the ability to self-extinguish.
It is beneficial to use polystyrene as insulation due to its long service life. It is resistant to low and high temperatures, moisture and mechanical stress.
Features of installation and use

In many cases, the insulation has to be placed indoors. This feature is typical for multi-storey buildings. Experts do not recommend insulating houses with foam from the inside. Due to the flammability and release of toxic gases during melting, the material is harmful to the health of residents, and can be life threatening. Another disadvantage of insulation with expanded polystyrene from the inside is the lack of air exchange. A good ventilation device is required in the room.Inexpensive insulation is suitable for buildings with temporary residence.
External insulation options
When preparing a construction project, you need to choose what kind of foam to insulate the house outside and what thickness the material should be. Slabs with a thickness of 50-100 mm are suitable, their density should be from 25 kg / cu. m. Expanded polystyrene with such characteristics is used for installation on walls with subsequent plastering. This is the wet way. The insulation is fixed to the facade with a special solution or glue. Plates are stacked in a checkerboard pattern. A finishing layer of plaster is applied to their surface, always with a reinforcing mesh.

The second option is a ventilated facade. Foam for insulation in this way is used less often. In this case, it is inferior in functionality to its main competitor - mineral wool.
Installation sequence:
- Preparation - leveling and priming the walls.
- Sheathing device for facing material.
- Fixation of heat insulator plates with special glue and disc dowels.
- Installation of a ventilated facade - siding, aluminum or fiber cement panels.
Expanded polystyrene with wet insulation will last longer. It does not crumble under the protective layer of the solution. The use of foam insulation for ventilated facades increases the danger to human life in the event of a building fire.
Foam grades and scope
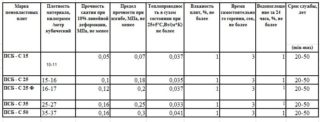
The most common type of foam is expanded polystyrene. The material is available in various densities and mechanical strengths. Main brands:
- PPT-10 - low density slabs used in multilayer structures.
- PPT-15 - foam insulation for non-loadable insulation of temporary huts, containers, wagons. They can be laid on the ceiling, attic.
- PPT-20 and 25 - the material is used for thermal insulation of facades, ceilings, balconies, water and sewer pipes. In frame houses, it serves as the basis for sandwich panels.
- PPT-35 - high density polystyrene suitable for screed mounting. It is used for insulation of foundations, floors, storage facilities.
In product marking, the figure indicates density - the weight of the material per cubic meter. In addition, the letter designations tell about the properties of foam:
- A - smooth edge of the slab;
- B - material with an L-shaped edge;
- H - insulation for outdoor use;
- C - self-extinguishing.
The high density of the material increases its tensile strength, expands the possibilities of application. Together with the indicators, the cost of products rises.
Advantages and disadvantages of foam

Before using expanded polystyrene boards as thermal insulation, it is worth examining their advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- Low thermal conductivity for an energy efficient system.
- Polyfoam of all wall insulation is the most affordable.
- Under normal conditions, it has no effect on the human body. The material has no harmful emissions.
- The low weight of the boards simplifies transportation and installation.
- Wide scope of application - insulation is used in the construction of residential buildings, in the construction of industrial facilities, insulation of bridges, pipelines.
- Ease of installation speeds up the process of thermal insulation, allows you to do the job without special skills and tools.
- Plating the room with polystyrene helps to reduce the noise level.

Disadvantages:
- The main disadvantage, due to which polystyrene is not recommended for insulating houses, is the flammability of the material. During a fire, toxic smoke poses a threat to people.
- When installed outside the building, protection from ultraviolet rays, which destroy the expanded polystyrene, is required.When choosing a finishing paint, take into account its low resistance to acetone and other solvents.
- The lack of vapor permeability during insulation from the inside leads to dampness on the walls.
- The material is destroyed by rodents. They make nests by gnawing the slabs onto polystyrene balls.
The numerous advantages of the material have made it a popular insulation material. To protect yourself from possible flammability problems, you should buy plates with the addition of flame retardants.








