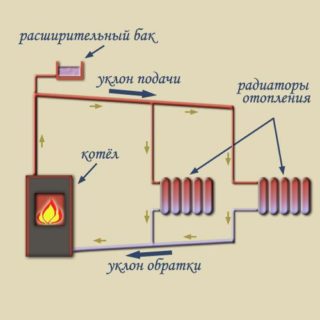
Reliability, stability and long service life of any engineering networks are directly related to the correct calculation of the components. An expansion tank for heating is an important element in the design of air heating in a private house. There are no trifles in the selection and installation. Remaining in frosts without heat means endangering your health, as well as provoking breakdowns of radiators and pipelines.
Purpose of the device

The physical properties of the liquid - to increase in volume when heated and the impossibility of compression at low pressures - imply the mandatory installation of expansion tanks in heating systems.
When heated from 10 to 100 degrees, water increases in volume by 4%, and glycolic liquids (antifreezes) by 7%.
A heating constructed using a boiler, piping and radiators has a finite internal volume. The water heated in the boiler, increasing in volume, does not find its outlet. The pressure in the pipes, radiator, heat exchanger rises to critical values that can rupture structural elements, squeeze out gaskets.
Private heating systems can withstand, depending on the type of pipes and radiators, up to 5 atm. Safety valves in safety groups or in boiler protection equipment are triggered at 3 bar. This pressure arises when water is heated in a closed container to 110 degrees. Working limits are considered to be 1.5 - 2 atm.
To accumulate excess coolant, expansion tanks are installed.
After cooling, the volume of the coolant returns to its previous values. To prevent airing of the radiators, water is returned to the system.
All possible types of devices are divided into two classes: expansion tanks for heating, closed and open.
Open type

Open type tanks for heating are used most often in gravity (gravity) systems.
Tank design
For self-production, you will need any container - a bucket, a canister, a large diameter pipe section.
A hole is made in the bottom of the tank through which the tank is connected to the heating system by means of a supply pipe. In the upper part, a cover is installed, through which the level of the coolant is controlled and, if necessary, topping up is carried out.
The tank is not left without a lid to avoid dust, insects and foreign objects getting into the water.
For convenience, an air valve is installed in the cover. In this case, the system is filled through a separate tap from the water supply - the valve releases air, but will not allow excess water to overflow.
An expansion tank is mounted at the highest point of the heating system. According to the principle of communicating vessels, the coolant will not flow out of the tank.
For safety, the container is equipped with an overflow hose with outlet to the sewer or outside the house. If too much liquid is collected, it will be discharged through the hose in a safe mode, not flooding the room.
It is undesirable to use plastic containers, since the temperature of the water / antifreeze before entering the radiators is close to 90 degrees or higher. The plastic will collapse, the coolant will pour out into the room (into the attic).
Device operation

As the heat carrier heats up, it expands. The surplus is discharged into the expander. After cooling down, the water returns to the piping and radiator system.
The tank communicates with air, the excess of which is discharged into the room.
Device Requirements
There are no great requirements for the design of the tank. Two conditions are met:
- choose a container volume sufficient to ensure heating and cooling cycles;
- the tank must be in communication with air.
The shape can be any, but it is undesirable for the horizontal dimensions (width or diameter) to be greater than the vertical dimensions (height). The larger the surface area, the more water evaporates when heated, therefore, you will have to do more control and topping up.
For open systems, only water is chosen as the coolant. Alcohol and glycol additives quickly evaporate from the heated antifreeze, which dramatically increases the cost of maintenance - the coolant will have to be topped up regularly and in large quantities. As additives, chemicals that are hazardous when inhaled are often used, which, when evaporated, harm the health of residents.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages are related to the design and operation of the device.
Positive properties include:
- the cheapness of the purchased device and the ability to make it yourself from scrap materials;
- simplicity of design, in which there are no additional mechanical elements (pumps, membranes);
- the ability to do without alteration of the system when replacing the gravity (gravity) boiler with a heater with forced circulation;
- autonomy of work;
At the same time, the use of gravity systems and open expansion tanks is not always possible. Restrictions are imposed on the number of storeys in the building - no more than 6 - 7 meters from the bottom of the boiler to the upper level of the coolant in the tank.
The water level must be checked regularly, including during summer. With a lack of water, the circulation of the coolant will stop. Contact between the internal cavities of metal pipes and radiators causes oxidation or corrosion, which reduces the life of the heating. In addition, rust deposits create hydraulic resistance to water flow.
Do not use open heating systems if electrode boilers are used in the system, which are demanding on the chemical composition of the coolant. As evaporation proceeds, the conductivity changes, which affects the performance of the water heater.
Volume calculation
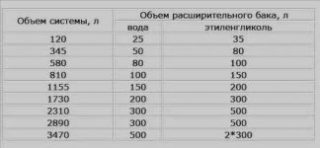
Most often tap water is used to refuel the heating system. Its temperature does not change much throughout the year. On average, the values tend to 13 degrees in winter and around 16-18 in summer. When heated from 10 to 90 degrees, the water will add 4.5% in volume. Antifreeze will expand by 6-7.5% in volume.
Taking into account the need for a small reserve, the volume of the expansion tank should be 10% of the total capacity of the boiler heat exchanger, piping and radiators.
You can roughly calculate the required volume in different ways. They do this at the stage of design and purchase of materials.
The capacity of one section of the radiator is indicated in the product passport. The volume of the coolant in one running meter of the pipe is calculated according to the data of special tables. For example, a meter of ¾-inch steel pipe holds 0.43 liters of water, and a 2-inch pipe holds about 2.4 liters. By adding the data obtained, the approximate capacity of the heating system is obtained.
The second way is practical. The finished system, without a tank, is filled with water. The volume is obtained according to the readings of the meter or by the number of buckets of water if the filling is carried out manually.
Installation site requirements

