Most often, insulation that performs simultaneous noise protection functions can be in demand when repairing old apartment buildings with prefabricated or monolithic reinforced concrete slabs. Among the most popular building materials for these purposes is the usual insulation polystyrene foam or its extruded version. This is due to its low cost and ease of installation.
Extruded polystyrene foam and its difference from conventional
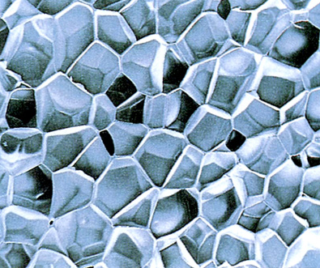
Conventional expanded polystyrene is produced in closed forms from granules that are foamed and compressed when exposed to hot steam. Extruded polystyrene foam insulation in the form of slabs is made by pushing through special slots calibrated in width and height, a mass of expanded polystyrene obtained at high pressure, temperature, with the introduction of a foaming agent into it. Such material has increased strength, uniform distribution of closed pores. The plate form of release allows the use of dense polystyrene foam as insulation and sound-insulating material in a variety of areas.
Material specifications:
- density - 8 ... 45 kg / m3;
- compressive and flexural strength - 0.25 ... 0.50 MPa;
- daily water absorption - 0.2% of the volume;
- thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.028… 0.042 W / (mC);
- vapor permeability coefficient - no more than 0.05 mg / mchPa;
- flammability group - G3;
- temperature range - from -50 to +75 оС.
These figures are highly manufacturer dependent. Among the most popular are Knauf, Ursa, Technonikol, etc.

Material properties:
- has high moisture resistance;
- resistant to biological pollution;
- effective sound insulation - up to -35 dB;
- low cost;
- with the use of fire retardants, resistant to long-term high-temperature fire exposure;
- neutral to weak chemical influences, including atmospheric;
- environmentally friendly and safe under normal use;
- the term of use is from 50 years and more.
Extruded polystyrene foam is produced in the form of plates 100-200 mm in width and 800-1400 mm in length. The thickness of the slabs varies from 10 to 40 in 10 mm increments.
Applications
Extruded polystyrene foam is used as a heat insulator and noise suppressor in many areas of industry, but it is most widely used in the construction industry.
Building material and waterproofing

In the construction of buildings and structures, EPS is used for different purposes. First of all, this is thermal insulation and noise protection. Extruded polystyrene insulation has extremely low water absorption and water permeability. If the humidity regime of the room to be insulated is not too aggressive, you can save on waterproofing as a separate type of work.
Heat insulating element
Expanded polystyrene is used in the form of plates, which are convenient to install on vertical and horizontal surfaces.For fastening, special adhesives are used, as well as dowels with screws, wire, metal and plastic tapes. Sealing of seams is carried out with silicone mastics, which retain rubber-like properties after setting. This is necessary so that over time shrinkage gaps and cracks do not appear in the seams, which worsen the heat-shielding and sound-insulating properties. Another option is to use panels of a special configuration - with locks (spikes and cutouts) at the ends.
For the construction of enclosing structures
In the structures of walls and floors, extruded polystyrene foam is used in the following options:
- direct installation "end-to-end" on work surfaces inside or outside (facades or insulated attics);
- installation in cells of wooden or metal frame elements for sheathing with sheet trim;
- in the form of prefabricated sandwich panels, where it is clamped between two sheets of wood, plastic or profiled metal based trim for use in the construction of frame houses and other lightweight prefabricated structures.
Sometimes on sale you can find stamped siding panels with extruded polystyrene foam sprayed on the reverse side. They combine facade insulation with decorative finishing.
As a universal insulation
EPPS is used as the most inexpensive universal insulation for thermal protection:
- machines and mechanisms (including construction);
- kilns;
- industrial premises and workshops with heavy (high-temperature) operation;
- boiler rooms;
- boiler rooms;
- warm garages;
- premises for keeping pets;
- free-standing and built-in baths, saunas and swimming pools;
- chimneys and outlets;
Also, the material is used in permafrost conditions in the construction of light buildings or roads and railways to isolate frozen soil from thawing, entailing unintended subsidence.
As glass
Polystyrene panels and slabs of small thickness transmit up to 60% of the light incident on them. This property is sometimes used to reduce heat loss and illuminate rooms with diffused light, where the use of transparent glass is impractical. It can be:
- changing rooms;
- showers and toilet cabins;
- refrigerating chambers;
- warehouses
- places for butchering carcasses.
Such light sources additionally combine the properties of thermal protection and sound insulation.
Floor insulation options
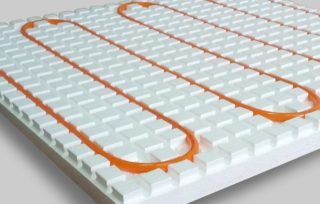
Foam board insulation for floor insulation can be used in several ways. If the floor is wooden, the empty space between the beams, joists and the floor covering is filled with expanded polystyrene plates using layers and cutting them to the required height.
When renovating old houses, under the floors, you can find a backfill of ash and slag or expanded clay, which must first be carefully removed and the resulting voids from dust with a vacuum cleaner and wet cleaning. Replacement with expanded polystyrene will significantly improve the heat protection and sound insulation of such floors.
Expanded polystyrene for underfloor heating is rarely used. More often for these purposes, slabs of mineral fiber stone wool are used. The material for the warm floor must be of high density and temperature resistance.
Insulation under the screed

When using expanded polystyrene on the floor under the screed, if the floor is reinforced concrete, it is better to level the concrete surface with a cement-sand or waterproof putty composition up to 1 ... 2 cm thick.In the case of using wooden purlins or logs for a board, chipboard, plywood floor, expanded polystyrene should fill the space between them to the required height.
If there are no logs, polystyrene foam under the screed in the form of plates or panels is installed "end-to-end"; for fastening, foamed polyurethane (in cans) or adhesives and mastics based on vinyl acetate, acrylates, silicone can be used. On top of the slabs, arrange a protective-leveling screed made of cement-sand mortar or expanded clay concrete with a thickness of at least 5 cm.
To improve waterproofing and vapor permeability between the mortar, it is recommended to overlap one or two layers of rolled polyethylene film on the extruded polystyrene foam under the screed. Linoleum, laminate, parquet, porcelain stoneware or ordinary tiles, self-leveling self-leveling floor can be used as a topcoat for such a floor.
Laying on the ground

When installing thermal insulation directly on the ground, which often happens when insulating the floors of the first floors of old basement high-rise buildings, the base should be aligned as accurately as possible in the horizontal plane. If necessary, you need to apply open pit or river dry sand.
Before laying, it is better to use rolled geotextiles, which create a membrane that protects the overlying wooden or concrete structures from the influence of the natural moisture contained in the soil. At the end of this stage, the same algorithm should be continued as in the insulation under the screed.
Anyone, even an unskilled master, can independently cope with work on insulation with the help of extruded polystyrene foam. However, to select a material, explain the technology and methods of its laying, get answers to other questions, it is better to use the advice of a specialist with experience in thermal insulation. Often, inviting a third-party master helps save time and money in the event of a marriage and the need for rework.