The open-type expansion tank is installed at the highest point of the system. This is usually the second floor or attic.
In the first case, it is better to choose a non-residential premises - during the heating operation, the coolant makes noise when moving through the pipes, gurgling sounds sound unpleasant, especially at night. In addition, some of the water evaporates, increasing the humidity in the room.
When installing a tank in the attic, measures are taken to insulate the container. If this is not done, most of the heat (10% of the coolant in the tank) will heat the air.
When the coolant supply is interrupted, the non-insulated tank will quickly cool down. After a while, the water will freeze. Even if the container does not rupture, the supply pipes will have to be heated.
Provides quick access to the lid for checking the level and adding water.
Closed type

The expansion tank for closed-type heating is mounted in systems with forced circulation of the coolant.
Design advantages:
- tightness - water (antifreeze) does not boil away and cannot spill out in the room;
- installation in any section of the pipeline;
- antifreeze liquid can be poured into the system, which excludes defrosting during emergency power outages;
- control of the state of the coolant by instruments;
- lack of contact with air and a lower rate of corrosion propagation.
Sealed models are more expensive than open options, but in the total estimate for the heating system, the cost takes a small part.
The tightness of the structure does not allow "excess" water to flow out, so the pressure can reach critical values. In this regard, when installing closed expansion tanks, a safety group must be installed, which also increases costs.
Design options

The design of the cisterns may vary, but the same principle remains everywhere.
The body is made of durable metal by stamping. The inside is covered with an anti-corrosion compound.
The tank is divided into an air and working cavity by an elastic, chemically resistant membrane.
There are blue and red tanks on sale. Blue items are for water supply. It is not allowed to use them for heating, since the membranes are not designed for high temperatures. For heating, only red tanks are purchased.
A threaded branch pipe is welded into the lower part of the body for connection to the pipeline.
A nipple with a spool is installed on the opposite side. Through it, until the system is filled, a pressure of 1 - 1.5 atm is created in the air cavity. This is necessary to start boilers with automation.
The main part is an elastic butyl or ethylene-propylene membrane that divides the tank into two cavities.
As it heats up, the coolant is squeezed out into the working chamber of the tank. The diaphragm gasket is deformed, the air is compressed, while increasing the pressure. If the pressure in the system exceeds 3 - 3.5 atm, the safety group will operate, bleeding off part of the excess fluid. In some models, the safety valve is already built-in at the factory.
When the water cools down, the pressure decreases, the coolant flows from the tank into the pipeline.
Installation features
Installing the tank into the system or replacing (repairing) is not difficult even for a master with little plumbing skills.
A set of tools and accessories will need a minimum:
- spanners;
- winding on the thread according to the preferences of the master (flax, fum);
- thread adapters (if necessary);
- bracket for attaching the tank to the wall.
Before the start of installation, an audit of the available material resources is carried out and the necessary is purchased in addition.

Installation requirements:
- The tightness of the tank allows it to be installed anywhere, but preference is given to the section of the return pipe at the very entrance to the boiler. At this point, the temperature of the coolant is about 40-50 degrees (at the exit from the boiler 90-100), which will extend the life of the membrane.
- The circulation pump is located closer to the boiler so as not to create water turbulence.
- The tank is connected via a quick-disconnect connection (American) so that it can be quickly dismantled for repair or replacement.
- A ball valve is mounted in front of the tank (up to the American one), by closing it you can remove the tank without draining the coolant from the entire system.
- The tank must be fixed to a solid wall base; for this, the kit includes a mounting bracket and a clamp of the required diameter. Without reliable fastening, when filling with coolant, the mass of the tank can reach 20–30 kg, which can damage the supply pipes.
After installation, you can check the system in action.
An expansion tank is an obligatory component of heating systems, from the design features of which they proceed when choosing one or another type of reserve capacity. Installation is simple and does not require configuration while meeting important installation requirements.








